Abstract
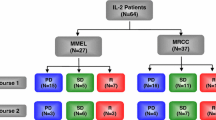
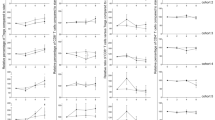
Recently, novel molecular targeted agents markedly changed the treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC), with promising results. However, there is little understanding of how these agents affect immune cell populations in RCC, an immunogenic tumor. Therefore, we investigated the changes in the peripheral blood immune cells in 58 RCC patients during the first 4 weeks of treatment with sorafenib, sunitinib, everolimus, or temsirolimus and evaluated whether these changes were associated with clinical outcomes. The immunological parameters were the proportion of type-1 (Th1) and type-2 (Th2) T cells, regulatory T cells (Treg), mature dendritic cells, and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR). The changes in these immune cells varied with the agents and the clinical response, dichotomized by the median progression-free survival (PFS) time (PFS-short or PFS-long). A significant decrease in the Th1/Th2 ratio was seen after sunitinib treatment only in the PFS-short group, suggesting a shift toward Th2 that down-regulates host immunity. The NLRs indicative of the balance between host immunity and cancer-related inflammation were consistently lower in the PFS-long group than in the PFS-short group, suggesting that lower NLR is associated with better clinical response. Only sunitinib decreased NLR remarkably regardless of PFS status, which may favor anti-tumor immunity. When patients were dichotomized by the cutoff values, Th1/Th2 ratio was not associated with PFS in any targeted therapy, while lower pre-treatment NLR was associated with longer PFS in each targeted therapy. In addition, in RCC patients given sequential targeted therapy, those with a lower baseline NLR survived significantly longer compared with the counterparts. Moreover, those whose baseline NLR was sustained low during the initial therapy survived the longest. Our results suggest the diverse changes in host immune cells in RCC patients during targeted therapy. The changes in NLR during the early phase of targeted therapy may be a powerful discriminator of who will benefit from the subsequent treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dermott DF. Immunotherapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2009;115(Supp 1):2298–305.
Motzer RJ, Mazumdar M, Bacik J, Berg W, Amsterdam A, Ferrara J. Survival and prognostic stratification of 670 patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2530–40.
Motzer RJ, Michaelson MD, Rosenberg J, Bukowski RM, Curti BD, George DJ, Hudes GR, Redman BG, Margolin KA, Wilding G. Sunitinib efficacy against advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2007;178:1883–7.
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Solska E, Desai AA, Rolland F, Demkow T, Hutson TE, Gore M, Freeman S, Schwartz B, Shan M, Simantov R, Bukowski RM, TARGET Study Group. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:125–34.
Rini BI, Escudier B, Tomczak P, Kaprin A, Szczylik C, Hutson TE, Michaelson MD, Gorbunova VA, Gore ME, Rusakov IG, Negrier S, Ou YC, Castellano D, Lim HY, Uemura H, Tarazi J, Cella D, Chen C, Rosbrook B, Kim S, Motzer RJ. Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011;378:1931–9.
Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, Dutcher J, Figlin R, Kapoor A, Staroslawska E, Sosman J, McDermott D, Bodrogi I, Kovacevic Z, Lesovoy V, Schmidt-Wolf IG, Barbarash O, Gokmen E, O’Toole T, Lustgarten S, Moore L, Motzer RJ, Global ARCC Trial. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2271–81.
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, Grünwald V, Thompson JA, Figlin RA, Hollaender N, Urbanowitz G, Berg WJ, Kay A, Lebwohl D, Ravaud A, RECORD-1 Study Group. Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet. 2008;372:449–56.
Gabrilovich D. Mechanisms and functional significance of tumour-induced dendritic-cell defects. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:941–52.
Hoffmann TK, Müller-Berghaus J, Ferris RL, Johnson JT, Storkus WJ, WhitesideTL. Alterations in the frequency of dendritic cell subsets in the peripheralcirculation of patients with squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:1787–93. Erratum in: Clin Cancer Res. 2003.
Della Bella S, Gennaro M, Vaccari M, Ferraris C, Nicola S, Riva A, Clerici M, Greco M, Villa ML. Altered maturation of peripheral blood dendritic cells in patients with breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2003;89:1463–72.
van Cruijsen H, van der Veldt AA, Vroling L, Oosterhoff D, Broxterman HJ, Scheper RJ, Giaccone G, Haanen JB, van den Eertwegh AJ, Boven E, Hoekman K, deGruijl TD. Sunitinib-induced myeloid lineage redistribution in renal cell cancer patients: CD1c+ dendritic cell frequency predicts progression-free survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:5884–92.
Griffiths RW, Elkord E, Gilham DE, Ramani V, Clarke N, Stern PL, Hawkins RE. Frequency of regulatory T cells in renal cell carcinoma patients and investigation of correlation with survival. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2007;56:1743–53.
Wolf AM, Wolf D, Steurer M, Gastl G, Gunsilius E, Grubeck-Loebenstein B. Increase of regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood of cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:606–12.
