Abstract
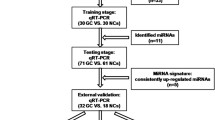
Recent studies have shown that microRNAs can be stably detected in human plasma and have the potential as non-invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis of cancers. This study evaluates the potential application of plasma microRNAs for the early detection of gastric cancer (GC). We first measured the plasma expression levels of 15 selected microRNAs (miR-1, -106a, -106b, -17-5p, -20a, -21, -221, -27a, -34, -376c, -378, -423-5p, -451, -486, -744) in 30 GC patients and 30 age- and gender-matched healthy controls and then validated those microRNAs that differentiating GC and controls in another 60 GC patients and 60 matched controls using quantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction. The areas under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to test the sensitivity and specificity of GC diagnosis using these identified plasma microRNAs. Three plasma microRNAs, miR-106b, miR-20a, and miR-221, were significantly elevated in GC patients than in healthy controls (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the areas under the ROC curves using miR-106b, miR-20a, and miR-221 for GC diagnosis were 0.7733 (95 % CI, 0.7758–0.8409), 0.8593 (95 % CI, 0.8046–0.9139), and 0.7960 (95 % CI, 0.7256–0.8664), respectively. Furthermore, these three microRNAs had a statistically significant elevation in GC patients compared with healthy controls at each of the four stages. However, there were no significant differences in the plasma levels of the three microRNAs among the four TNM stages (P > 0.05). Plasma miR-106b, miR-20a, and miR-221 have the potential as novel, non-invasive biomarkers for the early detection of GC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917.
Wang J, Yu JC, Kang WM, Ma ZQ. Treatment strategy for early gastric cancer. Surg Oncol. 2011;21:119–23.
Hartgrink HH, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC, van de Velde CJ. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2009;3749:477–90.
Leung WK, Wu MS, Kakugawa Y, et al. Screening for gastric cancer in Asia: current evidence and practice. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:279–87.
Meireles SI, Cristo EB, Carvalho AF, et al. Molecular classifiers for gastric cancer and nonmalignant diseases of the gastric mucosa. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1255–65.
Zhang X, Yang JJ, Kim YS, Kin KY, Ahn WS, Yang S. An 8-gene signature, including methylated and down-regulated glutathione peroxidase 3, of gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 2010;36:405–14.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–8.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–66.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:189–98.
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, et al. Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis of gastric cancer: a microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:136–46.
Liu N, Chen NY, Cui RX, et al. Prognostic value of a microRNA signature in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:633–41.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:10513–8.
Gilad S, Meiri E, Yogev Y, et al. Serum microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e3148.
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008;18:997–1006.
Zhou J, Yu L, Gao X, et al. Plasma microRNA panel to diagnose hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:4781–8.
Foss KM, Sima C, Uqolini D, Neri M, Allen KE, Weiss GJ. MiR-1254 and miR-574-5p: serum-based microRNA biomarkers for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6:482–8.
Hausler SF, Keller A, Chandran PA, et al. Whole blood-derived miRNA profiles as potential new tools for ovarian cancer screening. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:693–700.
Chen ZH, Zhang GL, Li HR, et al. A panel of five circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for prostate cancer. Prostate. 2012;72:1443–52.
Tsujiura M, Ichikawa D, Komatsu S, et al. Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients with gastric cancers. Br J Cancer. 2010;102:1174–9.
Liu R, Zhang CN, Hu ZB, et al. A five-microRNA signature identified from genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling serves as a fingerprint for gastric cancer diagnosis. Eur J Cancer. 2010;47:784–91.
Konishi H, Ichikawa D, Komatsu S, et al. Detection of gastric cancer-associated microRNAs on microRNA microarray comparing pre- and post-operative plasma. Br J Cancer. 2012;106:740–7.
Liu HS, Zhu L, Liu BY, et al. Genome-wide microRNA profiles identify miR-378 as a serum biomarker for early detection of gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2012;316:196–203.
Song MY, Pan KF, Su HJ, et al. Identification of serum microRNAs as novel non-invasive biomarkers for early detection of gastric cancer. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e33608.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Yoshioka Y, Takeshita F, Matsuki Y, Ochiyal T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:17442–52.
Zen K, Zhang CY. Circulating microRNAs: a novel class of biomarkers to diagnose and monitor human cancers. Med Res Rev. 2010;72:9798–807.
Reid G, Kirschner MB, van Zandwijk N. Circulating microRNAs: association with disease and potential use as biomarkers. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011;80:193–208.
Skog J, Wurdinger T, van Rijn S, et al. Glioblastoma micro vesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:1470–6.
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:654–9.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Gansu Province Science and Technology Support Plan grant (No. 0708NKC125). The funders have no roles in the study design, data collection, data analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, H., Yuan, Y., Hao, YF. et al. Plasma microRNAs serve as novel potential biomarkers for early detection of gastric cancer. Med Oncol 30, 452 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0452-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0452-0