Abstract
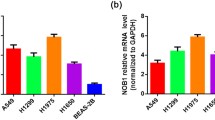
Ribosomal protein L22 (RPL22), an RNA-binding protein, is a constituent of the 60S large ribosomal subunit. As reported, RPL22 is not required in protein synthesis, and mutations of RPL22 were the main cause of macrolide resistance in bacteria. In vertebrates, RPL22 mutation might increase the proliferation of cells and then increase cancer risk. However, to our knowledge, RPL22 has not been implicated in any lung diseases, especially in lung cancer. In this study, we compared the expression of RPL22 gene in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissues, plasma as well as human lung cancer cell line LTEP-a-2 with that in normal lung tissues and cells, using real-time RT-qPCR, Western blot, quantitative immunohistochemistry analysis, and ELISA. Our studies showed that the expression of RPL22 was significantly down-regulated in mRNA and protein expression level in NSCLC; however, there was no significant difference of RPL22 levels in plasma between normal and NSCLC patients. Further analysis indicated that down-regulation of RPL22 might be involved in the carcinogenesis of NSCLC, yet not an effective biomarker in plasma for early diagnosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herbst RS, Heymach JV, Lippman SM. Lung cancer. The New Engl J Med. 2008;359(13):1367–80.
Brambilla E, Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B, Shimosato Y. The new World Health Organization classification of lung tumours. Eur Respir J. 2001;18(6):1059–68.
Giaccone G. Oncogenes and anti oncogenes in lung tumorigenesis. Chest. 1996;109(5 Suppl):130S–4S.
Zajac-Kaye M. Myc oncogene: a key component in cell cycle regulation and its implication for lung cancer. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam, Netherlands). 2001;34(Suppl 2):S43–6.
Johnson L, Mercer K, Greenbaum D, Bronson RT, Crowley D, Tuveson DA, Jacks T. Somatic activation of the K-ras oncogene causes early onset lung cancer in mice. Nature. 2001;410(6832):1111–6.
Hwang SJ, Cheng LS, Lozano G, Amos CI, Gu X, Strong LC. Lung cancer risk in germline p53 mutation carriers: association between an inherited cancer predisposition, cigarette smoking, and cancer risk. Hum Genet. 2003;113(3):238–43.
Vazquez A, Bond EE, Levine AJ, Bond GL. The genetics of the p53 pathway, apoptosis and cancer therapy. Nat Rev. 2008;7(12):979–87.
Warner JR, McIntosh KB. How common are extra ribosomal functions of ribosomal proteins? Mol Cell. 2009;34(1):3–11.
Sun XX, Wang YG, Xirodimas DP, Dai MS. Perturbation of 60S ribosomal biogenesis results in ribosomal protein L5- and L11-dependent p53 activation. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(33):25812–21.
Lohrum MA, Ludwig RL, Kubbutat MH, Hanlon M, Vousden KH. Regulation of HDM2 activity by the ribosomal protein L11. Cancer Cell. 2003;3(6):577–87.
Jin A, Itahana K, O’Keefe K, Zhang Y. Inhibition of HDM2 and activation of p53 by ribosomal protein L23. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(17):7669–80.
Chen D, Zhang Z, Li M, Wang W, Li Y, Rayburn ER, Hill DL, Wang H, Zhang R. Ribosomal protein S7 as a novel modulator of p53–MDM2 interaction: binding to MDM2, stabilization of p53 protein, and activation of p53 function. Oncogene. 2007;26(35):5029–37.
He H, Sun Y. Ribosomal protein S27L is a direct p53 target that regulates apoptosis. Oncogene. 2007;26(19):2707–16.
Lee SB, Kwon IS, Park J, Lee KH, Ahn Y, Lee C, Kim J, Choi SY, Cho SW, Ahn JY. Ribosomal protein S3, a new substrate of Akt, serves as a signal mediator between neuronal apoptosis and DNA repair. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(38):29457–68.
Wang Q, Yang C, Zhou J, Wang X, Wu M, Liu Z. Cloning and characterization of full-length human ribosomal protein L15 cDNA which was overexpressed in esophageal cancer. Gene. 2001;263(1–2):205–9.
Henry JL, Coggin DL, King CR. High-level expression of the ribosomal protein L19 in human breast tumors that overexpress erbB-2. Cancer Res. 1993;53(6):1403–8.
Zheng SE, Yao Y, Dong Y, Lin F, Zhao H, Shen Z, Sun YJ, Tang LN. Down-regulation of ribosomal protein L7A in human osteosarcoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009;135(8):1025–31.
Wang S, Huang J, He J, Wang A, Xu S, Huang SF, Xiao S. RPL41, a small ribosomal peptide deregulated in tumors, is essential for mitosis and centrosome integrity. Neoplasia (New York, NY). 2010;12(3):284–93.
