Abstract
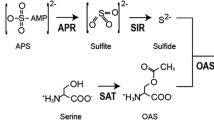
l-Cysteine desulfhydrase (DES; EC 4.4.1.1) is the most important enzyme that catalyzes the decomposition of l-cysteine to pyruvate, ammonia, and hydrogen sulfide (H2S), the latter of which has recently been recognized as the third gasotransmitter for multiple signaling events in plants. Previous results showed the existence of DES activity in Brassica napus; however, the gene encoding the true DES protein has not been characterized yet. Here, a rapeseed DES gene was isolated and sequenced. It shared high homology with Arabidopsis DES1, and encodes a polypeptide with 323 amino acids of 34.5 kDa. Subsequently, prokaryotic expression and biochemical analysis demonstrated that this protein predominantly catalyzes the breakdown of l-cysteine with the side reaction of l-cysteine synthesis [O-acetyl-l-serine(thiol)lyase activity], and was designated as BnDES1. Corresponding analysis of structural features was also in agreement with the above proposition. Molecular evidence showed that BnDES1 mRNA was widely expressed, but with the higher expression level in flowers. Further results showed that the BnDES1 transcripts were differentially up-regulated by several plant growth regulators and chemicals. Overall, the above findings provide evidence showing that BnDES1 is a potentially important enzyme responsible for the H2S production, and may play an important role in plant growth regulators and chemical stimuli responses.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hell, R. (1997). Molecular physiology of plant sulfur metabolism. Planta, 202, 138–148.
Rennenberg, H. (1984). The fate of excess sulfur in higher plants. Annual Review of Plant Physiology, 35, 121–153.
Hawkesford, M. J., & De Kok, L. J. (2006). Managing sulphur metabolism in plants. Plant, Cell and Environment, 29, 382–395.
Schmidt, A., & Jäger, K. (1992). Open questions about sulfur metabolism in plants. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 43, 325–349.
Bonner, E. R., Cahoon, R. E., Knapke, S. M., & Jez, J. M. (2005). Molecular basis of cysteine biosynthesis in plants: Structural and functional analysis of O-acetylserine sulfhydrylase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 38803–38813.
Gruhlke, M. C. H., & Slusarenko, A. J. (2012). The biology of reactive sulfur species (RSS). Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 59, 98–107.
Noctor, G., Arisi, A. M., Jouanin, L., Kunert, K. J., Rennenberg, H., & Foyer, C. H. (1998). Glutathione: Biosynthesis, metabolism and relationship to stress tolerance explored in transformed plants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 49, 623–647.
Noctor, G., Mhamdi, A., Chaouch, S., Han, Y., Neukermans, J., Marquez-Garcia, B., et al. (2012). Glutathione in plants: An integrated overview. Plant, Cell and Environment, 35, 454–484.
Nappi, A. J., & Vass, E. (1997). Comparative studies of enhanced iron-mediated production of hydroxyl radical by glutathione, cysteine, ascorbic acid, and selected catechols. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1336, 295–302.
Park, S., & Imlay, J. A. (2003). High levels of intracellular cysteine promote oxidative DNA damage by driving the fenton reaction. Journal of Bacteriology, 185, 1942–1950.
Wirtz, M., Beard, K. F., Lee, C. P., Boltz, A., Schwarzlaender, M., Fuchs, C., et al. (2012). Mitochondrial cysteine synthase complex regulates O-acetylserine biosynthesis in plants. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287, 27941–27947.
Heeg, C., Kruse, C., Jost, R., Gutensohn, M., Ruppert, T., Wirtz, M., et al. (2008). Analysis of the Arabidopsis O-acetylserine(thiol)lyase gene family demonstrates compartment-specific differences in the regulation of cysteine synthesis. Plant Cell, 20, 168–185.
Ikegami, F., & Murakoshi, I. (1994). Enzymic synthesis of non-protein β-substituted alanines and some higher homologues in plants. Phytochemistry, 35, 1089–1104.
Hatzfeld, Y., Maruyama, A., Schmidt, A., Noji, M., Ishizawa, K., & Saito, K. (2000). β-Cyanoalanine synthase is a mitochondrial cysteine synthase-like protein in spinach and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 123, 1163–1172.
Takahashi, H., & Saito, K. (1996). Subcellular localization of spinach cysteine synthase isoforms and regulation of their gene expression by nitrogen and sulfur. Plant Physiology, 112, 273–280.
Barroso, C., Romero, L. C., Cejudo, F. J., Vega, J. M., & Gotor, C. (1999). Salt-specific regulation of the cytosolic O-acetylserine(thiol)lyase gene from Arabidopsis thaliana is dependent on abscisic acid. Plant Molecular Biology, 40, 729–736.
Schäfer, H. J., Haag-Kerwer, A., & Rausch, T. (1998). cDNA cloning and expression analysis of genes encoding GSH synthesis in roots of the heavy-metal accumulator Brassica juncea L.: Evidence for Cd-induction of a putative mitochondrial γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase isoform. Plant Molecular Biology, 37, 89–97.
Domínguez-Solís, J. R., Gutiérrez-Alcalá, G., Romero, L. C., & Gotor, C. (2001). The cytosolic O-acetylserine(thiol)lyase gene is regulated by heavy metals and can function in cadmium tolerance. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 9297–9302.
