Abstract
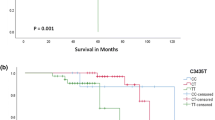
Imatinib mesylate (IM) has so far been the standard of care for treating chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), but the initial striking efficacy of this drug has been overshadowed by the development of clinical resistance, which may in part be caused by pharmacogenetic variability. The ATP-binding cassette, subfamily B, member 1 (ABCB1) gene codes for P-glycoprotein (P-gp), a membrane-bound efflux transporter known to affect the pharmacokinetics of many drugs. IM is a substrate of the P-gp-mediated efflux. ABCB1 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have been reported as modulators of ABCB1-mediated transport, affecting IM’s bioavailability and consequently the treatment outcome of IM therapy. We aimed to examine the association between ABCB1 SNPs and the likelihood of achieving optimal response in IM-treated CML patients. Three ABCB1 SNPs (C1236T, G2677T, and C3435T) were genotyped in 100 Egyptian patients with CML undergoing IM therapy using polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) assay. The optimal response rate did not differ significantly between C1236T, G2677T, or C3435T genotypes (P > 0.05). Optimal response rate was significantly different among patients with the CGC, TTT, TGC, CGT, TGT, CTC, CTT, and TTC haplotypes (P = 0.023). The 1236T-2677G-3435T haplotype was significantly associated with lower probability of achieving optimal response (P = 0.001). ABCB1 SNPs haplotype analysis should be taken into account in an attempt to get clearer insights into who is likely to respond optimally to IM for identifying CML patients who may not respond optimally to standard-dose IM therapy and potentially need an individualized therapeutic approach.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melo JV, Barnes DJ. Chronic myeloid leukemia as a model of disease evolution in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(6):441–53.
Kantarjian HM, Cortes J, La Rosee P, Hochhaus A. Optimizing therapy for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase. Cancer. 2010;116(6):1419–30.
Kantarjian HM, Talpaz M, Giles F, O’Brien S, Cortes J. New insights into the pathophysiology of chronic myeloid leukemia and imatinib resistance. Ann Intern Med. 2006;145(12):913–23.
Haiat S, Decleves X, Mittaine B, Legrand O, Francart S, Rio B, Vekhoff A, Chast F, Marie JP, Bardin C. Determination of imatinib plasma levels by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): evaluation of pharmacokinetic variability and haematological consequences. Blood, ASH annual meeting abstracts 2006; 108: Abstract 1375.
Illmer T, Schaich M, Platzbecker U, Freiberg-Richter J, Oelschlägel U, von Bonin M, Pursche S, Bergemann T, Ehninger G, Schleyer E. P-glycoprotein-mediated drug efflux is a resistance mechanism of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells to treatment with imatinib mesylate. Leukemia. 2004;18(3):401–8.
Wolf SJ, Bachtiar M, Wang J, Sim TS, Chong SS, Lee CG. An update on ABCB1 pharmacogenetics: insights from a 3D model into the location and evolutionary conservation of residues corresponding to SNPs associated with drug pharmacokinetics. Pharmacogenomics. 2011;11(5):315–25.
Ieiri I, Takane H, Otsubo K. The MDR1 (ABCB1) gene polymorphism and its clinical implications. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2004;43(9):553–76.
Marzolini C, Paus E, Buclin T, Kim RB. Polymorphisms in human MDR1 (P-glycoprotein): recent advances and clinical relevance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2004;75(1):13–33.
Leschziner GD, Andrew T, Pirmohamed M, Johnson MR. ABCB1 genotype and PGP expression, function and therapeutic drug response: a critical review and recommendations for future research. Pharmacogenomics. 2007;7(3):154–79.
Pauli-Magnus C, Kroetz DL. Functional implications of genetic polymorphisms in the multidrug resistance gene MDR1 (ABCB1). Pharm Res. 2004;21(6):904–13.
Woodahl EL, Ho RJ. The role of MDR1 genetic polymorphisms in interindividual variability in P-glycoprotein expression and function. Curr Drug Metab. 2004;5(1):11–9.
Gardner ER, Burger H, van Schaik RH, van Oosterom AT, de Bruijn EA, Guetens G, Prenen H, de Jong FA, Baker SD, Bates SE, Figg WD, Verweij J, Sparreboom A, Nooter K. Association of enzyme and transporter genotypes with the pharmacokinetics of imatinib. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006;80(2):192–201.
