Abstract
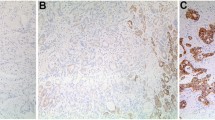
Previous studies have suggested that insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) acts as a tumor suppressor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). The present study was designed to investigate the clinical and prognostic significance of IGFBP-3 in ESCC patients. In this study, IGFBP-3 was detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in paraffin-embedded tissues from 110 ESCC patients, of which 110 were from primary cancer sites and 56 from matched adjacent non-malignant sites. Differences in IGFBP-3 expression and clinical characteristics were compared by χ2 test. Correlations between prognostic outcomes and with IGFBP-3 expression were investigated using Kaplan–Meier analysis and the Cox proportional hazards model. Among adjacent non-malignant tissues, 83.9% of individual tissue staining was scored as either high for IGFBP-3. However, among ESCC cases, only 51.8% of the cancer tissues were scored as high IGFBP-3 expression. In addition, IGFBP-3 expression inversely correlated with pathological classification (P < 0.05 for T, N, and M classifications) and clinical staging (P = 0.006). Furthermore, patients with higher levels of IGFBP-3 had prolonged overall survival (P < 0.001). In conclusion, reduced IGFBP-3 expression may be a risk factor for advanced clinicopathological classification and poor patient survival. These findings suggest that IGFBP-3 may serve as a useful marker for the prognostic evaluation of ESCC patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107.
Suntharalingam M. Definitive chemoradiation in the management of locally advanced esophageal cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007;17(1):22–8. doi:10.1016/j.semradonc.2006.09.008.
Rohatgi PR, Swisher SG, Correa AM, Wu TT, Liao Z, Komaki R et al. Failure patterns correlate with the proportion of residual carcinoma after preoperative chemoradiotherapy for carcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer. 2005;104(7):1349–55. doi:10.1002/cncr.21346.
Di Fiore F, Lecleire S, Rigal O, Galais MP, Ben Soussan E, David I, et al. Predictive factors of survival in patients treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy for squamous cell esophageal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12(26):4185–90.
Luthra R, Wu TT, Luthra MG, Izzo J, Lopez-Alvarez E, Zhang L et al. Gene expression profiling of localized esophageal carcinomas: association with pathologic response to preoperative chemoradiation. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(2):259–67. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.03.3688.
He LR, Liu MZ, Li BK, Rao HL, Liao YJ, Guan XY et al. Prognostic impact of H3K27me3 expression on locoregional progression after chemoradiotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:461. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-9-461.
He LR, Liu MZ, Li BK, Jia WH, Zhang Y, Liao YJ et al. High expression of EZH2 is associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(1):138–47. doi:10.1002/ijc.25031.
He LR, Liu MZ, Li BK, Rao HL, Liao YJ, Zhang LJ et al. Clusterin as a predictor for chemoradiotherapy sensitivity and patient survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(12):2354–60. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01349.x.
Hollowood AD, Lai T, Perks CM, Newcomb PV, Alderson D, Holly JM. IGFBP-3 prolongs the p53 response and enhances apoptosis following UV irradiation. Int J Cancer. 2000;88(3):336–41. doi:10.1002/1097-0215(20001101)88:3<336::AID-IJC3>3.0.CO;2-A.
Hwa V, Oh Y, Rosenfeld RG. The insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) superfamily. Endocr Rev. 1999;20(6):761–87.
Rajah R, Valentinis B, Cohen P. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 induces apoptosis and mediates the effects of transforming growth factor-beta1 on programmed cell death through a p53- and IGF-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(18):12181–8.
Williams AC, Collard TJ, Perks CM, Newcomb P, Moorghen M, Holly JM, et al. Increased p53-dependent apoptosis by the insulin-like growth factor binding protein IGFBP-3 in human colonic adenoma-derived cells. Cancer Res. 2000;60(1):22–7.
Takaoka M, Harada H, Andl CD, Oyama K, Naomoto Y, Dempsey KL et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor regulates aberrant expression of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3. Cancer Res. 2004;64(21):7711–23. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0715.
Yoshino K, Motoyama S, Koyota S, Shibuya K, Usami S, Maruyama K et al. IGFBP3 and BAG1 enhance radiation-induced apoptosis in squamous esophageal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;404(4):1070–5. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.12.115.
