Abstract
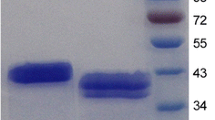
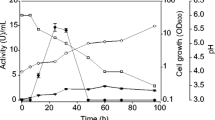
The Aspergillus aculeatus MRC11624 man1 gene, encoding an endo-β-1,4-mannanase, was cloned and expressed in the promising heterologous enzyme producer, the ascomycetous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Both single- and multi-copy transformants were constructed, and the secretion of the enzyme was evaluated as an in-frame fusion with the LIP2 secretion signal, as well as with its natural secretion signal. In shake-flask analysis, the highest volumetric enzyme activity (13,073 nkat/ml) and specific enzyme activity (1,020 nkat/(mg dcw)) were obtained with a multi-copy integrant utilizing β-mannanase’s own secretion signal. The best β-mannanase-producing strain was subsequently evaluated in batch fermentation and resulted in a maximum volumetric enzyme activity of 6,719 nkat/ml. Fed batch fermentations resulted in a 3.9-fold increase in volumetric enzyme activity compared with batch fermentation, and a maximum titre of 26,139 nkat/ml was obtained. The results reported in this study indicate that Y. lipolytica is a promising producer of A. aculeatus β-mannanase, producing higher β-mannanase activity than that of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae or Aspergillus niger when cultivated in shake flasks, which is encouraging for the use of the enzyme in industrial processes such as extraction of vegetable oil from leguminous seeds and the reduction in viscosity of coffee extracts.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arcand, N., Kluepfel, D., Paradis, F. W., Morosoli, R., & Shareck, F. (1993). Beta-mannanase of Streptomyces lividans 66: Cloning and DNA sequence of the manA gene and characterization of the enzyme. The Biochemical Journal, 290, 857–863.
Stålbrand, H., Saloheimo, A., Vehmaanperä, J., Henrissat, B., & Pentillä, B. (1995). Cloning and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of a Trichoderma reesei β-mannanase gene containing a cellulose binding domain. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 61(3), 1090–1097.
Setati, M. E., Ademark, P., van Zyl, W. H., Hahn-Hägerdal, B., & Stålbrand, H. (2001). Expression of the Aspergillus aculeatus endo-β-1, 4-mannanse encoding gene (man1) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and characterization of the recombinant protein. Protein Expression and Purification, 2, 105–114.
Zhang, Q., Yan, X., & Tang, W. (2006). Cloning, sequence analysis, and heterologous expression of a β-mannanase gene from Bacillus subtilis Z-2. Molecular Biology, 40(3), 418–424. doi:10.1134/S0026893306030034.
Sachslehner, A., Foidl, G., Foidl, N., Gübitz, G., & Haltrich, D. (2000). Hydrolysis of isolated coffee mannan and coffee extract by mannanases of Sclerotium rolfsii. Journal of Biotechnology, 80, 127–134. doi:10.1016/S0168-1656(00)00253-4.
Suurnäkki, A., Clark, T., Allison, R., Buchert, J., & Viikari, L. (1996). Mannanase aided bleaching of soft-wood Kraft pulp. In K. Messner & E. Srebotnik (Eds.), Biotechnology in pulp and paper industry—Advances in applied and fundamental research (pp. 69–74). Vienna: WUA Universitätsverlag.
Montiel, M.-D., Rodríguez, J., Pérez-Leblic, M.-I., Hernández, M., Arias, M.-E., & Copa-Patiño, J.-L. (1999). Screening of mannanases in actinomycetes and their potential application in the bleaching of pine Kraft pulps. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 52, 240–245. doi:10.1007/s002530051515.
Fickers, P., Benetti, P.-H., Waché, Y., Marty, A., Mauersberger, S., Smit, M. S., et al. (2005). Hydrophobic substrate utilization by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica, and its potential applications. FEMS Yeast Research, 5, 527–543. doi:10.1016/j.femsyr.2004.09.004.
Madzak, C., Tréton, B., & Blanchin-Roland, S. (2000). Strong hybrid promoters and integrative expression/secretion vectors for quasi-constitutive expression of heterologous proteins in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2, 207–216.
Madzak, C., Gaillardin, C., & Beckerich, J.-M. (2004). Heterologous protein expression and secretion in the non-conventional yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Journal of Biotechnology, 109, 63–81. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2003.10.027.
Barth, G., & Gaillardin, C. (1997). Physiology and genetics of the dimorphic fungus Yarrowia lipolytica. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 19, 219–237. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.1997.tb00299.x.
Van Zyl, P. J., Moodley, V., Rose, S. H., Roth, R. L., & van Zyl, W. H. (2009). Production of the Aspergillus aculeatus endo-1, 4-β-mannanase in A. niger. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 36, 611–617. doi:10.1007/s10295-009-0551-x.
