Abstract
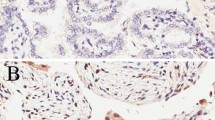
The expression of survivin, an inhibitor of apoptosis can be seen in most tumors and is correlated with the angiogenic factor vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). But little is known about their contribution in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). This study was designed to investigate the expression of survivin and VEGF in SCLC, and to explore their correlation with clinical-pathological feature and prognosis. Forty-five patients with pathological histology of SCLC were entered into this study. Forty-five cases of matched adjacent non-tumor samples and 10 samples of operated patients with benign lung tumor were also included as control. The expression of survivin and VEGF was detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC, SP). These two sets of data were processed and tested for correlation with major patients’ characteristics, and overall survival. The correlations between survivin and VEGF expressions and the clinical-pathological features were evaluated by chi-square test. The correlation between survivin and VEGF expressions was analyzed by Spearman’s rank correlation test; the overall survival was analyzed by the Kaplan–Meier method; and the relationship between clinical and pathological features and overall survival was analyzed by the Cox proportional hazard models. Positive expression rate of survivin and VEGF was significantly higher in SCLC than those of adjacent non-tumor tissues and benign lung tumor tissues (73.3 vs. 15.6 vs. 0 %, P < 0.05) and (75.6 vs. 20 vs. 0 %, P < 0.05), respectively. Survivin and VEGF expressions were significantly associated with lymph node metastasis (P = 0.003, 0.011) and clinical stage (P = 0.006, 0.021). The expression of survivin was significantly coincident with the expression of VEGF (r = 0.644, P = 0.000). The median overall survival in survivin positive group and VEGF positive group was significantly shorter than those in survivin negative and VEGF negative group, respectively (log-rank P = 0.000). Moreover, multivariate analysis showed that survivin expression (HR 0.224; 95 % CI 0.074–0.675; P = 0.008) and VEGF expression (HR 0.172; 95 % CI 0.054–0.559; P = 0.003) were statistically independent predictive factors of poorer prognosis for SCLC patients. Our results indicated that survivin and VEGF were over-expressed in small-cell lung cancer, each of them may be an independent poor prognostic factor.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SCLC:
-
Small-cell lung cancer
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- IAP:
-
Inhibitors of apoptosis
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small-cell lung cancer
- SP technique:
-
Streptavidin-peroxidase-biotin technique
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- NPC:
-
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300.
Yip D, Harper PG. Predictive and prognostic factors in small cell lung cancer: current status. Lung Cancer. 2000;28:173–85.
Batus M, Myint R, Coon J, Basu S, Kaiser K, Fidler M, Bonomi P. N-cadherin, E-cadherin, ERCC1, and c-kit expression in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and potential for new therapeutic targets. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27(Suppl 15s):(abstract e22157).
Cañadas I, Arumi M, Lema L, Martinez A, Grande E, Bellosillo B, Rojo F, Rovira A, Albanell J, Arriola E. MET in small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC): effects of a MET inhibitor in SCLC cell lines and prognostic role of MET status in patients. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27 (Suppl 15s):(abstract e14617).
Gonzalez R, Silva JM, Sanchez A, Dominguez G, Garcia JM, Chen XQ, Stroun M, Provencio M, España P, Anker P, Bonilla F. Microsatellite alterations and TP53 mutations in plasma DNA of small-cell lung cancer patients: follow-up study and prognostic significance. Ann Oncol. 2000;11:1097–104.
Srinivasula SM, Ashwell JD. IAPs: what’s in a name? Mol Cell. 2008;30:123–35.
Hernandez JM, Farma JM, Coppola D, Hakam A, Fulp WJ, Chen DT, Siegel EM, Yeatman TJ, Shibata D. Expression of the antiapoptotic protein survivin in colon cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2011;10:188–93.
Adamkov M, Halasova E, Kajo K, Machalekova K, Vybohova D, Varga I, Rajcany J. Survivin: a promising biomarker in breast carcinoma. Neoplasma. 2010;57:572–7.
Park E, Gang EJ, Hsieh YT, Schaefer P, Chae S, Klemm L, Huantes S, Loh M, Conway EM, Kang ES, Hoe Koo H, Hofmann WK, Heisterkamp N, Pelus L, Keerthivasan G, Crispino J, Kahn M, Müschen M, Kim YM. Targeting survivin overcomes drug resistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2011;118:2191–9.
