Abstract
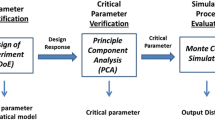
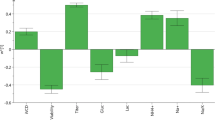
The goal of quality by design (QbD) in cell culture manufacturing is to develop manufacturing processes which deliver products with consistent critical quality attributes (CQAs). QbD approaches can lead to better process understanding through the use of process parameter risk ranking and statistical design of experiments (DOE). The QbD process starts with an analysis of process parameter risk with respect to CQAs and key performance indicators (KPIs). Initial DOE study designs and their factor test ranges are based on the outcomes of the process parameter risk ranking exercises. Initial DOE studies screen factors for significant influences on CQAs as well as characterize responses for process KPIs. In the case study provided here, multifactor process characterization studies using a scale-down model resulted in significant variation in charge heterogeneity of a monoclonal antibody (MAb) as measured by ion-exchange chromatography (IEC). Iterative DOE studies, using both screening and response surface designs, were used to narrow the operating parameter ranges so that charge heterogeneity could be controlled to an acceptable level. The data from the DOE studies were used to predict worst-case conditions, which were then verified by testing at those conditions. Using the approach described here, multivariate process parameter ranges were identified that yield acceptable CQA levels and that still provide operational flexibility for manufacturing.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
FDA (2006) Guidance for industry. Q8 pharmaceutical development. http://www.fda.gov/cder/guidance/6746fnl.pdf.
Moran, E. B., McGowan, S. T., McGuire, J. M., Frankland, J. E., Oyebade, I. A., Waller, W., et al. (2000). A systematic approach to the validation of process control parameters for monoclonal antibody production in fed-batch culture of a murine myeloma. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 69(3), 242–255.
Xie, L., Wu, H., Shen, M., Augsberger, L. L., Lyon, R. C., Khan, M. A., et al. (2008). Quality-by-design (QbD): Effects of testing parameters and formulation variables on the segregation tendency of pharmaceutical powder measured by the ASTM D 6940-04 segregation tester. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 97(10), 4485–4497.
McKenzie, P., Kiang, S., Tom, J., Rubin, A. E., & Futran, M. (2006). Can pharmaceutical process development become high tech? AIChE Journal, 52(12), 3990–3994.
Parenteral Drug Association (2005). Process validation of protein manufacturing. Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, 59, 1–28 (PDA technical report No. 42).
Chaderjian, W. B., Chin, E. T., Harris, R. J., & Etcheverry, T. M. (2005). Effect of copper sulfate on performance of a serum-free CHO cell culture process and the level of free thiol in the recombinant antibody expressed. Biotechnology Progress, 21, 550–553.
van Hoek, P., Harms, J., Wang, X., & Rathore, A. S. (2009) Case study in definition of process design space for a microbial fermentation step. In A. S. Rathore & R. Mhatre (Eds.), Quality by design for biopharmaceuticals (pp. 85–109) New York: Wiley.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horvath, B., Mun, M. & Laird, M.W. Characterization of a Monoclonal Antibody Cell Culture Production Process Using a Quality by Design Approach. Mol Biotechnol 45, 203–206 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9267-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9267-4