Abstract
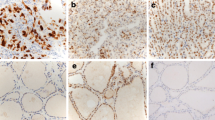
The aim of this study was to evaluate the expressions of oncoproteins and to correlate the results with clinicopathologic parameters in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). Papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) is the most common form and accounts for about 80% of all thyroid cancers. Although PTC generally has a good prognosis, some patients suffer from local recurrence and/or distant metastasis. Oncogenes have reported to be related not only in carcinogenesis but also in tumor prognosis, tumor type, differentiation and site of tumor in epithelial malignant tumors such as thyroid, breast, ovarian, and stomach cancer. This study was planned retrospectively and was performed in 87 patients (47 PTC, 40 benign lesions). The data of clinicopathologic parameters and tissue samples were collected from the archives. Sections stained with H&E were evaluated for each case and after confirming the diagnosis of PTC, oncoprotein expressions were determined by immunohistochemical analysis. The differences of oncoprotein expressions in PTC compared with control group were statistically significant. Cyclin D1 and p53 expressions were significantly increased in PTC. The expressions of bcl-2 and c-erbB-2 in PTC were found as increased, but the correlation between these proteins and poor prognostic parameters were not significant. We suggest that increased expressions of cyclin D1 and p53 could be used as prognostic factors in patients with PTC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melck A, Masoudi H, Griffith OL, Rajput A, Wilkins G, Bugis S, et al. Cell cycle regulators show diagnostic and prognostic utility for differentiated thyroid cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:3403–11.
Duntas L, Grab-Duntas BM. Risk and prognostic factors f or differentiated thyroid cancer. Hell J Nucl Med. 2006;9:156–62.
Cady B, Rossi R. An expanded view of risk group definition in differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Surgery. 1988;104:947–53.
Hay ID, Grant CS, Taylor WF, McConahey WM. Ipsilateral lobectomy versus bilateral lobar resection in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective analysis of surgical outcome using a novel prognostic scoring system. Surgery. 1987;102:1088–95.
Hay ID, Bergstralh EJ, Goellner JR, Ebersold JR, Grant CS. Predicting outcome in papillary thyroid carcinoma: development of a reliable prognostic scoring system in a cohort of 1, 779 patients surgically treated at one institution during 1940 through 1989. Surgery. 1993;114:1050–8.
Moore D, Ohene-Finko D, Garcia B, Chakrabarti S. Apoptosis in thyroid neoplasms: relationship with p53 and bcl-2 expression. Histopathology. 1998;32:35–42.
Utrilla JC, Martin-Lacave I, San Martin MV, Fernandez-Santos JM, Galera-Davidson H. Expression of c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in human thyroid tumours. Histopathology. 1999;34:60–5.
Muro-Cacho CA, Holt T, Klotch D, Mora L, Livingston S, Futran N. Cyclin D1 expression as a prognostic parameter in papillary carcinoma of the thyroid. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999;120:200–7.
Rojeski MT, Gharib H. Nodular thyroid disease: evaluation and management. N Engl J Med. 1985;313:428–36.
Tantawy A, Youins L, Hamza M. Expression of c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in cancer of the larynx in relation to invasion of the cartilagenous framework and prognosis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1999;256:72–7.
Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, Holt JA, Wong SG, Keith DE. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989;244:707–12.
Lazzereschi D, Sambuco L, Carnovale Scalzo C, Ranieri A, Mincione G, Nardi F. Cyclin D1 and cyclin E expression in malignant thyroid cells and in human thyroid carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1998;76:806–11.
Zou M, Shi Y, Farid NR, al-Sedairy ST. Inverse association between cyclin D1 overexpression and retinoblastoma gene mutation in thyroid carcinomas. Endocrine. 1998;8:61–4.
Yunis JJ, Frizzera G, Oken MM, McKenna J, Theologides A, Arnesen M. Multiple recurrent genomic defects in follicular lymphoma. A possible model for cancer. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:79–84.
Lal G, Clark OH. Thyroid, parathyroid and adrenal. In: Schwartz SI, editor. Principles of surgery. New York: F.C.Brunicardi-Hill Book Comp; 2005. p. 1395–470.
Pilloti S, Collini P, Rike F, Cattoretti G, Del Bo R, Pierotti MA. Bcl-2 protein expression in carcinomas originating from the follicular epithelium of the thyroid gland. J Pathol. 1994;172:337–42.
Morita N, Ikeda Y, Takami H. Clinical significance of p53 protein expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma. World J Surg. 2008;32:2617–22.
Hay ID, Grant CS, Taylor WF, McConahey WM. Ipsilateral lobectomy versus bilateral lobar resection in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective analysis of surgical outcome using a novel prognostic scoring system. Surgery. 1987;102:1088–95.
Horie S, Maeta H, Endo K, Ueta T, Takashima K, Terada T. Overexpression of p53 protein and MDM2 in papillary carcinomas of the thyroid: correlations with clinicopathologic features. Pathol Int. 2001;51:11–5.
Temmim L, Ebraheem AK, Baker H, Sinowatz F. Cyclin D1 protein expression in human thyroid gland and thyroid cancer. Anat Histol Embryol. 2006;35:125–9.
