Abstract
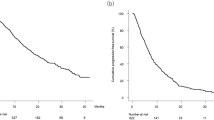
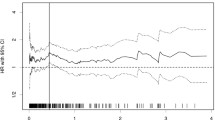
C-reactive protein (CRP) is known to be associated with poor prognosis in patients with various malignancies. We investigated the relationship between the pretreatment serum CRP level and survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in various stages of the disease. A cohort of 133 patients with newly diagnosed HCC was prospectively evaluated. The patients were divided into two groups: high-CRP group (n = 27) with the pretreatment serum CRP level ≧ 1.0 mg/dl and low-CRP group (n = 106) with the CRP level < 1.0 mg/dl. They were followed 22 months in average (1–69 months) and clinicopathological variables, and overall survivals between the two groups were compared at the end of the follow-up period. There was a significant difference between the two groups in aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, total serum bilirubin, albumin, α-fetoprotein level, maximal tumor diameter, frequency of vascular invasion and extrahepatic metastases. Patients in the high-CRP group had higher Child-Pugh scores, higher Cancer of the Liver Italian Program scores and higher Japan Integrated Staging scores than patients in the low-CRP group. The overall survival rates in the high-CRP group were significantly lower than those in the low-CRP group. Survival rates were similar in tumor stage and liver function-matched patients. On multivariate analysis, pretreatment serum CRP level was independently associated with overall survival. Our results demonstrate that the pretreatment serum CRP level is associated with tumor progression and reduced liver function and is an independent poor prognostic marker in patients with HCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang JD, Roberts LR. Hepatocellular carcinoma: a global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7:448–58.
Stiff GM, Gomez D, Prasad KR. C-reactive protein in liver cancer surgery. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008;34:727–9.
Nozoe T, Saeki H, Sugimachi K. Significance of preoperative elevation of serum C-reactive protein as an indicator of prognosis in esophageal carcinoma. Am J Surg. 2001;182:197–201.
Rashid SA, Quigley JO, Axon ATR, Cooper EH. Plasma protein profiles and prognosis in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 1982;45:390–4.
Nozoe T, Matsumata T, Kitamura M, Sugimachi K. Significance of preoperative elevation of serum C-reactive protein as an indicator for prognosis in colorectal cancer. Am J Surg. 1998;176:335–8.
McMillan DC, Canna K, McArdlle CS. Systemic inflammatory response predicts survival following curative resection of colorectal cancer. Br J Surg. 2003;90:215–9.
Ueno H, Okada S, Okusaka T, Ikeda M. Prognostic factors in patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma receiving systemic chemotherapy. Oncology. 2000;59:296–301.
Scott HR, McMillan DC, Forrest LM, Brown DJF, McArdlle CS, Milroy R. The systemic inflammatory response, weight loss, performance status and survival in patients with inoperable non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2002;87:264–7.
Fujikawa K, Matsui Y, Oka H, Fukuzawa S, Takeuchi H. Serum C-reactive protein level and the impact of cytoreductive surgery in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 1999;162:1934–7.
Pierce BL, et al. Elevated biomarkers of inflammation are associated with reduced survival among breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3437–44.
Kodama J, et al. Serum C-reactive protein as a prognostic factor in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1999;82:107–10.
Hashimoto K, et al. The impact of preoperative serum C-reactive protein on the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2005;103:1856–64.
Nagaoka S, et al. Serum C-reactive protein levels predict survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2007;27:1091–7.
Tokushige K, et al. Prospective study of hepatocellular carcinoma in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in comparison with hepatocellular carcinoma caused by chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:960–7.
Minagawa M, Ikai I, Matsuyama Y, Yamaoka Y, Makuuchi M. Staging of hepatocellular carcinoma. Assessment of the Japanese TNM and AJCC/UICC TNM systems in a cohort of 13,772 patients in Japan. Ann Surg. 2007;245:909–22.
Edmondson HA, Steiner PE. Primary carcinoma of the liver: a study of 100 cases among 48,900 necropsies. Cancer. 1954;7:462–503.
The Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) Investigators. A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435 patients. Hepatology. 1998;28:751–5.
Kudo M, et al. Validation of a new prognostic staging system for hepatocellular carcinoma: the JIS score compared with the CLIP score. Hepatology. 2004;40:1396–405.
Makuuchi M, et al. Development of evidence-based clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan. Hepatol Res. 2008;38:37–51.
Heikkila K, Eblahim S, Lawlor D. A systematic review of the association between circulating concentrations of C-reactive protein and cancer. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2007;61:824–32.
Legouffe E, et al. C-reactive protein serum level is a valuable and simple prognostic marker in non Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leukemia Lymphoma. 1998;31:351–7.
Chun JM, et al. Prognostic factors after early recurrence in patients who underwent curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2011;103:148–51.
Mahmoud FA, Rivera NI. The role of C-reactive protein as a prognostic indicator in advanced cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2002;4:250–5.
Pawlic TM, et al. Critical appraisal of the clinical and pathologic predictors of survival after resection of large hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg. 2005;140:450–8.
Nathan H, Schulick RD, Choti MA, Pawlic TM. Predictors of survival after resection of early hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2009;249:799–805.
Sakata H, et al. Prognostic factors for hepatocellular carcinoma presenting with macroscopic portal vein tumor thrombus. Hepatogastroenterology. 2004;51:1575–80.
Pinter M, et al. Prognostic factors in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;34:949–59.
Huitzil-Melendez FD, et al. Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: which staging system best predict prognosis? J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2889–95.
Conflict of interest
The authors disclose no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kinoshita, A., Onoda, H., Takano, K. et al. Pretreatment serum C-reactive protein level predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol 29, 2800–2808 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0220-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0220-1