Gurney H, Wong M, Balleine RL, Rivory LP, McLachlan AJ, Hoskins JM, Wilcken N, Clarke CL, Mann GJ, Collins M, Delforce SE, Lynch K, Schran H. Imatinib disposition and ABCB1 (MDR1, P-glycoprotein) genotype. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;82(1):33–40.
Kimchi-Sarfaty C, Marple AH, Shinar S, Kimchi AM, Scavo D, Roma MI, Kim IW, Jones A, Arora M, Gribar J, Gurwitz D, Gottesman MM. Ethnicity-related polymorphisms and haplotypes in the human ABCB1 gene. Pharmacogenomics. 2007;8(1):29–39.
Dulucq S, Bouchet S, Turcq B, Lippert E, Etienne G, Reiffers J, Molimard M, Krajinovic M, Mahon FX. Multidrug resistance gene (MDR1) polymorphisms are associated with major molecular responses to standard-dose imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2008;112(5):2024–7.
Dulucq S, Preudhomme C, Guilhot F, Mahon FX. Is there really a relationship between Multidrug resistance gene (MDR1) polymorphisms and major molecular response to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2010;116(26):6145–6.
Kim DH, Sriharsha L, Xu W, Kamel-Reid S, Liu X, Siminovitch K, Messner HA, Lipton JH. Clinical relevance of a pharmacogenetic approach using multiple candidate genes to predict response and resistance to imatinib therapy in chronic myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(14):4750–8.
Takahashi N, Miura M, Scott SA, Kagaya H, Kameoka Y, Tagawa H, Saitoh H, Fujishima N, Yoshioka T, Hirokawa M, Sawada K. Influence of CYP3A5 and drug transporter polymorphisms on imatinib trough concentration and clinical response among patients with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. J Hum Genet. 2010;55(11):731–7.
Deenik W, van der Holt B, Janssen JJ, Chu IW, Valk PJ, Ossenkoppele GJ, van der Heiden IP, Sonneveld P, van Schaik RH, Cornelissen JJ. Polymorphisms in the multidrug resistance gene MDR1 (ABCB1) predict for molecular resistance in patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia receiving high-dose imatinib. Blood. 2010;16(26):6144–5.
Ni LN, Li JY, Miao KR, Qiao C, Zhang SJ, Qiu HR, Qian SX. Multidrug resistance gene (MDR1) polymorphisms correlate with imatinib response in chronic myeloid leukemia. Med Oncol. 2011;28(1):265–9.
Maffioli M, Camós M, Gaya A, Hernández-Boluda JC, Alvarez-Larrán A, Domingo A, Granell M, Guillem V, Vallansot R, Costa D, Bellosillo B, Colomer D, Cervantes F. Correlation between genetic polymorphims of the hOCT1 and MDR1 genes and the response to imatinib in patients newly diagnosed with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 2011;35(8):1014–9.
Angelini S, Soverini S, Ravegnini G, Barnett M, Turrini E, Thornquist M, Pane F, Hughes TP, White DL, Radich J, Kim DW, Saglio G, Cilloni D, Iacobucci I, Perini G, Woodman R, Cantelli-Forti G, Baccarani M, Hrelia P, Martinelli G. Association between imatinib transporters and metabolizing enzymes genotype and response in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia patients receiving imatinib therapy. Haematologica. 2013;98(2):193–200.
Vine J, Cohen SB, Ruchlemer R, Goldschmidt N, Levin M, Libster D, Gural A, Gatt ME, Lavie D, Ben-Yehuda D, Rund D. Polymorphisms in the human organic cation transporter and the multidrug resistance gene: correlation with imatinib levels and clinical course in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2014 [Epub ahead of print].
Baccarani M, Deininger MW, Rosti G, Hochhaus A, Soverini S, Apperley JF, Cervantes F, Clark RE, Cortes JE, Guilhot F, Hjorth-Hansen H, Hughes TP, Kantarjian HM, Kim DW, Larson RA, Lipton JH, Mahon FX, Martinelli G, Mayer J, Müller MC, Niederwieser D, Pane F, Radich JP, Rousselot P, Saglio G, Saußele S, Schiffer C, Silver R, Simonsson B, Steegmann JL, Goldman JM, Hehlmann R. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood. 2013;122(6):872–84.
