Abstract
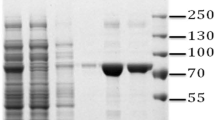
Oligopeptidases are enzymes involved in the degradation of short peptides (generally less than 30 amino acids in size) which help pathogens evade the host defence mechanisms. Leptospira is a zoonotic pathogen and causes leptospirosis in mammals. Proteome analysis of Leptospira revealed the presence of oligopeptidase A (OpdA) among other membrane proteins. To study the role of oligopeptidase in leptospirosis, the OpdA of L. interrogans was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli with a histidine tag (His-tag). The protein showed maximum expression at 37 °C with 0.5 mM of IPTG after 2 h of induction. Recombinant OpdA protein was purified to homogeneity using Ni-affinity chromatography. The purified OpdA showed more than 80% inhibition with a serine protease inhibitor but the activity was reduced to 30% with the cysteine protease inhibitor. The peptidase activity was increased significantly in the presence of Zn2+ at a neutral pH. Inhibitor assay indicate the presence of more than one active sites for peptidase activity as reported with the OpdA of E. coli and Salmonella. Over-expression of OpdA in E. coli BL21 (DE3) did not cause any negative effects on normal cell growth and viability. The role of OpdA as virulence factor in Leptospira and its potential as a therapeutic and diagnostic target in leptospirosis is yet to be identified.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waumans, Y., Baerts, L., Kehoe, K., De Lambeir, A. M., & Meester, I. (2015). The dipeptidyl peptidase family, prolyl oligopeptidase, and prolyl carboxypeptidase in the immune system and inflammatory disease, including atherosclerosis. Frontiers in Immunology, 6, 387. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00387.
Andrius, J., & Nomeda, K. (2015). Characterization of a novel thermostable oligopeptidase from Geobacillus thermoleovorans DSM 15325. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 25(7), 1070–1083.
Li, M., Chen, C., Davies, D. R., & Chiu, T. K. (2010). Induced-fit mechanism for prolyl endopeptidase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285(28), 21487–21495.
Coetzer, T. H., Goldring, J. P., & Huson, L. E. (2008). Oligopeptidase B: A processing peptidase involved in pathogenesis. Biochimie, 90, 336–344.
Swenerton, R. K., Zhang, S., Sajid, M., Medzihradszky, K. F., Craik, C. S., Kelly, B. L., et al. (2011). The oligopeptidase B of Leishmania regulates parasite enolase and immune evasion. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(1), 429–440. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.138313.
Motta, F. N., Bastos, I. M. D., Faudry, E., Ebel, C., Lima, M. M., Neves, D., et al. (2012). The Trypanosoma cruzi virulence factor oligopeptidase B (OPBTc) assembles into an active and stable dimer. PLoS ONE, 7(1), e30431.
Atas, A., Seddon, A. M., Ford, D. C., Cooper, I. A., Wren, B. W., Oyston, P. C., et al. (2016). YPTB3816 of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis strain IP32953 is a virulence-related metallo-oligopeptidase. BMC Microbiology, 16(1), 282.
Hooper, N. M. (1994). Families of zinc metalloproteases. FEBS Letters, 354, 1–6.
Vimr, E. R., Green, L., & Miller, C. G. (1983). Oligopeptidase-deficient mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Journal of Bacteriology, 153(3), 1259–1265.
Conlin, C. A., & Miller, C. G. (1992). Cloning and nucleotide sequence of opdA, the gene encoding oligopeptidase A in Salmonella typhimurium. Journal of Bacteriology, 174, 1631–1640.
Lorenzon, R. Z., Cunha, C. E., Marcondes, M. F., Machado, M. F., Juliano, M. A., Oliveira, V., et al. (2010). Kinetic characterization of the Escherichia coli oligopeptidase A (OpdA) and the role of the Tyr(607) residue. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 500(2), 131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2010.05.025.
Jiang, X., Zhang, M., Ding, Y., Yao, J., Chen, H., Zhu, D., et al. (1998). Escherichia coli prlC gene encodes a trypsin-like proteinase regulating the cell cycle. Journal of Biochemistry, 124(5), 980–985.
Costa, F., Hagan, J. E., Calcagno, J., Kane, M., Torgerson, P., Martinez-Silveira, M. S., et al. (2015). Global morbidity and mortality of leptospirosis: A systematic review. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 9(9), e0003898. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003898.
Faine, S. B., Bolin, A. C., & Perolat, P. (1999). Leptospira and leptospirosis. Melbourne: Med. Sci.
Levett, P. N. (2001). Leptospires. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 14, 236–296.
Morgan, J., Bornstein, S. L., Karpati, A. M., Bruce, M., Bolin, C. A., Austin, C. C., et al. (2002). Outbreak of leptospirosis among triathlon participants and community residents in Springfield, Illinois, 1998. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 34, 1593–1599.
Lau, C., Smythe, L., & Weinstein, P. (2010). Leptospirosis: An emerging disease in travellers. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8, 33–39.
McBride, A. J., Athanazio, D. A., Reis, M. G., & Ko, A. I. (2005). Leptospirosis. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases, 18(5), 376–386.
Sethi, S., Sharma, N., Kakkar, N., Taneja, J., Chatterjee, S. S., Banga, S. S., et al. (2010). Increasing trends of leptospirosis in northern India: A clinico-epidemiological study. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 4(1), e579. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0000579.
Sehgal, S. C. (2000). Leptospirosis on the horizon. The National Medical Journal of India, 13(5), 228–230.
