Abstract
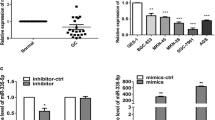
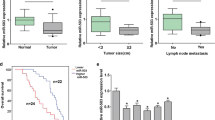
Accumulating evidence has shown that microRNAs are involved in multiple processes in cancer development and progression. Recently, miR-22 has been identified as a tumor-suppressing microRNA in many human cancers. However, the specific function of miR-22 in gastric cancer is unclear at this point. In this study, we first measured miR-22 expression level in 30 pairs of gastric cancer and matched normal tissues, two normal and six gastric cancer cell lines by real-time quantitative RT-PCR. We found that the expression of miR-22 in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines was much lower than that in normal control, respectively. Transfection of miR-22 expression plasmid could significantly inhibit the cell migration and invasion in SGC-7901 and NCL-N87 gastric cancer cell lines. Moreover, we also showed that Sp1 was negatively regulated by miR-22 at the posttranscriptional level, via a specific target site within the 3′UTR by luciferase reporter assay. The expression of Sp1 was inversely correlated with miR-22 expression in gastric cancer tissues, and knockdown of Sp1 by siRNA inhibited cell malignant behaviors. Thus, our findings suggest that miR-22 acts as tumor suppressor by targeting the Sp1 gene and inhibiting gastric cancer cell migration and invasion. The findings of this study contribute to current understanding of the functions of miR-22 in gastric cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Crew KD, Neugut AI. Epidemiology of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:354–62.
Yang L. Incidence and mortality of gastric cancer in China. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:17–20.
Hohenberger P, Gretschel S. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2003;362:305–15.
Crone SG, Jacobsen A, Federspiel B, Bardram L, Krogh A, Lund AH, et al. microRNA-146a inhibits G protein-coupled receptor-mediated activation of NF-kappaB by targeting CARD10 and COPS8 in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2012;11:71.
Zamore PD, Haley B. Ribo-gnome: the big world of small RNAs. Science. 2005;309:1519–24.
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell. 2003;115:787–98.
Xiong J, Du Q, Liang Z. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-22 inhibits the transcription of E-box-containing c-Myc target genes by silencing c-Myc binding protein. Oncogene. 2010;29:4980–8.
Bar N, Dikstein R. miR-22 forms a regulatory loop in PTEN/AKT pathway and modulates signaling kinetics. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e10859.
Ting Y, Medina DJ, Strair RK, Schaar DG. Differentiation-associated miR-22 represses Max expression and inhibits cell cycle progression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;394:606–11.
Tsuchiya N, Izumiya M, Ogata-Kawata H, Okamoto K, Fujiwara Y, Nakai M, et al. Tumor suppressor miR-22 determines p53-dependent cellular fate through post-transcriptional regulation of p21. Cancer Res. 2011;71:4628–39.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Liao CG, Kong LM, Song F, Xing JL, Wang LX, Sun ZJ, et al. Characterization of basigin isoforms and the inhibitory function of basigin-3 in human hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31:2591–604.
Tian Y, Luo A, Cai Y, Su Q, Ding F, Chen H, et al. MicroRNA-10b promotes migration and invasion through KLF4 in human esophageal cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:7986–94.
Patel JB, Appaiah HN, Burnett RM, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Wang G, Mehta R, et al. Control of EVI-1 oncogene expression in metastatic breast cancer cells through microRNA miR-22. Oncogene. 2011;30:1290–301.
Xu D, Takeshita F, Hino Y, Fukunaga S, Kudo Y, Tamaki A, et al. miR-22 represses cancer progression by inducing cellular senescence. J Cell Biol. 2011;193:409–24.
Hasegawa K, Wakino S, Tanaka T, Kimoto M, Tatematsu S, Kanda T, et al. Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 2 increases vascular endothelial growth factor expression through Sp1 transcription factor in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:1488–94.
Kong LM, Liao CG, Chen L, Yang HS, Zhang SH, Zhang Z, et al. Promoter hypomethylation up-regulates CD147 expression through increasing Sp1 binding and associates with poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15:1415–28.
Kong LM, Liao CG, Fei F, Guo X, Xing JL, Chen ZN. Transcription factor Sp1 regulates expression of cancer-associated molecule CD147 in human lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:1463–70.
Zhang J, Yang Y, Yang T, Liu Y, Li A, Fu S, et al. microRNA-22, downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and correlated with prognosis, suppresses cell proliferation and tumourigenicity. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:1215–20.
He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–31.
Wang F, Li Y, Zhou J, Xu J, Peng C, Ye F, et al. miR-375 is down-regulated in squamous cervical cancer and inhibits cell migration and invasion via targeting transcription factor SP1. Am J Pathol. 2011;179:2580–8.
Parkin DM, Pisani P, Ferlay J. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 1999;49(33–64):1.
Cawley S, Bekiranov S, Ng HH, Kapranov P, Sekinger EA, Kampa D, et al. Unbiased mapping of transcription factor binding sites along human chromosomes 21 and 22 points to widespread regulation of noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2004;116:499–509.
Yao JC, Wang L, Wei D, Gong W, Hassan M, Wu TT, et al. Association between expression of transcription factor Sp1 and increased vascular endothelial growth factor expression, advanced stage, and poor survival in patients with resected gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:4109–17.
Yuan P, Wang L, Wei D, Zhang J, Jia Z, Li Q, et al. Therapeutic inhibition of Sp1 expression in growing tumors by mithramycin a correlates directly with potent antiangiogenic effects on human pancreatic cancer. Cancer. 2007;110:2682–90.
Oue N, Aung PP, Mitani Y, Kuniyasu H, Nakayama H, Yasui W. Genes involved in invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer identified by array-based hybridization and serial analysis of gene expression. Oncology. 2005;69(Suppl 1):17–22.
Gupta GP, Massague J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 2006;127:679–95.
Klein CA. Cancer. The metastasis cascade. Science. 2008;321:1785–7.
Sreekumar R, Sayan BS, Mirnezami AH, Sayan AE. MicroRNA Control of Invasion and Metastasis Pathways. Front Genet. 2011;2:58.
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81101614 and 81171995).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mei-Mei Guo, Li-Hua Hu and Yong-Qiang Wang contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, MM., Hu, LH., Wang, YQ. et al. miR-22 is down-regulated in gastric cancer, and its overexpression inhibits cell migration and invasion via targeting transcription factor Sp1. Med Oncol 30, 542 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0542-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0542-7