Wang M, Liu BG, Yang ZY, Hong X, Chen GY. Significance of survivin expression: prognostic value and survival in stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Exp Ther Med. 2012;3:983–8.
Salz W, Eisenberg D, Plescia J, Garlick DS, Weiss RM, Wu XR, Sun TT, Altieri DC. A survivin gene signature predicts aggressive tumor behavior. Cancer Res. 2005;65:3531–4.
Trabulo S, Cardoso AM, Santos-Ferreira T, Cardoso AL, Simões S, Pedroso de Lima MC. Survivin silencing as a promising strategy to enhance the sensitivity of cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Mol Pharm. 2011;8:1120–31.
Nassar A, Lawson D, Cotsonis G, Cohen C. Survivin and caspase-3 expression in breast cancer: correlation with prognostic parameters, proliferation, angiogenesis, and outcome. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2008;16:113–20.
Kawasaki H, Toyoda M, Shinohara H, Okuda J, Watanabe I, Yamamoto T, Tanaka K. Expression of survivin correlates with apoptosis, proliferation, and angiogenesis during human colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer. 2001;91:2026–32.
Tanno S, Ohsaki Y, Nakanishi K, Toyoshima E, Kikuchi K. Human small cell lung cancer cells express functional VEGF receptors, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3. Lung Cancer. 2004;46:11–9.
Byrne AM, Bouchier-Hayes DJ, Harmey JH. Angiogenic and cell survival functions of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). J Cell Mol Med. 2005;9:777–94.
Lizasa T, Chang H, Suzuki M, Otsuji M, Yokoi S, Chiyo M, Motohashi S, Yasufuku K, Sekine Y, Iyoda A, Shibuya K, Hiroshima K, Fujisawa T. Overexpression of collagen XVIII is associated with poor outcome and elevated levels of circulating serum endostatin in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:5361–6.
Folkman J, Watson K, Ingber D, Hanahan D. Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia to neoplasia. Nature. 1989;339:58–61.
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Koukourakis MI. Angiogenesis in colorectal cancer: prognostic and therapeutic implications. Am J Clin Oncol. 2006;29:408–17.
Pavlyukov MS, Antipova NV, Balashova MV, Vinogradova TV, Kopantzev EP, Shakhparonov MI. Survivin monomer plays an essential role in apoptosis regulation. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:23296–307.
Kim K, Chie EK, Wu HG, Kim SG, Lee SH, Kang GH, Hyun CL, Ha SW. High survivin expression as a predictor of poor response to preoperative chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2011;26:1019–23.
Yang Y, Zhu J, Gou HF, Cao D, Jiang M, Hou M. Clinical significance of Cox-2, Survivin and Bcl-2 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Med Oncol. 2011;28:796–803.
Zhu HX, Wang QF, Hu CF, Zhang WC, Quan LP, Liu M, Xu NZ, Xiao ZF. High expression of survivin predicts poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma following radiotherapy. Tumor Biol. 2011;32:1147–53.
Yasumitsu A, Tabata C, Tabata R, Hirayama N. Clinical significance of serum vascular endothelial growth factor in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5:479–83.
Oshita F, Ito H, Ikehara M, Ohgane N, Hamanaka N, Nakayama H, Saito H, Yamada K, Noda K, Mitsuda A, Kameda Y. Prognostic impact of surviving, cyclin D1, integrin beta 1, and VEGF in patients with small adenocarcinoma of stage I lung cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 2004;27:425–8.
Ryan BM, Konecny GE, Kahlert S, Wang HJ, Untch M, Meng G, Pegram MD, Podratz KC, Crown J, Slamon DJ, Duffy MJ. Survivin expression in breast cancer predicts clinical outcome and is associated with HER2, VEGF, urokinase plasminogen activator and PAI-1. Ann Oncol. 2006;17:597–604.
O’Connor DS, Schechner JS, Adida C, Mesri M, Rothermel AL, Li F, Nath AK, Pober JS, Altieri DC. Control of apoptosis during angiogenesis by survivin expression in endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 2000;156:393–8.
Beierle EA, Nagaram A, Dai W, Iyengar M, Chen MK. VEGF-mediated survivin expression in neuroblastoma cells. J Surg Res. 2005;127:21–8.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all their colleagues who participated in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ping Chen and Jiang Zhu have been equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Zhu, J., Liu, Dy. et al. Over-expression of survivin and VEGF in small-cell lung cancer may predict the poorer prognosis. Med Oncol 31, 775 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0775-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0775-5