Abstract
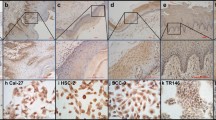
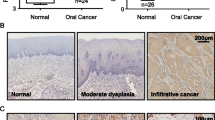
The Jun activation domain-binding protein 1 (Jab1) may be involved in degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27, but it has not been clarified. In this study, we observed expression levels of Jab1 and p27 in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) and normal oral mucosa tissue and evaluated whether the Jab1 expression is correlated with p27 protein levels and how it is clinically relevant OSCC. The clinicopathological features and immunohistochemical expression levels of Jab1 and p27 proteins were immunohistochemically studied in 206 specimens from patients who underwent surgical resection for OSCC. Survival analyses were performed by using the Kaplan–Meier method. Jab1 overexpression was detected in 83% (171 of 206) of OSCCs and 19% (4 of 21) of normal oral mucosa. While p27 expression was 60% in OSCCs. We found an inverse correlation between Jab1 and p27 expression levels (P < 0.001). Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed that Jab1 overexpression and p27 low expression were significantly associated with poor prognosis of patients. Our findings suggest that Jab1 expression is inversely correlated with p27 expression levels, suggesting that Jab1 overexpression contributes to pathogenesis of OSCC by degradating p27 expression. Furthermore, control of Jab1 could be a novel target of therapy in OSCCs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin D, L r E, Muir C. Estimates of the worldwide frequency of sixteen major cancers in 1980. Int J Cancer. 1988;41(2):184–97.
Khuri FR, Shin DM, Glisson BS, Lippman SM, Hong WK (eds). Treatment of patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: current status and future directions 2000.
Forastiere A, Koch W, Trotti A, Sidransky D. Head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(26):1890–900.
Choi S, Myers J. Molecular pathogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: implications for therapy. J Dent Res. 2008;87(1):14.
Claret FX, Hibi M, Dhut S, Toda T, Karin M. A new group of conserved coactivators that increase the specificity of AP-1 transcription factors. 1996.
Schwechheimer C, Deng XW. COP9 signalosome revisited: a novel mediator of protein degradation. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11(10):420–6.
Chamovitz DA, Segal D. JAB1/CSN5 and the COP9 signalosome: a complex situation. EMBO Rep. 2001;2(2):96.
Toyoshima H, Hunter T. p27, a novel inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to p21. Cell. 1994;78(1):67–74.
Yoshida A, Yoneda-Kato N, Panattoni M, Pardi R, Kato J. CSN5/Jab1 controls multiple events in the mammalian cell cycle. FEBS Lett. 2010.
Tomoda K, Kubota Y, Kato J. Degradation of the cyclin-dependent-kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 is instigated by Jab1. Nature. 1999;398(6723):160–5.
Sherr CJ. Cancer cell cycles. Science. 1996;274(5293):1672.
Shackleford TJ, Claret FX. JAB1/CSN5: a new player in cell cycle control and cancer. Cell Division. 2010;5(26). doi:10.1186/1747-1028-5-26.
Wang Y, Cheng C, Ji Y, Zhao Y, Zou L, Shen A. Expression of Jun activation domain-binding protein 1 and Ser10 phosphorylated p27 protein in human epithelial ovarian carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009;135(7):951–9.
Berg JP, Zhou Q, Breuhahn K, Schirmacher P, Patil MA, Chen X, et al. Inverse expression of Jun activation domain binding protein 1 and cell cycle inhibitor p27Kip1: influence on proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2007;38(11):1621–7.
Kouvaraki MA, Rassidakis GZ, Tian L, Kumar R, Kittas C, Claret FX. Jun activation domain-binding protein 1 expression in breast cancer inversely correlates with the cell cycle inhibitor p27Kip1. Cancer Res. 2003;63(11):2977.
Shintani S, Li C, Mihara M, Hino S, Nakashiro K, Hamakawa H. Skp2 and jab1 expression are associated with inverse expression of p27 < sup > KIP1 </sup > and poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oncology. 2000;65(4):355–62.
Kouvaraki MA, Korapati AL, Rassidakis GZ, Tian L, Zhang Q, Chiao P, et al. Potential role of Jun activation domain? binding protein 1 as a negative regulator of p27kip1 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2006;66(17):8581.
Tomoda K, Kubota Y, Arata Y, Mori S, Maeda M, Tanaka T, et al. The cytoplasmic shuttling and subsequent degradation of p27Kip1 mediated by Jab1/CSN5 and the COP9 signalosome complex. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(3):2302.
Ahn J, Hong SA, Lee S, Kim J, Oh YS, Park S, et al. Cytoplasmic localization of Jab1 and p27 Kip1 might be associated with invasiveness of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endocr J. 2009;56(5):707.
Sui L, Dong Y, Ohno M, Watanabe Y, Sugimoto K, Tai Y, et al. Jab1 expression is associated with inverse expression of p27kip1 and poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7(12):4130.
Korbonits M, Chahal HS, Kaltsas G, Jordan S, Urmanova Y, Khalimova Z, et al. Expression of phosphorylated p27Kip1 protein and Jun activation domain-binding protein 1 in human pituitary tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87(6):2635.
Wang F, Wang Y, Yu X, Yang D, Wang Z, Lu C, et al. Significance of Jab1 expression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009;43(6):520.
Hashimoto N, Yachida S, Okano K, Wakabayashi H, Imaida K, Kurokohchi K, et al. Immunohistochemically detected expression of p27 kip1 and skp2 predicts survival in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(2):395–403.
Kuo MYP, Hsu HY, Kok SH, Kuo RC, Yang H, Hahn LJ, et al. Prognostic role of p27Kip1 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma in Taiwan. Oral Oncol. 2002;38(2):172–8.
Shimada M, Kitagawa K, Dobashi Y, Isobe T, Hattori T, Uchida C, et al. High expression of Pirh2, an E3 ligase for p27, is associated with low expression of p27 and poor prognosis in head and neck cancers. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(5):866–72.
Esteva FJ, Sahin AA, Rassidakis GZ, Yuan LXH, Smith TL, Yang Y, et al. Jun activation domain binding protein 1 expression is associated with low p27kip1levels in node-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(15):5652.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Science and Technology Program in Shaanxi Province of China (2009K17-3, 2010K14-3, 2011K13-3), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (xjj20100216).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, L., Huang, S., Ren, W. et al. Jun activation domain-binding protein 1 expression in oral squamous cell carcinomas inversely correlates with the cell cycle inhibitor p27. Med Oncol 29, 2499–2504 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0177-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0177-0