Abstract
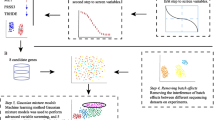
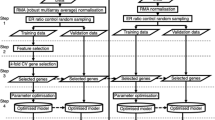
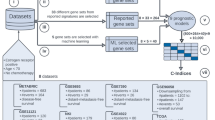
Large amount of expression data were generated by high-throughput experimental techniques such as microarray. Single algorithm cannot be widely accepted as suitable method for mining of gene expression data. Therefore, integration of different algorithms and extraction of more useful information from the expression data are the key problems for identification of biomarkers. Here, we used three machine learning algorithms to select feature genes based on gene profiling data of gastric cancer (GC). Then, a common divisor was extracted as candidate feature genes aggregation for Tree Building and Tree Pruning analysis by Decision Tree (DT) algorithm. Real-time quantitative PCR and immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining were used to validate the relative expression levels of the candidate feature genes. Receiver operating characteristic curves were used to analyse the classification sensitivity and specificity of the feature genes. A total of 174, 202, 149 feature genes were selected by Class Information Index, Information Gain Index and Relief algorithms, with a common divisor consisting of 32 genes. Using a DT algorithm to contribute to the classification rule sets, we identified COL2A1 and ATP4B as candidate biomarkers of GC. The expression levels of these two genes were validated by real-time PCR and IHC with high sensitivity (>90 %) and specificity (>90 %) in both training and test samples. We first introduced an integral and systematic data-mining model for identification of biomarkers based on gene expression data. The two-gene signature obtained by our predictive model could be used for recognizing the biological characteristic of GC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lau SK, Boutros PC, Pintilie M, Blackhall FH, Zhu CQ, Strumpf D, Johnston MR, Darling G, Keshavjee S, Waddell TK, Liu N, Lau D, Penn LZ, Shepherd FA, Jurisica I, Der SD, Tsao MS. Three-gene prognostic classifier for early-stage non small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(35):5562–9.
Yoshihara K, Tajima A, Komata D, Yamamoto T, Kodama S, Fujiwara H, Suzuki M, Onishi Y, Hatae M, Sueyoshi K, Fujiwara H, Kudo Y, Inoue I, Tanaka K. Gene expression profiling of advanced-stage serous ovarian cancers distinguishes novel subclasses and implicates ZEB2 in tumor progression and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(8):1421–8.
Yan Z, Li J, Xiong Y, Xu W, Zheng G. Identification of candidate colon cancer biomarkers by applying a random forest approach on microarray data. Oncol Rep. 2012;28(3):1036–42.
Peyre M, Commo F, Dantas-Barbosa C, Andreiuolo F, Puget S, Lacroix L, Drusch F, Scott V, Varlet P, Mauguen A, Dessen P, Lazar V, Vassal G, Grill J. Portrait of ependymoma recurrence in children: biomarkers of tumor progression identified by dual-color microarray-based gene expression analysis. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(9):e12932.
Colombo J, Fachel AA, De Freitas Calmon M, Cury PM, Fukuyama EE, Tajara EH, Cordeiro JA, Verjovski-Almeida S, Reis EM, Rahal P. Gene expression profiling reveals molecular marker candidates of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2009;21(3):649–63.
Crispi S, Calogero RA, Santini M, Mellone P, Vincenzi B, Citro G, Vicidomini G, Fasano S, Meccariello R, Cobellis G, Menegozzo S, Pierantoni R, Facciolo F, Baldi A, Menegozzo M. Global gene expression profiling of human pleural mesotheliomas: identification of matrix metalloproteinase 14 (MMP-14) as potential tumour target. PLoS ONE. 2009;4(9):e7016.
Fèvre-Montange M, Champier J, Durand A, Wierinckx A, Honnorat J, Guyotat J, Jouvet A. Microarray gene expression profiling in meningiomas: differential expression according to grade or histopathological subtype. Int J Oncol. 2009;35(6):1395–407.
Li W, Wang R, Yan Z, Bai L, Sun Z. High accordance in prognosis prediction of colorectal cancer across independent datasets by multi-gene module expression profiles. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(3):e33653.
Yang S, Chen J, Guo Y, Lin H, Zhang Z, Feng G, Hao Y, Cheng J, Liang P, Chen K, Wu H, Li Y. Identification of prognostic biomarkers for response to radiotherapy by DNA microarray in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Int J Oncol. 2012;40(5):1590–600.
Lahat G, Tuvin D, Wei C, Wang WL, Pollock RE, Anaya DA, Bekele BN, Corely L, Lazar AJ, Pisters PW, Lev D. Molecular prognosticators of complex karyotype soft tissue sarcoma outcome: a tissue microarray-based study. Ann Oncol. 2010;21(5):1112–20.
Yan Z, Xiong Y, Xu W, Gao J, Cheng Y, Wang Z, Chen F, Zheng G. Identification of hsa-miR-335 as a prognostic signature in gastric cancer. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(7):e40037.
Quackenbush J. Microarray analysis and tumour classification. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2463–72.
Allison DB, Cui X, Page GP, Sabripour M. Microarray data analysis: from disarray to consolidation and consensus. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7(1):55–65.
Yang L. Incidence and mortality of gastric cancer in China. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:17–20.