Hughes T, Deininger M, Hochhaus A, Branford S, Radich J, Kaeda J, Baccarani M, Cortes J, Cross NC, Druker BJ, Gabert J, Grimwade D, Hehlmann R, Kamel-Reid S, Lipton JH, Longtine J, Martinelli G, Saglio G, Soverini S, Stock W, Goldman JM. Monitoring CML patients responding to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: review and recommendation for harmonizing current methodology for detecting BCR-ABL transcripts and kinase domain mutations and for expressing results. Blood. 2006;108(1):28–37.
Cross NCP, White HE, Muller MC, Saglio G, Hochhaus A. Standardized definitions of molecular response in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2012;26(10):2172–5.
Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Johne A, Meisel C, Hoffmeyer S, Schwab M, Schaeffeler E, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U, Roots I. Frequency of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the P-glycoprotein drug transporter MDR1 gene in white subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001;69(3):169–74.
Roberts RL, Joyce PR, Mulder RT, Begg EJ, Kennedy MA. A common P-glycoprotein polymorphism is associated with nortriptyline-induced postural hypotension in patients treated for major depression. Pharmacogenomics J. 2002;2(3):191–6.
Norusis M. SPSS 17.0 advanced statistical procedures companion. 2009; Upper Saddle-River: Prentice Hall.
Guo SW, Thompson EA. Performing the exact test of Hardy–Weinberg proportion for multiple alleles. Biometrics. 1992;48(2):361–72.
Devlin B, Risch N. A comparison of linkage disequilibrium measures for fine-scale mapping. Genomics. 1995;29(2):311–22.
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics. 2005;21(2):263–5.
Kantarjian HM, Giles F, Gattermann N, Bhalla K, Alimena G, Palandri F, Ossenkoppele GJ, Nicolini FE, O’Brien SG, Litzow M, Bhatia R, Cervantes F, Haque A, Shou Y, Resta DJ, Weitzman A, Hochhaus A, le Coutre P. Nilotinib (formerly AMN107), a highlyselective BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is effective in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase following imatinib resistance and intolerance. Blood. 2007;110(10):3540–6.
Hochhaus A, Kantarjian HM, Baccarani M, Lipton JH, Apperley JF, Druker BJ, Facon T, Goldberg SL, Cervantes F, Niederwieser D, Silver RT, Stone RM, Hughes TP, Muller MC, Ezzeddine R, Countouriotis AM, Shah NP. Dasatinib induces notable hematologic and cytogenetic responses in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia after failure of imatinib therapy. Blood. 2007;109(6):2303–9.
Saglio G, Kim DW, Issaragrisil S, le Coutre P, Etienne G, Lobo C, Pasquini R, Clark RE, Hochhaus A, Hughes TP, Gallagher N, Hoenekopp A, Dong M, Haque A, Larson RA, Kantarjian HM. ENESTnd Investigators. Nilotinib versus imatinib for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(24):2251–9.
Kantarjian H, Shah NP, Hochhaus A, Cortes J, Shah S, Ayala M, Moiraghi B, Shen Z, Mayer J, Pasquini R, Nakamae H, Huguet F, Boqué C, Chuah C, Bleickardt E, Bradley-Garelik MB, Zhu C, Szatrowski T, Shapiro D, Baccarani M. Dasatinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(24):2260–70.
Kantarjian HM, Hochhaus A, Saglio G, De Souza C, Flinn IW, Stenke L, Goh YT, Rosti G, Nakamae H, Gallagher NJ, Hoenekopp A, Blakesley RE, Larson RA, Hughes TP. Nilotinib versus imatinib for the treatment of patients with newly diagnosed chronic phase, Philadelphia chromosome-positive, chronic myeloid leukaemia: 24-month minimum follow-up of the phase 3 randomised ENESTnd trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(9):841–51.
Kantarjian HM, Shah NP, Cortes JE, Baccarani M, Agarwal MB, Undurraga MS, Wang J, Ipiña JJ, Kim DW, Ogura M, Pavlovsky C, Junghanss C, Milone JH, Nicolini FE, Robak T, Van Droogenbroeck J, Vellenga E, Bradley-Garelik MB, Zhu C, Hochhaus A. Dasatinib or imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: 2-year follow-up from a randomized phase 3 trial (DASISION). Blood. 2012;119(5):1123–9.
Sakaeda T, Nakamura T, Okimura K. MDR1 genotype related pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Biol Pharm Bull. 2002;25(11):1391–400.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, M.A.M., Elsalakawy, W.A. ABCB1 haplotypes but not individual SNPs predict for optimal response/failure in Egyptian patients with chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia receiving imatinib mesylate. Med Oncol 31, 279 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0279-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0279-y