Lehtopolku M, Kotilainen P, Haanpera-Heikkinen M, Nakari UM, Hanninen ML, Huovinen P, Siitonen A, Eerola E, Jalava J, Hakanen AJ. Ribosomal mutations as the main cause of macrolide resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;55(12):5939–41.
Elia A, Vyas J, Laing KG, Clemens MJ. Ribosomal protein L22 inhibits regulation of cellular activities by the Epstein–Barr virus small RNA EBER-1. Eur J Biochem/FEBS. 2004;271(10):1895–905.
Anderson SJ, Lauritsen JP, Hartman MG, Foushee AM, Lefebvre JM, Shinton SA, Gerhardt B, Hardy RR, Oravecz T, Wiest DL. Ablation of ribosomal protein L22 selectively impairs alphabeta T cell development by activation of a p53-dependent checkpoint. Immunity. 2007;26(6):759–72.
Sun K, Xue H, Wang H, Wang Q, Zuo XR, Xie WP, Wang H. The effects of siRNA against RPL22 on ET-1-induced proliferation of human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Int J Mol Med. 2012;30(2):351–7.
Rao S, Lee SY, Gutierrez A, Perrigoue J, Thapa RJ, Tu Z, Jeffers JR, Rhodes M, Anderson S, Oravecz T, et al. Inactivation of ribosomal protein L22 promotes transformation by induction of the stemness factor, Lin28B. Blood. 2012;120(18):3764–73.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods (San Diego, CA). 2001;25(4):402–8.
Shimizu M, Saitoh Y, Itoh H. Immunohistochemical staining of Ha-ras oncogene product in normal, benign, and malignant human pancreatic tissues. Hum Pathol. 1990;21(6):607–12.
Amsterdam A, Sadler KC, Lai K, Farrington S, Bronson RT, Lees JA, Hopkins N. Many ribosomal protein genes are cancer genes in zebra fish. PLoS Biol. 2004;2(5):E139.
Zimmermann RA. The double life of ribosomal proteins. Cell. 2003;115(2):130–2.
Mazumder B, Sampath P, Seshadri V, Maitra RK, DiCorleto PE, Fox PL. Regulated release of L13a from the 60S ribosomal subunit as a mechanism of transcript-specific translational control. Cell. 2003;115(2):187–98.
Chavez-Rios R, Arias-Romero LE, Almaraz-Barrera Mde J, Hernandez-Rivas R, Guillen N, Vargas M. L10 ribosomal protein from Entamoeba histolytica share structural and functional homologies with QM/Jif-1: proteins with extra ribosomal functions. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2003;127(2):151–60.
Khanna N, Reddy VG, Tuteja N, Singh N. Differential gene expression in apoptosis: identification of ribosomal protein S29 as an apoptotic inducer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;277(2):476–86.
Wang H, Zhao LN, Li KZ, Ling R, Li XJ, Wang L. Overexpression of ribosomal protein L15 is associated with cell proliferation in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2006;6:91.
Naora H, Takai I, Adachi M, Naora H. Altered cellular responses by varying expression of a ribosomal protein gene: sequential coordination of enhancement and suppression of ribosomal protein S3a gene expression induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1998;141(3):741–53.
Shenoy N, Kessel R, Bhagat T, Bhattacharya S, Yu Y, McMahon C, Verma A. Alterations in the ribosomal machinery in cancer and hematologic disorders. J Hematol Oncol. 2012;5(1):32.
Fok V, Mitton-Fry RM, Grech A, Steitz JA. Multiple domains of EBER 1, an Epstein–Barr virus noncoding RNA, recruit human ribosomal protein L22. RNA (New York, NY). 2006;12(5):872–82.
Samanta M, Takada K. Modulation of innate immunity system by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded non-coding RNA and oncogenesis. Cancer Sci. 2010;101(1):29–35.
Le S, Sternglanz R, Greider CW. Identification of two RNA-binding proteins associated with human telomerase RNA. Mol Biol Cell. 2000;11(3):999–1010.
Chen LK, Huang H, Liao H, Liu GZ, Zeng YD, Dinglin XX, Xu GC, Wei WD. Chemotherapy with concurrent brain and thoracic radiotherapy in brain-only metastases of treatment naive small-cell lung cancer: a phase II study. Med Oncol (Northwood, London, England). 2012;29(3):1687–92.
Liloglou T, Bediaga NG, Brown BR, Field JK, Davies MP. Epigenetic biomarkers in lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2012.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Mingxia Yang) under contract No. 30901708.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Sun, H., Wang, H. et al. Down-regulation of ribosomal protein L22 in non-small cell lung cancer. Med Oncol 30, 646 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0646-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0646-0