Abstract
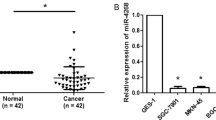
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a type of small noncoding RNAs that are strongly implicated in carcinogenesis. However, the potential diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic roles of the majority of miRNAs in the pathological processes of tumorigenesis remain largely unknown. Our and others’ data revealed that miR-204-5p was significantly downregulated in gastrointestinal tumor tissues compared with adjacent noncancerous tissues. The downregulation of miR-204-5p was confirmed in our gastric cancer (GC) cohort, and we showed that ectopic expression of miR-204-5p inhibited, whereas silencing miR-204-5p expression promoted GC cell proliferation in vitro. Subsequent mechanistic investigations identified that USP47 and RAB22A are direct functional targets of miR-204-5p in GC. Silencing the expression of USP47 and RAB22A using siRNA phenocopied the proliferation-inhibiting function of miR-204-5p in GC cells. Our results uncovered that miR-204-5p acts as a tumor suppressor in GC through inhibiting USP47 and RAB22A.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–97.
He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5(7):522–31.
Di Leva G, Garofalo M, Croce CM. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014;9:287–314.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
Hou Z, Xie L, Yu L, Qian X, Liu B. MicroRNA-146a is down-regulated in gastric cancer and regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis. Med Oncol. 2012;29(2):886–92.
Li C, Li JF, Cai Q, Qiu QQ, Yan M, Liu BY, et al. MiRNA-199a-3p: a potential circulating diagnostic biomarker for early gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2013;108(2):89–92.
Chen Y, Zuo J, Liu Y, Gao H, Liu W. Inhibitory effects of miRNA-200c on chemotherapy-resistance and cell proliferation of gastric cancer SGC7901/DDP cells. Chin J Cancer. 2010;29(12):1006–11.
Liu D, Xia P, Diao D, Cheng Y, Zhang H, Yuan D, et al. MiRNA-429 suppresses the growth of gastric cancer cells in vitro. J Biomed Res. 2012;26(5):389–93.
Sacconi A, Biagioni F, Canu V, Mori F, Di Benedetto A, Lorenzon L, et al. miR-204 targets Bcl-2 expression and enhances responsiveness of gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3:e423.
Li X, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Liu X, Gong T, Li M, et al. miRNA-223 promotes gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting tumor suppressor EPB41L3. Mol Cancer Res. 2011;9(7):824–33.
Zhang L, Wang X, Chen P. MiR-204 down regulates SIRT1 and reverts SIRT1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition, anoikis resistance and invasion in gastric cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:290.
Zhou X, Li L, Su J, Zhang G. Decreased miR-204 in H. pylori-associated gastric cancer promotes cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting SOX4. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e101457.
Shin VY, Chu KM. MiRNA as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(30):10432–9.
Zhang R, Wang W, Li F, Zhang H, Liu J. MicroRNA-106b~25 expressions in tumor tissues and plasma of patients with gastric cancers. Med Oncol. 2014;31(10):243.
Huang Z, Huang D, Ni S, Peng Z, Sheng W, Du X. Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(1):118–26.
Yin Y, Zhang B, Wang W, Fei B, Quan C, Zhang J, et al. miR-204-5p inhibits proliferation and invasion and enhances chemotherapeutic sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by down-regulating RAB22A. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1030.
Ying Z, Li Y, Wu J, Zhu X, Yang Y, Tian H, et al. Loss of miR-204 expression enhances glioma migration and stem cell-like phenotype. Cancer Res. 2013;73(2):990–9.
Li W, Jin X, Zhang Q, Zhang G, Deng X, Ma L. Decreased expression of miR-204 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(6):3287–92.
Kaneko S, Yoshimura T. Time trend analysis of gastric cancer incidence in Japan by histological types, 1975–1989. Br J Cancer. 2001;84(3):400–5.
Verdecchia A, Corazziari I, Gatta G, Lisi D, Faivre J, Forman D, et al. Explaining gastric cancer survival differences among European countries. Int J Cancer. 2004;109(5):737–41.
Chen Z, Sangwan V, Banerjee S, Mackenzie T, Dudeja V, Li X, et al. miR-204 mediated loss of Myeloid cell leukemia-1 results in pancreatic cancer cell death. Mol Cancer. 2013;12(1):105.
Lee Y, Yang X, Huang Y, Fan H, Zhang Q, Wu Y, et al. Network modeling identifies molecular functions targeted by miR-204 to suppress head and neck tumor metastasis. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010;6(4):e1000730.
Mikhaylova O, Stratton Y, Hall D, Kellner E, Ehmer B, Drew AF, et al. VHL-regulated MiR-204 suppresses tumor growth through inhibition of LC3B-mediated autophagy in renal clear cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2012;21(4):532–46.
Bao W, Wang HH, Tian FJ, He XY, Qiu MT, Wang JY, et al. A TrkB-STAT3-miR-204-5p regulatory circuitry controls proliferation and invasion of endometrial carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:155.
Chung TK, Lau TS, Cheung TH, Yim SF, Lo KW, Siu NS, et al. Dysregulation of microRNA-204 mediates migration and invasion of endometrial cancer by regulating FOXC1. Int J Cancer. 2012;130(5):1036–45.
Gong M, Ma J, Li M, Zhou M, Hock JM, Yu X. MicroRNA-204 critically regulates carcinogenesis in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2012;14(8):1007–17.
Parsons JL, Dianova II, Khoronenkova SV, Edelmann MJ, Kessler BM, Dianov GL. USP47 is a deubiquitylating enzyme that regulates base excision repair by controlling steady-state levels of DNA polymerase beta. Mol Cell. 2011;41(5):609–15.
Peschiaroli A, Skaar JR, Pagano M, Melino G. The ubiquitin-specific protease USP47 is a novel beta-TRCP interactor regulating cell survival. Oncogene. 2010;29(9):1384–93.
Huang Z, Wen P, Kong R, Cheng H, Zhang B, Quan C, et al. USP33 mediates Slit-Robo signaling in inhibiting colorectal cancer cell migration. Int J Cancer. 2014;. doi:10.1002/ijc.29226.
Pereira-Leal JB, Seabra MC. Evolution of the Rab family of small GTP-binding proteins. J Mol Biol. 2001;313(4):889–901.
Bourne HR, Sanders DA, McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991;349(6305):117–27.
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by grants from the National Natural 39 Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81000867, 81272299, and 81301784) and Medical Key Professionals Program of Jiangsu Province (RC2011031).
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interests. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Yin, Y., Hu, Y. et al. MicroRNA-204-5p inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation by downregulating USP47 and RAB22A. Med Oncol 32, 331 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0331-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0331-y