Abstract
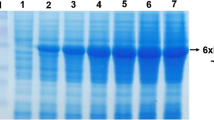
A new lipase gene designated as SlLipA was isolated from Serratia liquefaciens S33 DB-1 by the genomic-walking method. The cloned gene contained an open reading frame (ORF) of 1,845 bp encoding 615 amino acids with a conserved GXSXG motif. Genome sequence analysis showed that an aldo/keto reductase gene closed to the SlLipA gene. The lipase gene was cloned into the expression vector pPICZαA and successfully integrated into the heterologous host, methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris GS115. Five transformants could be expressed as secreted recombinant proteins with the high activity on Triglyceride–Agarose plate and as candidates to produce the recombinant enzyme. A C-terminal His tag was used for its purification. The lipase activity of different transformants against substrate para-nitrophenyl laurate (p-NPL) varied from 14 to 16 U ml−1. For the substrates para-nitrophenyl caprate (p-NPC), p-NPL, para-nitrophenyl myristate (p-NPM), para-nitrophenyl palmitate (p-NPP), and para-nitrophenyl stearate (p-NPS), the specific activity was shown to be preferred to long acyl chain length of p-NPS.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balcao, V. M., & Malcata, F. X. (1998). Lipase catalyzed modification of milkfat. Biotechnology Advances, 16, 309–341.
Keskin, S. O., Sumnu, G., & Sahin, S. (2004). Usage of enzymes in a novel baking process. Nahrung, 48, 156–160.
Jaeger, K. E., & Eggert, T. (2002). Current opinion in biotechnology. Lipases for Biotechnology, 13, 390–397.
Matsumoto, T., Ito, M., Fukuda, H., & Kondo, A. (2004). Enantioselective transesterification using lipase-displaying yeast whole-cell biocatalyst. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 64, 481–485.
Barbara, F. H. (1995). Liposomes offer hope as medical tools. Information, 6, 793–802.
Fukuda, H., Kondo, A., & Noda, H. (2001). Biodiesel fuel production by transesterification of oils. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 92, 405–416.
Stock, I., Burak, S., Sherwood, K. J., Grüger, T., & Wiedemann, B. (2003). Natural antimicrobial susceptibilities of strains of ‘unusual’ Serratia species: S. ficaria, S. fonticola, S. odorifera, S. plymuthica and S. rubidaea. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 51, 865–885.
Inami, M., Kawamura, I., Tsujimoto, S., Yasuno, T., Lacey, E., Hirosumi, J., et al. (2005). FR177391, a new anti-hyperlipidemic agent from Serratia. II. Pharmacological activity of FR177391. Journal of Antibiotics (Tokyo), 58, 640–647.
Legakis, N. J., Nicolas, K. J., Xilinas, M., & Papavassiliou, J. (1978). Differentiation of Serratia marcescens and Serratia liquefaciens by tests for lipase and phospholipase production. Journal of Medicinal Microbiology, 11, 225–231.
Zou, W. X., Liu, H., & Yu, W. H. (1996). Isolation of lipase-producing Serratia liquefaciens and characterization of its lipase. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science), 32, 713–716.
Liu, H., Zou, W. X., & Yu, W. H. (1995). Studies on the extracellular lipase production of Serratia liquefaciens S33 DB-1. Microbiology (China), 22, 343–346.
Ellis, S. B., Brust, P. F., Koutz, P. J., Waters, A. F., Harpold, M. M., & Gingeras, T. R. (1985). Isolation of alcohol oxidase and two other methanol regulatable genes from the yeast Pichia pastoris. Molecular and Cell Biology, 5, 1111–1121.
Koutz, P. J., Davis, G. R., Stillman, C., Barringer, K., Cregg, J. M., & Thill, G. (1989). Structural comparison of the Pichia pastoris alcohol oxidase genes. Yeast, 5, 167–177.
Jette, J. F., & Ziomek, E. (1994). Determination of lipase activity by a Rhodamine–Triglyceride–Agarose assay. Analytical Biochemistry, 219, 256–260.
