Abstract
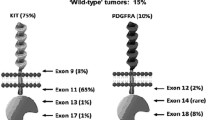
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are the most common human sarcoma. Most of the data available on GISTs derive from retrospective studies of patients referred to oncology centers. The MolecGIST study sought to determine and correlate clinicopathological and molecular characteristics of GISTs. Tumor samples and clinical records were prospectively obtained and reviewed for patients diagnosed in France during a 24-month period. Five hundred and ninety-six patients were included, of whom 10% had synchronous metastases. GISTs originated from the stomach, small bowel or other site in 56.4, 30.2 and 13.4% of cases, respectively. The main prognostic markers, tumor localization, size and mitotic index were not independent variables (P < 0.0001). Mutational status was determined in 492 (83%) patients, and 138 different mutations were identified. KIT and PDGFRA mutations were detected in 348 (71%) and 74 (15%) patients, respectively, contrasting with 82.8 and 2.1% in patients with advanced GIST (MetaGIST) (P < 0.0001). Further comparison of localized GISTs in the MolecGIST cohort with advanced GISTs from previous clinical trials showed that the mutations of PDGFRA exon18 (D842V and others) as well as KIT exon11 substitutions (W557R and V559D) were more likely to be seen in patients with localized GISTs (odds ratio 7.9, 3.1, 2.7 and 2.5, respectively), while KIT exon 9 502_503dup and KIT exon 11 557_559del were more frequent in metastatic GISTs (odds ratio of 0.3 and 0.5, respectively). These data suggest that KIT and PDGFRA mutations and standardized mitotic count deserve to be investigated to evaluate the relapse risk of GISTs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cassier PA, Ducimetière F, Lurkin A, et al. A prospective epidemiological study of new incident GISTs during two consecutive years in Rhône Apes region: incidence and molecular distribution of GIST in a European region. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:165–70.
Corless CL, Fletcher JA, Heinrich MC. Biology of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3813–25.
Rubin BP, Heinrich MC, Corless CL. Gastrointestinal stromal tumour. Lancet. 2007;369:1731–41.
Hirota S, Isozaki K, Moriyama Y, et al. Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science. 1998;279:577–80.
Verweij J, Casali PG, Zalcberg J, et al. Progression-free survival in gastrointestinal stromal tumours with high-dose imatinib: randomised trial. Lancet. 2004;364:1127–34.
Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Duensing A, et al. PDGFRA activating mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science. 2003;299:708–10.
De Matteo RP, Lewis JJ, Leung D, Mudan SS, Woodruff JM, Brennan MF. Two hundred gastrointestinal stromal tumors: recurrence patterns and prognostic factors for survival. Ann Surg. 2000;231:51–8.
Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: pathology and prognosis at different sites. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2006;23:70–83.
Singer S, Rubin BP, Lux ML, et al. Prognostic value of KIT mutation type, mitotic activity, and histologic subtype in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:3898–905.
Agaimy A, Wünsch PH, Hofstaedter F, et al. Minute gastric sclerosing stromal tumors (GIST tumorlets) are common in adults and frequently show c-KIT mutations. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:113–20.
Fletcher CD, Berman JJ, Corless C, et al. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a consensus approach. Hum Pathol. 2002;33:459–65.
Gold JS, Gönen M, Gutiérrez A, et al. Development and validation of a prognostic nomogram for recurrence-free survival after complete surgical resection of localised primary gastrointestinal stromal tumour: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:1045–52.
Joensuu H. Risk stratification of patients diagnosed with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Hum Pathol. 2008;39:1411–9.
DeMatteo RP, Ballman KV, Antonescu CR, et al. Adjuvant imatinib mesylate after resection of localised, primary gastrointestinal stromal tumour: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;373:1097–104.
Emile JF, Lemoine A, Bienfait N, Terrier P, Azoulay D, Debuire B. Length analysis of polymerase chain reaction products: a sensitive and reliable technique for the detection of mutations in KIT exon 11 in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2002;11:107–12.
Hostein I, Faur N, Primois C, et al. BRAF mutation status in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;133:141–8.
Hostein I, Debiec-Rychter M, Olschwang S, et al. A quality control program for mutation detection in KIT and PDGFRA in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. J Gastroenterol. 2011;46:586–94.
Antonescu CR, Sommer G, Sarran L, et al. Association of KIT exon 9 mutations with nongastric primary site and aggressive behavior: KIT mutation analysis and clinical correlates of 120 gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:3329–37.
Lasota J, Dansonka-Mieszkowska A, Sobin LH, Miettinen M. A great majority of GISTs with PDGFRA mutations represent gastric tumors of low or no malignant potential. Lab Invest. 2004;84:874–83.
Martín J, Poveda A, Llombart-Bosch A, et al. Deletions affecting codons 557–558 of the c-KIT gene indicate a poor prognosis in patients with completely resected gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a study by the Spanish group for sarcoma research (GEIS). J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6190–8.
Bachet JB, Hostein I, Le Cesne A, et al. Prognosis and predictive value of KIT exon 11 deletion in GISTs. Br J Cancer. 2009;101:7–11.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Meta-Analysis Group (MetaGIST). Comparison of two doses of imatinib for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a meta-analysis of 1, 640 patients. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1247–53.
Casali PG, Blay JY. ESMO/CONTICANET/EUROBONET consensus panel of experts gastrointestinal stromal tumours: ESMO clinical practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:98–102.
Corless CL, Ballman KV, Antonescu CD et al. Relation of tumor pathologic and molecular features to outcome after surgical resection of localized primary gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST): results of the intergroup phase III trial ACOSOG Z9001. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:15s (suppl; abstr 10006).
Steigen SE, Eide TJ, Wasag B, Lasota J, Miettinen M. Mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a population-based study from northern Norway. APMIS. 2007;115:289–98.
Lasota J, Miettinen M. Clinical significance of oncogenic KIT and PDGFRA mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Histopathology. 2008;53:245–66.
Wozniak A, Rutkowski P, Piskorz A, et al. Progonostic value of KIT/PDGFRA mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST): polish clinical GIST registry experience. Ann Oncol. 2011 (in press).
Du CY, Shi YQ, Zhou Y, Fu H, Zhao G. The analysis of status and clinical implication of KIT and PDGFRA mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). J Surg Oncol. 2008;98:175–8.
Braggio E, de Braggio DA, Small IA, et al. Prognostic relevance of KIT and PDGFRA mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Anticancer Res. 2010;30:2407–14.
Braconi C, Bracci R, Bearzi I, et al. KIT and PDGFRalpha mutations in 104 patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs): a population-based study. Ann Oncol. 2008;19:706–10.
Acknowledgments
MolecGIST study was supported by grants from Ligue contre le Cancer, Institut National du Cancer (INCa) and unrestricted grants from Novartis Pharma. The authors would like to thank patients who participated to MolecGIST study and their families, as well as all the pathologists, oncologists, surgeons, gastroenterologists, physicians and clinical research assistants who participated to the collection of the data. The list is available on http://www.gist-france.org/remerciements.html.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emile, J.F., Brahimi, S., Coindre, J.M. et al. Frequencies of KIT and PDGFRA mutations in the MolecGIST prospective population-based study differ from those of advanced GISTs. Med Oncol 29, 1765–1772 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-0074-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-0074-y