Abstract
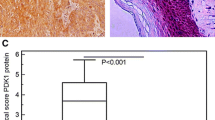
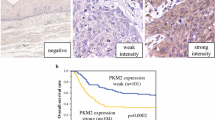
Enhanced glycolysis is a common trait of many types of human cancers. This study was to detect the expression pattern of three regulatory enzymes during glycolysis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and to investigate their correlation with patients’ outcome based on banked pathology material. A total of 141 surgically resected specimens of primary ESCC patients without prior treatments were retrospectively recruited from the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical College Hospital from 2007 to 2009. Expression of HK1, PFKB, and PKM2 in ESCC specimens was analyzed by immunohistochemical staining and Western blotting analysis. HK1-shRNA was used to knock down HK1 expression in ESCC cells, and the functional significance was assessed by CCK8 assay. It was found that the expression of two glycolytic enzymes, HK1 and PKM2, was associated with disease progression, invasion, and poor survival of patients with ESCC. Silence of HK1-inhibited cell proliferation in vitro and suppressed phospho-S6 kinase expression. Our findings suggest that activation of key enzymes in glycolysis might serve as potential therapeutic targets and/or prognostic factors for patients with ESCC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 2013;381(9864):400–12.
Kim T, Grobmyer SR, Smith R, Ben-David K, Ang D, Vogel SB, Hochwald SN. Esophageal cancer—the five year survivors. J Surg Oncol. 2011;103(2):179–83.
Shahbaz Sarwar CM, Luketich JD, Landreneau RJ, Abbas G. Esophageal cancer: an update. Int J Surg. 2010;8(6):417–22.
Kaz AM, Grady WM. Epigenetic biomarkers in esophageal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014;342(2):193–9.
Yokobori T, Kuwano H. Molecular biological review of esophageal cancer. Kyobu geka Japanese J Thorac Surg. 2013;66(1):73–84.
Lepage C, Drouillard A, Jouve JL, Faivre J. Epidemiology and risk factors for oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Dig Liver Dis. 2013;45(8):625–9.
Icard P, Poulain L, Lincet H. Understanding the central role of citrate in the metabolism of cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1825(1):111–6.
Jang M, Kim SS, Lee J. Cancer cell metabolism: implications for therapeutic targets. Exp Mol Med. 2013;45:e45.
Pare G, Chasman DI, Parker AN, Nathan DM, Miletich JP, Zee RY, Ridker PM. Novel association of HK1 with glycated hemoglobin in a non-diabetic population: a genome-wide evaluation of 14,618 participants in the Women’s Genome Health Study. PLoS Genet. 2008;4(12):e1000312.
Bonnefond A, Vaxillaire M, Labrune Y, Lecoeur C, Chevre JC, Bouatia-Naji N, Cauchi S, Balkau B, Marre M, Tichet J, et al. Genetic variant in HK1 is associated with a proanemic state and A1C but not other glycemic control-related traits. Diabetes. 2009;58(11):2687–97.
Pinney SE, Ganapathy K, Bradfield J, Stokes D, Sasson A, Mackiewicz K, Boodhansingh K, Hughes N, Becker S, Givler S, et al. Dominant form of congenital hyperinsulinism maps to HK1 region on 10q. Horm Res Paediatr. 2013;80(1):18–27.
Jiang L, Ren J, Xiao X, Tang YY, Weng HQ, Yang Q, Wu MJ, Tang W. Proteomic analysis of bladder cancer by iTRAQ after bifidobacterium infantis-mediated HSV-TK/GCV suicide gene treatment. Biol Chem. 2013;394(10):1333–42.
Filipp FV. Cancer metabolism meets systems biology: pyruvate kinase isoform PKM2 is a metabolic master regulator. J Carcinogenesis. 2013;12:14.
Yang W, Lu Z. Nuclear PKM2 regulates the Warburg effect. Cell Cycle. 2013;12(19):3154–8.
Zhang X, He C, He C, Chen B, Liu Y, Kong M, Wang C, Lin L, Dong Y, Sheng H. Nuclear PKM2 expression predicts poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 2013;209(8):510–5.
Nemazanyy I, Espeillac C, Pende M, Panasyuk G. Role of PI3K, mTOR and Akt2 signalling in hepatic tumorigenesis via the control of PKM2 expression. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013;41(4):917–22.
Lv L, Xu YP, Zhao D, Li FL, Wang W, Sasaki N, Jiang Y, Zhou X, Li TT, Guan KL, et al. Mitogenic and oncogenic stimulation of K433 acetylation promotes PKM2 protein kinase activity and nuclear localization. Mol Cell. 2013;52(3):340–52.
Jiang Y, Li X, Yang W, Hawke DH, Zheng Y, Xia Y, Aldape K, Wei C, Guo F, Chen Y et al: PKM2 Regulates chromosome segregation and mitosis progression of tumor cells. Mol Cell. 2014;53(1):75–87.
Elstrom RL, Bauer DE, Buzzai M, Karnauskas R, Harris MH, Plas DR, Zhuang H, Cinalli RM, Alavi A, Rudin CM, et al. Akt stimulates aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64(11):3892–9.
Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ. Glycolysis in cancer: a potential target for therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(7–8):1358–66.
Suh DH, Kim MA, Kim H, Kim MK, Kim HS, Chung HH, Kim YB, Song YS. Association of overexpression of hexokinase II with chemoresistance in epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin Exp Med. 2013. doi:10.1007/s10238-013-0250-9.
Peschiaroli A, Giacobbe A, Formosa A, Markert EK, Bongiorno-Borbone L, Levine AJ, Candi E, D’Alessandro A, Zolla L, Finazzi Agro A, et al. miR-143 regulates hexokinase 2 expression in cancer cells. Oncogene. 2013;32(6):797–802.
Gregersen LH, Jacobsen A, Frankel LB, Wen J, Krogh A, Lund AH. MicroRNA-143 down-regulates hexokinase 2 in colon cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:232.
Peng Q, Zhou J, Zhou Q, Pan F, Zhong D, Liang H. Silencing hexokinase II gene sensitizes human colon cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil. Hepatogastroenterology. 2009;56(90):355–60.
Palmieri D, Fitzgerald D, Shreeve SM, Hua E, Bronder JL, Weil RJ, Davis S, Stark AM, Merino MJ, Kurek R, et al. Analyses of resected human brain metastases of breast cancer reveal the association between up-regulation of hexokinase 2 and poor prognosis. Mol Cancer Res MCR. 2009;7(9):1438–45.
Peng QP, Zhou JM, Zhou Q, Pan F, Zhong DP, Liang HJ. Downregulation of the hexokinase II gene sensitizes human colon cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil. Chemotherapy. 2008;54(5):357–63.
Gjesing AP, Nielsen AA, Brandslund I, Christensen C, Sandbaek A, Jorgensen T, Witte D, Bonnefond A, Froguel P, Hansen T, et al. Studies of a genetic variant in HK1 in relation to quantitative metabolic traits and to the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. BMC Med Genet. 2011;12:99.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wenfeng Li, Zhengyang Xu and Junfeng Hong have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Xu, Z., Hong, J. et al. Expression patterns of three regulation enzymes in glycolysis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: association with survival. Med Oncol 31, 118 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0118-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0118-1