Li JF, Chu YW, Wang GM, Zhu TY, Rong RM, Hou J, Xu M. The prognostic value of peritumoral regulatory T cells and its correlation with intratumoral cyclooxygenase-2 expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2009;103:399–405.
Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–73.
Kuby J, Cameron J, Todd C, Mitchell J. Immunology. 4th ed. New York: Freeman and Company; 2000.
Kobayashi M, Kobayashi H, Pollard RB, Suzuki F. A pathogenic role of Th2 cells and their cytokine products on the pulmonary metastasis of murine B16 melanoma. J Immunol. 1998;160:5869–73.
Zitvogel L, Mayordomo JI, Tjandrawan T, DeLeo AB, Clarke MR, Lotze MT, Storkus WJ. Therapy of murine tumors with tumor peptide-pulsed dendritic cells:dependence on T cells, B7 costimulation, and T helper cell 1-associated cytokines. J Exp Med. 1996;183:87–97.
Tsung K, Meko JB, Peplinski GR, Tsung YL, Norton JA. IL-12 induces T helper1 -directed antitumor response. J Immunol. 1997;158:3359–65.
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008;454:436–44.
Casamassima A, Picciariello M, Quaranta M, Berardino R, Ranieri C, Paradiso A, Lorusso V, Guida M. C-reactive protein: a biomarker of survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with subcutaneous interleukin-2 based immunotherapy. J Urol. 2005;173:52–5.
Komai Y, Saito K, Sakai K, Morimoto S. Increased preoperative serum C-reactive protein level predicts a poor prognosis in patients with localized renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2007;99:77–80.
Walsh SR, Cook EJ, Goulder F, Justin TA, Keeling NJ. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2005;91:181–4.
Yamanaka T, Matsumoto S, Teramukai S, Ishiwata R, Nagai Y, Fukushima M. The baseline ratio of neutrophils to lymphocytes is associated with patient prognosis in advanced gastric cancer. Oncology. 2007;73:215–20.
Cho H, Hur HW, Kim SW, Kim SH, Kim JH, Kim YT, Lee K. Pre-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is elevated in epithelial ovarian cancer and predicts survival after treatment. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009;58:15–23.
Ohno Y, Nakashima J, Ohori M, Hatano T, Tachibana M. Pretreatment neutrophil- to-lymphocyte ratio as an independent predictor of recurrence in patients with nonmetastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2010;184:873–8.
Keizman D, Ish-Shalom M, Huang P, Eisenberger MA, Pili R, Hammers H, Carducci MA. The association of pre-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio with response rate, progression free survival and overall survival of patients treated with sunitinib for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:202–8.
Cetin B, Berk V, Kaplan MA, Afsar B, Tufan G, Ozkan M, Isikdogan A, Benekli M, Coskun U, Buyukberber S. Is the Pretreatment Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio an Important Prognostic Parameter in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma? Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2012;. doi:10.1016/j.clgc.2012.09.001.
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:228–47.
Jung T, Schauer U, Heusser C, Neumann C, Rieger C. Detection of intracellular cytokines by flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1993;159:197–207.
Reis e Sousa C. Activation of dendritic cells: translating innate into adaptive immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004;16:21–5.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik C, Kim ST, Chen I, Bycott PW, Baum CM, Figlin RA. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:115–24.
Fisher RI, Rosenberg SA, Fyfe G. Long-term survival update for high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Cancer J Sci Am. 2000;6(Suppl 1):S55–7.
Atzpodien J, Hoffmann R, Franzke M, Stief C, Wandert T, Reitz M. Thirteen-year, long-term efficacy of interferon 2 alpha and interleukin 2-based home therapy in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2002;95:1045–50.
Onishi T, Ohishi Y, Imagawa K, Ohmoto Y, Murata K. An assessment of the immunological environment based on intratumoral cytokine production in renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 1999;83:488–92.
Finke JH, Rini B, Ireland J, Rayman P, Richmond A, Golshayan A, Wood L, Elson P, Garcia J, Dreicer R, Bukowski R. Sunitinib reverses type-1 immune suppression and decreases T-regulatory cells in renal cell carcinoma patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:6674–82.
Nagai H, Mukozu T, Matsui D, Kanekawa T, Kanayama M, Wakui N, Momiyama K, Shinohara M, Iida K, Ishii K, Igarashi Y, Sumino Y. Sorafenib prevents escape from host immunity in liver cirrhosis patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;. doi:10.1155/2012/607851.
Salas NR, Ireland JL, Ko JS, Elson P, Garcia JA, Wood L, Bukowski RM, Rini BI, Finke JH. Immune cell changes in the peripheral blood of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) patients (pts) treated with sunitinib or temsirolimus. J Clin Oncol. 2008;15S:5099.
Curiel TJ. Tregs and rethinking cancer immunotherapy. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:1167–74.
Wolf D, Wolf AM, Rumpold H, Fiegl H, Zeimet AG, Muller-Holzner E, Deibl M, Gastl G, Gunsilius E, Marth C. The expression of the regulatory T cell-specific fork- head box transcription factor FoxP3 is associated with poor prognosis in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:8326–31.