Lin, S. F., Chiou, C. M., Yeh, C. M., & Tsai, Y. C. (1996). Purification and partial characterization of an alkaline lipase from Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes F-111. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 62, 1093–1095.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye-binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Winkler, U. K., & Stuckmann, M. (1979). Glycogen, hyaluronate, and some other polysaccharides greatly enhance the formation of exolipase by Serratia marcescens. Journal of Bacteriology, 138, 663–670.
Rủa, M. L., Schmidt-Dannert, C., Wahl, S., Sprauer, A., & Schmid, R. D. (1997). Thermoalkalophilic lipase of Bacillus thermocatenulatus: Large scale production, purification and properties, aggregation behaviour and its effect on activity. Journal of Biotechnology, 56, 89–102.
Schmidt-Dannert, C., Sztajer, H., Stocklein, W., Menge, U., & Schmid, R. D. (1994). Screening, purification and properties of a thermophilic lipase from Bacillus thermocatenulatus. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1214, 43–53.
Grimont, P. A. D., Grimont, F., & Irino, K. (1982). Biochemical characterization of Serratia liquefaciens sensu stricto, Serratia proteamaculans, and Serratia grimesii sp. nov. Curr. Microbiology, 7, 69–74.
Brick, D. J., Brumlik, M. J., Buckley, J. T, Cao, J. X., Davies, P. C., Misra, S., et al. (1995). A new family of lipolytic plant enzymes with members in rice, arabidopsis and maize. FEBS Letter, 377, 475–480.
Upton, C., & Buckley, J. T. (1995). A new family of lipolytic enzyme. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 20, 178–179.
Cregg, J. M., Vedvick, T. S., & Raschke, W. C. (1993). Recent advances in the expression of foreign genes in Pichia pastoris. Bio/Technology, 11, 905–910.
Scorer, C. A., Buckholz, R. G., Clare, J. J., & Romanos, M. A. (1993). The intracellular production and secretion of HIV-1 envelope protein in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Gene, 136, 111–119.
Buckholz, R. G., & Gleeson, M. A. G. (1991). Yeast systems for the commercial production of heterologous protein. Bio/Technology, 9, 1067–1072.
Cregg, J. M., & Higgins, D. R. (1995). Production of foreign proteins in the yeast. Pichia pastoris. Canadian Journal of Botany Supplement, 73, 5981–5987.
Nico-Farber, K., Harder, W., Ab, G., & Veenhuis, M. (1995). Review: Methylotrophic yeasts as factories for the production of foreign proteins. Yeast, 11, 1331–1344.
Sreekrishna, K., Potenz, R. H. B., Cruze, J. A., McCombie, W. R., Parker, K. A., Nelles, L., et al. (1988). High level expression of heterologous proteins in methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 28, 265–278.
Wegner, G. H. (1990). Emerging applications of the methylotrophic yeasts. FEMS Microbiology Review, 87, 279–284.
Jiang, Z. B., Luo, Y., Wang, G., Wang, H. P., Ma, Y. S., & Wei, D. Z. (2005). Cloning and expression of a novel lipase gene from Pseudomonas fluorescens B52. Molecular Biotechnology, 31, 95–102.
Li, X. Y., Tetling, S., Winkler, U. K., Jaeger, K. E., & Benedik, M. J. (1995). Gene cloning, sequence analysis, purification, and secretion by Escherichia coli of an extracellular lipase from Serratia marcescens. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 61, 2674–2680.
Tripathi, M. K., Roy, U., Jinwal, U. K., Jain, S. K., & Roy, P. K. (2004). Cloning, sequencing and structural features of a novel Streptococcus lipase. Enzyme Microbial Technology, 34, 437–445.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Wenxin Zou for kindly providing S. liquefaciens S33 DB-1 strain, and we thank China National “863” High-Tech Program, China Ministry of Education and Shanghai Science and Technology Committee for fund support under Project No. 2006AA020202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, H., Yu, S., Zhang, L. et al. Isolation of a Novel Lipase Gene from Serratia liquefaciens S33 DB-1, Functional Expression in Pichia pastoris and its Properties. Mol Biotechnol 38, 99–107 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-007-9007-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-007-9007-6