Noji, M., Saito, M., Nakamura, M., Aono, M., Saji, H., & Saito, K. (2001). Cysteine synthase overexpression in tobacco confers tolerance to sulfur-containing environmental pollutants. Plant Physiology, 126, 973–980.
Harada, E., Choi, Y., Tsuchisaka, A., Obata, H., & Sano, H. (2001). Transgenic tobacco plants expressing a rice cysteine synthase gene are tolerant to toxic levels of cadmium. Journal of Plant Physiology, 158, 655–661.
Youssefian, S., Nakamura, M., Orudgev, E., & Kondo, N. (2001). Increased cysteine biosynthesis capacity of transgenic tobacco overexpressing an O-acetylserine(thiol) lyase modifies plant responses to oxidative stress. Plant Physiology, 126, 1001–1011.
Lόpez-Martín, M. C., Becana, M., Romero, L. C., & Gotor, C. (2008). Knocking out cytosolic cysteine synthesis compromises the antioxidant capacity of the cytosol to maintain discrete concentrations of hydrogen peroxide in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 147, 562–572.
Burandt, P., Schmidt, A., & Papenbrock, J. (2001). Cysteine synthesis and cysteine desulfuration in Arabidopsis plants at different developmental stages and light conditions. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 39, 861–870.
Riemenschneider, A., Riedel, K., Hoefgen, R., Papenbrock, J., & Hesse, H. (2005). Impact of reduced O-acetylserine(thiol)lyase isoform contents on potato plant metabolism. Plant Physiology, 137, 892–900.
Papenbrock, J., Riemenschneider, A., Kamp, A., Schulz-Vogt, H. N., & Schmidt, A. (2007). Characterization of cysteine-degrading and H2S-releasing enzymes of higher plants—from the field to the test tube and back. Plant Biology, 9, 582–588.
Álvarez, C., Calo, L., Romero, L. C., García, I., & Gotor, C. (2010). An O-acetytlserine(thiol)lyase homolog with l-cysteine desulfhydrase activity regulates cysteine homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 152, 656–669.
Álvarez, C., Bermúdez, M. A., Romero, L. C., Gotor, C., & García, I. (2012). Cysteine homeostasis plays an essential role in plant immunity. New Phytologist, 193, 165–177.
Riemenschneider, A., Wegele, R., Schmidt, A., & Papenbrock, J. (2005). Isolation and characterization of a d-cysteine desulfhydrase protein from Arabidopsis thaliana. The FEBS Journal, 272, 1291–1304.
Todorovic, B., & Glick, B. R. (2008). The interconversion of ACC deaminase and d-cysteine desulfhydrase by directed mutagenesis. Planta, 229, 193–205.
Jin, Z., Shen, J., Qiao, Z., Yang, G., Wang, R., & Pei, Y. (2011). Hydrogen sulfide improves drought resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 414, 481–486.
Zhang, H., Tang, J., Liu, X., Wang, Y., Yu, W., Peng, W., et al. (2009). ydrogen sulfide promotes root organogenesis in Ipomoea batatas, Salix matsudana and Glycine max. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 51, 1086–1094.
Wang, Y., Li, L., Cui, W., Xu, S., Shen, W., & Wang, R. (2012). Hydrogen sulfide enhances alfalfa (Medicago sativa) tolerance against salinity during seed germination by nitric oxide pathway. Plant and Soil, 351, 107–119.
García-Mata, C., & Lamattina, L. (2010). Hydrogen sulphide, a novel gasotransmitter involved in guard cell signalling. New Phytologist, 188, 977–984.
Li, L., Wang, Y., & Shen, W. (2012). Roles of hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide in the alleviation of cadmium-induced oxidative damage in alfalfa seedling. BioMetals, 25, 617–631.
Bloem, E., Riemenschneider, A., Volker, J., Papenbrock, J., Schmidt, A., Salac, I., et al. (2004). Sulphur supply and infection with Pyrenopeziza brassicae influence l-cysteine desulphydrase activity in Brassica napus L. Journal of Experimental Botany, 55, 2305–2312.
Cao, Z., Geng, B., Xu, S., Xuan, W., Nie, L., Shen, W., et al. (2011). BnHO1, a haem oxygenase-1 gene from Brassica napus, is required for salinity and osmotic stress-induced lateral root formation. Journal of Experimental Botany, 62, 4675–4689.
Siegel, M. (1965). A direct microdetermination for sulfide. Analytical Biochemistry, 11, 126–132.
Gaitonde, M. K. (1967). A spectrophotometric method for the direct determination of cysteine in the presence of other naturally occurring amino acids. The Biochemical Journal, 104, 627–633.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Xie, Y., Xu, S., Han, B., Wu, M., Yuan, X., Han, Y., et al. (2011). Evidence of Arabidopsis salt acclimation induced by up-regulation of HY1 and the regulatory role of RbohD-derived reactive oxygen species synthesis. Plant Journal, 66, 280–292.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Programme, Grant no 2011CB109300) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant no. KYJ200912).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yanjie Xie and Diwen Lai have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Y., Lai, D., Mao, Y. et al. Molecular Cloning, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of a Novel Gene Encoding l-Cysteine Desulfhydrase from Brassica napus . Mol Biotechnol 54, 737–746 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-012-9621-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-012-9621-9