Zang SZ, Guo RF, Zhang L, Lu Y. Integration of statistical inference methods and a novel control measure to improve sensitivity and specificity of data analysis in expression profiling studies. J Biomed Inform. 2007;40:552–60.
Golub TR, Slonim DK, Tamayo P, Huard C, Gaasenbeek M, Mesirov JP, Coller H, Loh ML, Downing JR, Caligiuri MA, Bloomfield CD, Lander ES. Molecular classification of cancer: class discovery and class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science. 1999;286(5439):531–7.
Li YX, Ruan XG. Feature selection for cancer classification based on support vector machine. J Comput Res Dev. 2005;42:1796–801.
Lee C, Lee G. Information gain and divergence-based feature selection for machine learning-based text categorization. Inf Process Manag. 2006;42:155–65.
Kingsford C, Salzberg SL. What are decision trees? Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:1011–3.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 (-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Price ND, Trent J, El-Naggar AK, Cogdell D, Taylor E, Hunt KK, Pollock RE, Hood L, Shmulevich I, Zhang W. Highly accurate two-gene classifier for differentiating gastrointestinal stromal tumors and leiomyosarcomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(9):3414–9.
Zhang X, Yan Z, Zhang J, Gong L, Li W, Cui J, Liu Y, Gao Z, Li J, Shen L, Lu Y. Combination of hsa-miR-375 and hsa-miR-142-5p as a predictor for recurrence risk in gastric cancer patients following surgical resection. Ann Oncol. 2011;22(10):2257–66.
Gálvez-Rosas A, González-Huerta C, Borgonio-Cuadra VM, Duarte-Salazár C, Lara-Alvarado L, de los Angeles Soria-Bastida M, Cortés-González S, Ramón-Gallegos E, Miranda-Duarte A. A COL2A1 gene polymorphism is related with advanced stages of osteoarthritis of the knee in Mexican Mestizo population. Rheumatol Int. 2010;30(8):1035–9.
Hämäläinen S, Solovieva S, Hirvonen A, Vehmas T, Takala EP, Riihimäki H, Leino-Arjas P. COL2A1 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to osteoarthritis of the hand in Finnish women. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(10):1633–7.
Zhang Z, He JW, Fu WZ, Zhang CQ, Zhang ZL. Identification of three novel mutations in the COL2A1 gene in four unrelated Chinese families with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;413(4):504–8.
Mark PR, Torres-Martinez W, Lachman RS, Weaver DD. Association of a p.Pro786Leu variant in COL2A1 with mild spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita in a three-generation family. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155A(1):174–9.
Xu P, Yao J, Hou W. Relationships between COL2A1 gene polymorphisms and knee osteoarthritis in Han Chinese women. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38:2377–81.
Jamieson SE, de Roubaix LA, Cortina-Borja M, Tan HK, Mui EJ, Cordell HJ, Kirisits MJ, Miller EN, Peacock CS, Hargrave AC, Coyne JJ, Boyer K, Bessieres MH, Buffolano W, Ferret N, Franck J, Kieffer F, Meier P, Nowakowska DE, Paul M, Peyron F, Stray-Pedersen B, Prusa AR, Thulliez P, Wallon M, Petersen E, McLeod R, Gilbert RE, Blackwell JM. Genetic and epigenetic factors at COL2A1 and ABCA4 influence clinical outcome in congenital toxoplasmosis. PLoS ONE. 2008;3(6):e2285.
Zechi-Ceide RM, Jesus Oliveira NA, Guion-Almeida ML, Antunes LF, Richieri-Costa A, Passos-Bueno MR. Clinical evaluation and COL2A1 gene analysis in 21 Brazilian families with Stickler syndrome: identification of novel mutations, further genotype/phenotype correlation, and its implications for the diagnosis. Eur J Med Genet. 2008;51(3):183–96.
Gerth-Kahlert C, Grisanti S, Berger E, Höhn R, Witt G, Jung U. Bilateral vitreous hemorrhage in a newborn with Stickler syndrome associated with a novel COL2A1 mutation. J AAPOS. 2011;15(3):311–3.
Yaguchi H, Ikeda T, Osada H, Yoshitake Y, Sasaki H, Yonekura H. Identification of the COL2A1 mutation in patients with type I Stickler syndrome using RNA from freshly isolated peripheral white blood cells. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2011;15(4):231–7.
Richards AJ, McNinch A, Martin H, Oakhill K, Rai H, Waller S, Treacy B, Whittaker J, Meredith S, Poulson A, Snead MP. Stickler syndrome and the vitreous phenotype: mutations in COL2A1 and COL11A1. Hum Mutat. 2010;31(6):E1461–71.
Göõz M, Hammond CE, Larsen K, Mukhin YV, Smolka AJ. Inhibition of human gastric H(+)-K(+)-ATPase alpha-subunit gene expression by Helicobacter pylori. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000;278(6):G981–91.
Scarff KL, Judd LM, Toh BH, Gleeson PA, Van Driel IR. Gastric H(+), K(+)-adenosine triphosphatase beta subunit is required for normal function, development, and membrane structure of mouse parietal cells. Gastroenterology. 1999;117(3):605–18.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Jiangeng Li (Academy of Electronic Information & control Engineering, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing, China.) for the great help in processing the gene expression data using machine learning algorithms.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Z., Xu, W., Xiong, Y. et al. Highly accurate two-gene signature for gastric cancer. Med Oncol 30, 584 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0584-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0584-x