Wang S, Lloyd RV, Hutzler MJ, Safran MS, Patwardhan NA, Khan A. The role of cell cycle regulatory protein, cyclin D1, in the progression of thyroid cancer. Mod Pathol. 2000;13:882–7.
Lantsov D, Meirmanov S, Nakashima M, Kondo H, Saenko V, Naruke Y, et al. Cyclin D1 overexpression in thyroid papillary microcarcinoma: its association with tumour size and aberrant beta-catenin expression. Histopathology. 2005;47:248–56.
Khoo ML, Beasley NJ, Ezzat S, Freeman JL, Asa SL. Overexpression of cyclin D1 and underexpression of p27 predict lymph node metastases in papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:1814–8.
Hung MC, Lau YK. Basic science of HER-2/neu: a review. Semin Oncol. 1999;26(4 Suppl 12):51–9.
Carroway KL 3rd, Sweeney C. Localization and modulation of ErbB receptor tyrosine kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13:1225–30.
Nagy P, Jenei A, Damjanovich S, Jovin TM, Szölosi J. Complexity of signal transduction mediated by ErbB2: clues to the potential of receptor-targeted cancer therapy. Pathol Oncol Res. 1999;5:255–71.
Kremser R, Obrist P, Spizzo G, Erler H, Kendler D, Kemmler G. Her2/neu overexpression in differentiated thyroid carcinomas predicts metastatic disease. Virchows Arch. 2003;442:322–8.
Tan M, Yao J, Yu D. Overexpression of the c-erbB-2 gene enhanced intrinsic metastasis potential in human breast cancer cells without increasing their transformation abilities. Cancer Res. 1997;57:1199–205.
Schneider PM, Hung MC, Chiocca SM, Manning J, Zhao XY, Fang K, et al. Differential expression of the c-erbB-2gene in human small cell and non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1989;49:4968–71.
Yoshida K, Tsuda T, Matsumura T, Tsujino T, Hattori T, Ito H, et al. Amplification of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene and oncogenes in human gastric carcinomas. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1989;57:285–90.
Tsugawa K, Yonemura Y, Hirono Y, Fushida S, Kaji M, Miwa K, et al. Amplification of the c-met, c-erbB-2 and epidermal growth factor receptor gene in human gastric cancers: correlation to clinical features. Oncology. 1998;55:475–81.
Paterson MC, Dietrich KD, Danyluk J, Paterson AH, Lees AW, Jamil N, et al. Correlation between c-erbB-2 amplification and risk of recurrent disease in node-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1991;51:556–67.
Freudenberg LS, Sheu S, Görges R, Mann K, Bokler S, Frilling A, et al. Prognostic value of c-erbB-2 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Nuklearmedizin. 2005;44:179–84.
Mondi MM, Rich R, Ituarte P, Wong M, Bergman S, Clark OH, et al. HER2 expression in thyroid tumors. Am Surg. 2003;69:1100–3.
Fanidi A, Harrington EA, Evan GI. Cooperative interaction between c- myc and bcl-2 proto-oncogenes. Nature. 1992;359:554–6.
Mitselou A, Peschos D, Dallas P, Charalabopoulos K, Agnantis NJ, Vougiouklakis T. Immunohistochemical analysis of bcl-2 protein in papillary thyroid carcinomas and papillary microcarcinomas of the thyroid gland. Exp oncol. 2004;26:282–6.
Duan H, Heckman CA, Boxer LM. Histone deacetylase inhibitors down- regulate bcl-2 expression and induce apoptosis in t(14;18) lymphomas. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:1608–19.
Aksoy M, Giles Y, Kapran Y, Terzioglu T, Tezelman S. Expression of bcl-2 in papillary thyroid cancers and its prognostic value. Acta Chir Belg. 2005;105:644–8.
Mitselou A, Loachim E, Kitsou E, Vougiouklakis Th, Zagorianakou N, Makrydimas G, et al. Immunohistochemical study of apoptosis-related bcl-2 protein and its correlation with proliferation indices (Ki-67, PCNA), tumor suppressor genes (p53, pRb), the oncogene c-erbB-2, sex steroid hormone receptors and other clinicopathological features, in normal, hyperplastic and neoplastic endometrium. In vivo. 2003;17:469–77.
Loachim E, Kitsiou E, Mitselou A, Zagorianakou N, Charalabopoulos K, Salmas M, et al. P21 (waf/cip 1) protein expression in normal, hyperplastic and malignant endometrium. Correlation with hormone receptor status, c-erbB-2 oncoprotein, bcl-2 and other cell cycle related proteins (pb, p53, ki-67, PCNA). Exp Oncol. 2003;25:200–5.
Siironen P, Louhimo J, Nordling S, Ristimaki A, Maenpaa H, Haapiainen R, et al. Prognostic factors in papillary thyroid cancer: an evaluation of 601 consecutive patient. Tumour Biol. 2005;26:57–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balta, A.Z., Filiz, A.I., Kurt, Y. et al. Prognostic value of oncoprotein expressions in thyroid papillary carcinoma. Med Oncol 29, 734–741 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-9969-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-9969-x