Sambrook, J., Fitsch, E. F., & Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual (3rd ed.). Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
Nicaud, J.-M., Madzak, C., Van den Broek, P., Gysler, C., Duboc, P., Niederberger, P., et al. (2002). Protein expression and secretion in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. FEMS Yeast Research, 2, 371. 279.
Xuan, J.-W., Fournier, P., & Gaillardin, C. (1988). Cloning of the LYS5 gene encoding saccharopine dehydrogenase from the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica by target integration. Current Genetics, 14, 15–21. doi:10.1007/BF00405848.
Nicaud, J.-M., Fabre, E., & Gaillardin, C. (1989). Expression of invertase activity in Yarrowia lipolytica and its use as a selective marker. Current Genetics, 16, 253–260. doi:10.1007/BF00422111.
Livak, K. J., & Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT method. Methods (San Diego, Calif.), 25, 402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262.
Pfaffl, M. W. (2001). A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Research, 29(9), e45. doi:10.1093/nar/29.9.e45.
Ausubel, F. M., Brent, R., Kingston, R. E., Moore, D. D., Seidman, J. G., Smith, J. A., et al. (1998). Current protocols in molecular biology. USA: Wiley.
Bailey, M. J., Biely, P., & Poutanen, K. (1992). Interlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity. Journal of Biotechnology, 23, 257–270. doi:10.1016/0168-1656(92)90074-J.
Miller, G. L., Blum, R., Glennon, W. E., & Burton, A. L. (1960). Measurement of carboxymethylcellulase activity. Analytical Biochemistry, 2, 127–132. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(60)90004-X.
Juretzek, T., Le Dall, M., Mauersberger, S., Gaillardin, C., Barth, G., & Nicaud, J.-M. (2001). Vectors for gene expression and amplification in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Yeast (Chichester, England), 18, 97–113. doi:10.1002/1097-0061(20010130)18:2<97::AID-YEA652>3.0.CO;2-U.
Hamsa, P. V., & Chattoo, B. B. (1994). Cloning and growth-regulated expression of the gene encoding hepatitis B virus middle surface antigen in Yarrowia lipolytica. Gene, 43, 165–170. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90092-2.
Swennen, D., Paul, M.-F., Vernis, L., Beckerich, J.-M., Fournier, A., & Gaillardin, C. (2002). Secretion of active anti-Ras single-chain Fv antibody by the yeasts Yarrowia lipolytica and Kluveromyces lactis. Microbiology, 148, 41–50.
Pignéde, G., Wang, H., Fudalej, F., Seman, M., Gaillardin, C., & Nicaud, J.-M. (2006). Autocloning and amplification of LIP2 in Yarrowia lipolytica. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 6(8), 3283–3289.
Müller, S., Sandal, T., Kamp-Hansen, P., & Dalbøge, H. (1998). Comparison of expression systems in the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Hansenula polymorpha, Kluyveromyces lactis, Schizosaccharomces pombe and Yarrowia lipolytica. Cloning of two novel promoters from Yarrowia lipolytica. Yeast (Chichester, England), 14, 1267–1283. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(1998100)14:14<1267::AID-YEA327>3.0.CO;2-2.
Park, C. S., Chang, C. C., & Ryu, D. D. Y. (2000). Expression and high-level secretion of Trichoderma reesei endoglucanase I in Yarrowia lipolytica. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 87(1), 1–15. doi:10.1385/ABAB:87:1:1.
Verdoes, J. C., van Diepeningen, A. D., Punt, P. J., Debets, P. J., Stouthamer, A. J., & van den Hondel, C. A. M. J. J. (1994). Evaluation of molecular and genetic approaches to generate glucoamylase overproducing strains of Aspergillus niger. Journal of Biotechnology, 36, 165–175. doi:10.1016/0168-1656(94)90052-3.
Thompson, A., & Gasson, M. J. (2001). Location event of a reporter gene on expression levels and on native synthesis in Lactococcus lactis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67(8), 3434–3439. doi:10.1128/AEM.67.8.3434-3439.2001.
Acknowledgements
Y. lipolytica Po1h and vectors pINA1291, pINA1293 and pINA1313 were kindly provided by the Laboratory of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics (UMR1238) from INRA/CNRS/AgroParisTech (Thiverval Grignon, France). The Aspergillus aculeaus man1 gene was kindly provided by the laboratory of Prof. W. H van Zyl (University of Stellenbosch, Stellenbosch, South Africa).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roth, R., Moodley, V. & van Zyl, P. Heterologous Expression and Optimized Production of an Aspergillus aculeatus Endo-1,4-β-mannanase in Yarrowia lipolytica . Mol Biotechnol 43, 112–120 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-009-9187-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-009-9187-3