Monahan, A. M., Callanan, J. J., & Nally, J. E. (2008). Proteomic analysis of Leptospira interrogans shed in urine of chronically infected hosts. Infection and Immunity, 76, 4952–4958.
Xue, F., Dong, H., Wu, J., Wu, Z., Hu, W., Sun, A., et al. (2010). Transcriptional responses of Leptospira interrogans to host innate immunity: Significant changes in metabolism, oxygen tolerance, and outer membrane. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 4(10), e857. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0000857.
Mehrotra, P., Ramakrishnan, G., Dhandapani, G., Srinivasan, N., & Madanan, M. G. (2017). Comparison of Leptospira interrogans and Leptospira biflexa genomes: Analysis of potential leptospiral-host interactions. Molecular BioSystems, 13(5), 883–891. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6mb00856a.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227(5259), 680–685.
Coelho, D. F., Saturnino, T. P., Fernandes, F. F., Mazzola, P. G., Silveira, E., & Tambourgi, E. B. (2016). Azocasein substrate for determination of proteolytic activity: Reexamining a traditional method using bromelain samples. BioMed Research International, 2016, 1–6.
de Telleria, E. L., Araujo, A. P., Secundino, N. F., D’Avila-Levy, C. M., & Traub-Cseko, Y. M. (2010). Trypsin-like serine proteases in Lutzomyia longipalpis—Expression, activity and possible modulation by Leishmania infantum chagasi. PLoS ONE, 5, e10697.
Fraga, T. R., Barbosa, A. S., & Isaac, L. (2011). Leptospirosis: Aspects of innate immunity, immunOpdAthogenesis and immune evasion from the complement system. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology, 73(5), 408–419. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3083.2010.02505.x.
Robbins, G. T., Hahn, B. L., Evangelista, K. V., Padmore, L., Aranda, P. S., & Coburn, J. (2015). Evaluation of cell binding activities of Leptospira ECM adhesins. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 9(4), e0003712. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003712.
Stevenson, B., Choy, H. A., Pinne, M., Rotondi, M. L., Miller, M. C., Demoll, E., et al. (2007). Leptospira interrogans endostatin-like outer membrane proteins bind host fibronectin, laminin and regulators of complement. PLoS ONE, 2(11), e1188. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001188.
Amamura, T. A., Fraga, T. R., Vasconcellos, S. A., Barbosa, A. S., & Isaac, L. (2017). Pathogenic Leptospira secreted proteases target the membrane attack complex: A potential role for thermolysin in complement inhibition. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 958. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00958.
Raja, V., Shanmughapriya, S., Kanagavel, M., Artiushin, S. C., Velineni, S., Timoney, J. F., et al. (2015). In vivo-expressed proteins of virulent Leptospira interrogans serovar Autumnalis N2 elicit strong IgM responses of value in conclusive diagnosis. Clinical and Vaccine Immunology, 23(1), 65–72. https://doi.org/10.1128/CVI.00509-15.
Conlin, C. A., Trun, N. J., Silhavy, T. J., & Miller, C. G. (1992). Escherichia coli prlC encodes an endopeptidase and is homologous to the Salmonella typhimurium opdA gene. Journal of Bacteriology, 174(18), 5881–5887.
Lundstrom, K., Wagner, R., Reinhart, C., Desmyter, A., Cherouati, N., Magnin, T., et al. (2006). Structural genomics on membrane proteins: Comparison of more than 100 GPCRs in 3 expression systems. Journal of Structural and Functional Genomics, 7, 77–91.
Massey-Gendel, E., Zhao, A., Boulting, G., Kim, H., Balamotis, M. A., Seligman, L. M., et al. (2009). Genetic selection system for improving recombinant membrane protein expression in E. coli. Protein Science, 18, 372–383.
Asdornnithee, S., Himeji, E., Akiyama, K., Sasaki, T., & Takata, R. (1995). Isolation and characterization of Pz-peptidase from Bacillus licheniformis N22. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 79, 200–204.
Awano, S., Ansai, T., Mochizuki, H., Yu, W., Tanzawa, K., Turner, A. J., et al. (1999). Sequencing, expression and biochemical characterization of the Porphyromonas gingivalis pepO gene encoding a protein homologous to human endothelin-converting enzyme. FEBS Letters, 460(1), 139–144.
Lin, B., Averett, W. F., Novak, J., Chatham, W. W., Hollingshead, S. K., Coligan, J. E., et al. (1996). Characterization of PepB, a group B streptococcal oligopeptidase. Infection and Immunity, 64, 3401–3406.
de Caler, E. V., Avalos, V. S., Haynes, P. A., Andrews, N. M., & Burleigh, B. A. (1998). Oligopeptidase B-dependent signalling mediates host cell invasion in Trypanosoma cruzi. EMBO Journal, 17, 4975–4986.
Conlin, C. A., & Miller, C. G. (2000). OpdA, a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium gene encoding a protease, is part of an operon regulated by heat shock. Journal of Bacteriology, 182(2), 518–521.
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge the financial support from Department of Science and Technology, Government of India (SR/S0/HS/078/2012) and Department of Higher education, Govt of Kerala, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anu, P.V., Madanan, M.G., Nair, A.J. et al. Heterologous Expression, Purification and Characterization of an Oligopeptidase A from the Pathogen Leptospira interrogans. Mol Biotechnol 60, 302–309 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-018-0073-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-018-0073-8