Zhao Z, Liu Y, He H, Chen X, Chen J, Lu YC. Candidate genes influencing sensitivity and resistance of human glioblastoma to Semustine. Brain Res Bull. 2011;86(3-4):189–94. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.07.010.
Guo BH, Zhang X, Zhang HZ, Lin HL, Feng Y, Shao JY et al. Low expression of Mel-18 predicts poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2010;21(12):2361–9. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq241.
Xiong J, Yang Q, Kang J, Sun Y, Zhang T, Margaret G et al. Simultaneous isolation of DNA, RNA, and protein from Medicago truncatula L. Electrophoresis. 2010. doi:10.1002/elps.201000425.
Butt AJ, Firth SM, King MA, Baxter RC. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 modulates expression of Bax and Bcl-2 and potentiates p53-independent radiation-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(50):39174–81. doi:10.1074/jbc.M908888199M908888199.
Baxter RC, Butt AJ, Schedlich LJ, Martin JL. Antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic activities of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2000;10 Suppl A:S10–1.
Oh Y, Muller HL, Lamson G, Rosenfeld RG. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-independent action of IGF-binding protein-3 in Hs578T human breast cancer cells. Cell surface binding and growth inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(20):14964–71.
Butt AJ, Williams AC. IGFBP-3 and apoptosis—a license to kill? Apoptosis. 2001;6(3):199–205.
Gill ZP, Perks CM, Newcomb PV, Holly JM. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP-3) predisposes breast cancer cells to programmed cell death in a non-IGF-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(41):25602–7.
Collard TJ, Guy M, Butt AJ, Perks CM, Holly JM, Paraskeva C, et al. Transcriptional upregulation of the insulin-like growth factor binding protein IGFBP-3 by sodium butyrate increases IGF-independent apoptosis in human colonic adenoma-derived epithelial cells. Carcinogenesis. 2003;24(3):393–401.
Torng PL, Lee YC, Huang CY, Ye JH, Lin YS, Chu YW et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) acts as an invasion-metastasis suppressor in ovarian endometrioid carcinoma. Oncogene. 2008;27(15):2137–47. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210864.
Torng PL, Lin CW, Chan MW, Yang HW, Huang SC, Lin CT. Promoter methylation of IGFBP-3 and p53 expression in ovarian endometrioid carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2009;8:120. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-8-120.
Chang YS, Wang L, Liu D, Mao L, Hong WK, Khuri FR, et al. Correlation between insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 promoter methylation and prognosis of patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8(12):3669–75.
Tomii K, Tsukuda K, Toyooka S, Dote H, Hanafusa T, Asano H et al. Aberrant promoter methylation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 gene in human cancers. Int J Cancer. 2007;120(3):566–73. doi:10.1002/ijc.22341.
Firth SM, Baxter RC. Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev. 2002;23(6):824–54.
Baylin SB, Herman JG. DNA hypermethylation in tumorigenesis: epigenetics joins genetics. Trends Genet. 2000;16(4):168–74. doi:S0168-9525(99)01971-X.
Hanafusa T, Yumoto Y, Nouso K, Nakatsukasa H, Onishi T, Fujikawa T et al. Reduced expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and its promoter hypermethylation in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2002;176(2):149–58. doi:S0304383501007364.
Ibanez de Caceres I, Dulaimi E, Hoffman AM, Al-Saleem T, Uzzo RG, Cairns P. Identification of novel target genes by an epigenetic reactivation screen of renal cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66(10):5021–8. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3365.
Wiley A, Katsaros D, Chen H, Rigault de la Longrais IA, Beeghly A, Puopolo M et al. Aberrant promoter methylation of multiple genes in malignant ovarian tumors and in ovarian tumors with low malignant potential. Cancer. 2006;107(2):299–308. doi:10.1002/cncr.21992.
Ikeda G, Isaji S, Chandra B, Watanabe M, Kawarada Y. Prognostic significance of biologic factors in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer. 1999;86(8):1396–405. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19991015)86:8<1396::AID-CNCR3>3.0.CO;2-H.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Major State Basic Research Program (973 project) of China (2010CB912802 and 2010CB529401). We would like to thank Dr. Qiao-Qiao Li for her valuable comments during the design of this study.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L., He, LR., Zhang, R. et al. Low expression of IGFBP-3 predicts poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oncol 29, 2669–2676 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-0133-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-0133-4