Abstract
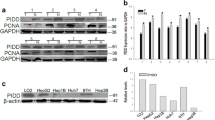
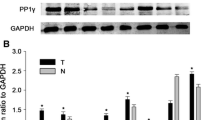
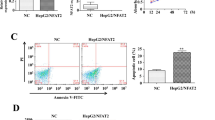
We investigated the role of XPD in cell apoptosis of hepatoma and its relationship with p53 during the regulation of hepatoma bio-behavior. RT–PCR and Western blot were used to detect the expression levels of XPD, p53, c-myc, and cdk2. The cell apoptosis and cell cycle were analyzed with flow cytometry. Compared with the control cells, XPD-transfected cells displayed a lower viability and higher apoptosis rate. A decreased expression of p53 gene was detected in XPD-transfected cells. In contrast, both c-myc and cdk2 showed increased expressions of mRNAs and proteins in the transfected cells. Our results indicate that XPD may play an important role in cell apoptosis of hepatoma by inducing an over-expression of p53, but suppressing expressions of c-myc and cdk2.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emmert S, Leibeling D, Rünger TM. Syndromes with genetic instability: model diseases for (skin) cancerogenesis. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2006;4:721–31.
Zhang J, Powell SN. The role of the BRCA1 tumor suppressor in DNA double-strand break repair. Mol Cancer Res. 2005;3:531–9.
Nakajima S, Lan L, Kanno S, Takao M, Yamamoto K, Eker AP, Yasui A. UV light-induced DNA damage and tolerance for the survival of nucleotide excision repair-deficient human cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:46674–7.
Lehmann AR. DNA repair-deficient diseases, xeroderma pigmentosum, Cockayne syndrome and trichothiodystrophy. Biochimie. 2003;85:1101–11.
Sung P, Bailly V, Weber C, Thompson LH, Prakash L, Prakash S. Human xeroderma pigmentosum group D gene encodes a DNA helicase. Nature. 1993;365:852–5.
Coin F, Marinoni J-C, Rodolfo C, Fribourg S, Pedrini AM, Egly J-M. Mutations in the XPD helicase gene result in XP and TTD phenotypes, preventing interaction between XPD and the p44 subunit of TFIIH. Nature Genet. 1998;20:184–8.
Lainé JP, Mocquet V, Bonfanti M, Braun C, Egly JM, Brousset P. Common XPD (ERCC2) polymorphisms have no measurable effect on nucleotide excision repair and basal transcription. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007;6:1264–70.
Robles AI, Harris CC. p53-mediated apoptosis and genomic instability diseases. Acta Oncol. 2001;40:696–701.
Askin DF, Diehl-Jones WL. The neonatal liver: part III: pathophysiology of liver dysfunction. Neonatal Netw. 2003;22:5–15.
Becker SA, Lee TH, Butel JS, Slagle BL. Hepatitis B virus X protein interferes with cellular DNA repair. J Virol. 1998;72:266–72.
Jaitovich-Groisman I, Benlimame N, Slagle BL, Perez MH, Alpert L, Song DJ, Fotouhi-Ardakani N, Galipeau J, Alaoui-Jamali MA. Transcriptional regulation of the TFIIH transcription repair components XPB and XPD by the hepatitis B virus x protein in liver cells and transgenic liver tissue. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:14124–32.
Uhring M, Poterszman A. DNA helicases and human diseases. Med Sci (Paris). 2006;22:1087–94.
Capovilla A, Arbuthnot P. Nucleotide excision repair by extracts of human fetal hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 2002;518:144–8.
Robles AI, Wang XW, Harris CC. Drug-induced apoptosis is delayed and reduced in XPD lymphoblastoid cell lines: possible role of TFIIH in p53-mediated apoptotic cell death. Oncogene. 1999;18:4681–8.
Jia L, Wang XW, Harris CC. Hepatitis B virus X protein inhibits nucleotide excision repair. Int J Cancer. 1999;80:875–9.
Giebler HA, Lemasson I, Nyborg JK. p53 recruitment of CREB binding protein mediated through phosphorylated CREB: a novel pathway of tumor suppressor regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:4849–58.
Smith ML, Ford JM, Hollander MC, Bortnick RA, Amundson SA, Seo YR, Deng CX, Hanawalt PC, Fornace AJ Jr. p53-mediated DNA repair responses to UV radiation: studies of mouse cells lacking p53, p21, and/or gadd45 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:3705–14.
Léveillard T, Andera L, Bissonnette N, Schaeffer L, Bracco L, Egly JM, Wasylyk B. Functional interactions between p53 and the TFIIH complex are affected by tumour-associated mutations. EMBO J. 1996;15:1615–24.
Wang XW, Vermeulen W, Coursen JD, Gibson M, Lupold SE, Forrester K, Xu G, Elmore L, Yeh H, Hoeijmakers JH, Harris CC. The XPB and XPD DNA helicases are components of the p53-mediated apoptosis pathway. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1219–32.
Cadoret A, Ovejero C, Saadi-Kheddouci S, Souil E, Fabre M, Romagnolo B, Kahn A, Perret C. Hepatomegaly in transgenic mice expressing an oncogenic form of beta-catenin. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3245–9.
Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Hironaka K, Factor VM, Thorgeirsson SS. Vitamin E down-modulates iNOS and NADPH oxidase in c-Myc/TGF-alpha transgenic mouse model of liver cancer. J Hepatol. 2004;41:815–22.
Hamajima N, Saito T, Matsuo K, Suzuki T, Nakamura T, Matsuura A, Okuma K, Tajima K. Genotype frequencies of 50 polymorphisms for 241 Japanese non-cancer patients. J Epidemiol. 2002;12:229–36.
Liu J, Akoulitchev S, Weber A, Ge H, Chuikov S, Libutti D, Wang XW, Conaway JW, Harris CC, Conaway RC, Reinberg D, Levens D. Defective interplay of activators and repressors with TFIH in xeroderma pigmentosum. Cell. 2001;104:353–63.
Liu J, He L, Collins I, Ge H, Libutti D, Li J, Egly JM, Levens D. The FBP interacting repressor targets TFIIH to inhibit activated transcription. Mol Cell. 2000;5:331–41.
Weber A, Liu J, Collins I, Levens D. TFIIH operates through an expanded proximal promoter to fine-tune c-myc expression. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:147–61.
Adamczewski JP, Rossignol M, Tassan JP, Nigg EA, Moncollin V, Egly JM. MAT1, cdk7 and cyclin H form a kinase complex which is UV light-sensitive upon association with TFIIH. EMBO J. 1996;15:1877–84.
Lolli G, Johnson LN. Recognition of Cdk2 by Cdk7. Proteins. 2007;67:1048–59.
Chen J, Larochelle S, Li X, Suter B. Xpd/Ercc2 regulates CAK activity and mitotic progression. Nature. 2003;424:228–32.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Junling Yang from Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences for enormous help. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30360037.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The co-first authors, Hong-yun Wang and Gao-fei Xiong, made equal contribution to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Hy., Xiong, Gf., Zhang, Jx. et al. The role of XPD in cell apoptosis and viability and its relationship with p53 and cdk2 in hepatoma cells. Med Oncol 29, 161–167 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-9818-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-9818-y