Bates GJ, Fox SB, Han C, Leek RD, Garcia JF, Harris AL, Banham AH. Quantification of regulatory T cells enables the identification of high-risk breast cancer patients and those at risk of late relapse. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:5373–80.
Kobayashi N, Hiraoka N, Yamagami W, Ojima H, Kanai Y, Kosuge T, Nakajima A, Hirohashi S. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells affect the development and progression of hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:902–11.
Porta C, Bonomi L, Lillaz B, Paglino C, Rovati B, Imarisio I, Morbini P, Villa C, Danova M, Mensi M, Rovereto B. Renal cell carcinoma-induced immunosuppression: an immunophenotypic study of lymphocyte subpopulations and circulating dendritic cells. Anticancer Res. 2007;27:165–73.
Gabrilovich DI, Corak J, Ciernik IF, Kavanaugh D, Carbone DP. Decreased antigen presentation by dendritic cells in patients with breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3:483–90.
Ormandy LA, Farber A, Cantz T, Petrykowska S, Wedemeyer H, Horning M, Lehner F, Manns MP, Korangy F, Greten TF. Direct ex vivo analysis of dendritic cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:3275–82.
Baldewijns MM, Thijssen VL, Van den Eynden GG, Van Laere SJ, Bluekens AM, Roskams T, van Poppel H, De Bruïne AP, Griffioen AW, Vermeulen PB. High-grade clear cell renal cell carcinoma has a higher angiogenic activity than low-grade renal cell carcinoma based on histomorphological quantification and qRT-PCR mRNA expression profile. Br J Cancer. 2007;96:1888–95.
Schips L, Dalpiaz O, Lipsky K, Langner C, Rehak P, Puerstner P, Pummer K, Zigeuner R. Serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and endostatin in renal cell carcinoma patients compared to a control group. Eur Urol. 2007;51:168–73.
Hipp MM, Hilf N, Walter S, Werth D, Brauer KM, Radsak MP, Weinschenk T, Singh-Jasuja H, Brossart P. Sorafenib, but not sunitinib, affects function of dendritic cells and induction of primary immune responses. Blood. 2008;111:5610–20.
van Cruijsen H, van der Veldt AA, Vroling L, Oosterhoff D, Broxterman HJ, Scheper RJ, Giaccone G, Haanen JB, van den Eertwegh AJ, Boven E, Hoekman K, de Gruijl TD. Sunitinib-induced myeloid lineage redistribution in renal cell cancer patients: CD1c+ dendritic cell frequency predicts progression-free survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:5884–92.
Kusumanto YH, Dam WA, Hospers GA, Meijer C, Mulder NH. Platelets and granulocytes, in particular the neutrophils, form important compartments for circulating vascular endothelial growth factor. Angiogenesis. 2003;6:283–7.
Nagaraj S, Schrum AG, Cho HI, Celis E, Gabrilovich DI. Mechanism of T cell tolerance induced by myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Immunol. 2010;15:3106–16.
Schmidt H, Bastholt L, Geertsen P, Christensen IJ, Larsen S, Gehl J, von der Maase H. Elevated neutrophil and monocyte counts in peripheral blood are associated with poor survival in patients with metastatic melanoma: a prognostic model. Br J Cancer. 2005;93:273–8.
Bellocq A, Antoine M, Flahault A, Philippe C, Crestani B, Bernaudin JF, Mayaud C, Milleron B, Baud L, Cadranel J. Neutrophil alveolitis in bronchioloalveolar carcinoma: induction by tumor-derived interleukin-8 and relation to clinical outcome. Am J Pathol. 1998;152:83–92.
Atzpodien J, Reitz M. Peripheral blood neutrophils as independent immunologic predictor of response and long-term survival upon immunotherapy in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2008;23:129–34.
Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, Warren MA, Golshayan AR, Sahi C, Eigl BJ, Ruether JD, Cheng T, North S, Venner P, Knox JJ, Chi KN, Kollmannsberger C, McDermott DF, Oh WK, Atkins MB, Bukowski RM, Rini BI, Choueiri TK. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: results from a large, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5794–9.
Donskov F, von der Maase H. Impact of immune parameters on long-term survival in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1997–2005.
Choueiri TK, Garcia JA, Elson P, Khasawneh M, Usman S, Golshayan AR, Baz RC, Wood L, Rini BI, Bukowski RM. Clinical factors associated with outcome inpatients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy. Cancer. 2007;110:543–50.
Saroha S, Uzzo RG, Plimack ER, Ruth K, Al-Saleem T. Lymphopenia is an Independent Predictor of Inferior Outcome in Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma. J Urol. 2013;. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2012.09.166.
Conflict of interest
There are no financial disclosures to declare from any author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, M., Kubo, T., Komatsu, K. et al. Changes in peripheral blood immune cells: their prognostic significance in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with molecular targeted therapy. Med Oncol 30, 556 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0556-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0556-1