Abstract
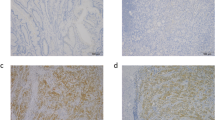
Inter-α-trypsin inhibitors (ITIs) are a family of serine protease inhibitors that comprise one light chain and a variable set of heavy chains (ITI heavy chains, ITIHs). ITIH5 is a new member of the ITIH family that contains two domains conserved in all known ITIHs: vault protein IT and von Willebrand type A. Recent studies suggest that ITIH5 expression may be altered in certain types of cancer. This study aimed to investigate ITIH5 expression in clinical tumor specimens from gastric cancer patients and its prognostic value for gastric cancer. ITIH5 expression was detected in fresh gastric cancer tissues (T) and the matched adjacent non-tumor tissues (ANT) using real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR and Western blotting. ITIH5 expression was retrospectively detected in 331 paraffin-embedded, banked samples using immunohistochemical staining. ITIH5 mRNA and protein expression was significantly downregulated in gastric cancer tissues compared to the ANT. There was a significant association between ITIH5 expression and histological grade (P = 0.020), N classification (P = 0.047), and clinical stage (P = 0.011). Patients with low ITIH5 expression had shorter survival compared to those with high ITIH5 expression. Multivariate analysis showed that ITIH5 expression was an independent prognostic factor for overall survival of gastric cancer patients (P = 0.034). Our data suggest that ITIH5 could play an important role in gastric cancer and may serve as a valuable prognostic biomarker and potential molecular therapy target for gastric cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jinawath N, Furukawa Y, Hasegawa S, et al. Comparison of gene-expression profiles between diffuse- and intestinal-type gastric cancers using a genome-wide cDNA microarray. Oncogene. 2004;23(40):6830–44.
Li YF, Wang DD, Zhao BW, et al. Poor prognosis of gastric adenocarcinoma with decreased expression of AHRR. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(8):e43555.
Tay ST, Leong SH, Yu K, et al. A combined comparative genomic hybridization and expression microarray analysis of gastric cancer reveals novel molecular subtypes. Cancer Res. 2003;63(12):3309–16.
Yang XB, Zhao JJ, Huang CY, et al. Decreased expression of the FOXO3a gene is associated with poor prognosis in primary gastric adenocarcinoma patients. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(10):e78158.
Wang P, Mai C, Wei YL, et al. Decreased expression of the mitochondrial metabolic enzyme aconitase (ACO2) is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 2013;30(2):552.
Chen Y, Pan K, Li S, et al. Decreased expression of V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 1 (VSIG1) is associated with poor prognosis in primary gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2012;106(3):286–93.
Miao R, Guo X, Zhi Q, et al. VEZT, a novel putative tumor suppressor, suppresses the growth and tumorigenicity of gastric cancer. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(9):e74409.
Kim K, Chun KH, Suh PG, Kim IH. Alterations in cell proliferation related gene expressions in gastric cancer. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2011;21(3):237–54.
Saeki N, Ono H, Sakamoto H, Yoshida T. Genetic factors related to gastric cancer susceptibility identified using a genome-wide association study. Cancer Sci. 2013;104(1):1–8.
Veeck J, Chorovicer M, Naami A, et al. The extracellular matrix protein ITIH5 is a novel prognostic marker in invasive node-negative breast cancer and its aberrant expression is caused by promoter hypermethylation. Oncogene. 2008;27(6):865–76.
Wei B, Song Y, Zhang Y, Hu M. microRNA-449a functions as a tumor-suppressor in gastric adenocarcinoma by targeting Bcl-2. Oncol Lett. 2013;6(6):1713–8.
Himmelfarb M, Klopocki E, Grube S, et al. ITIH5, a novel member of the inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain family is downregulated in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2004;204(1):69–77.
Oing C, Jost E, Dahl E, Wilop S, Brummendorf TH, Galm O. Aberrant DNA hypermethylation of the ITIH5 tumor suppressor gene in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Epigenetics. 2011;2(2):419–23.
Diarra-Mehrpour M, Bourguignon J, Sesboue R, et al. Human plasma inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor is encoded by four genes on three chromosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1989;179(1):147–54.
Diarra-Mehrpour M, Sarafan N, Bourguignon J, Bonnet F, Bost F, Martin JP. Human inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H3 gene. Genomic organization, promoter analysis, and gene linkage. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(41):26809–19.
Hamm A, Veeck J, Bektas N, et al. Frequent expression loss of Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain (ITIH) genes in multiple human solid tumors: a systematic expression analysis. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:25.
Lu Y, Liu P, Wen W, et al. Cross-species comparison of orthologous gene expression in human bladder cancer and carcinogen-induced rodent models. Am J Transl Res. 2010;3(1):8–27.
Pita JM, Banito A, Cavaco BM, Leite V. Gene expression profiling associated with the progression to poorly differentiated thyroid carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 2009;101(10):1782–91.
Huang L, Yoneda M, Kimata K. A serum-derived hyaluronan-associated protein (SHAP) is the heavy chain of the inter alpha-trypsin inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(35):26725–30.
Kobayashi H, Gotoh J, Hirashima Y, Fujie M, Sugino D, Terao T. Inhibitory effect of a conjugate between human urokinase and urinary trypsin inhibitor on tumor cell invasion in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(14):8361–6.
Zhao M, Yoneda M, Ohashi Y, et al. Evidence for the covalent binding of SHAP, heavy chains of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor, to hyaluronan. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(44):26657–63.
Paris S, Sesboue R, Delpech B, et al. Inhibition of tumor growth and metastatic spreading by overexpression of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor family chains. Int J Cancer. 2002;97(5):615–20.
Nagini S. Carcinoma of the stomach: a review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, molecular genetics and chemoprevention. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2012;4(7):156–69.
Zouridis H, Deng N, Ivanova T, et al. Methylation subtypes and large-scale epigenetic alterations in gastric cancer. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(156):156ra140.
Miotto E, Sabbioni S, Veronese A, et al. Frequent aberrant methylation of the CDH4 gene promoter in human colorectal and gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64(22):8156–9.
Graff JR, Herman JG, Lapidus RG, et al. E-cadherin expression is silenced by DNA hypermethylation in human breast and prostate carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1995;55(22):5195–9.
Bachman KE, Herman JG, Corn PG, et al. Methylation-associated silencing of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 gene suggest a suppressor role in kidney, brain, and other human cancers. Cancer Res. 1999;59(4):798–802.
Shao G, Berenguer J, Borczuk AC, Powell CA, Hei TK, Zhao Y. Epigenetic inactivation of Betaig-h3 gene in human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66(9):4566–73.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant 30973398.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Cong Mai, Jing-jing Zhao and Xiao-feng Tang have contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mai, C., Zhao, Jj., Tang, Xf. et al. Decreased ITIH5 expression is associated with poor prognosis in primary gastric cancer. Med Oncol 31, 53 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0053-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0053-1