Abstract
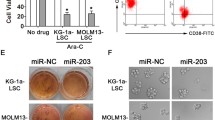
Relapse remains the biggest hurdle of leukemia therapy, while elucidating the molecular mechanism holds promise for the solution. Recently, microRNAs are emerging as an important regulator of cell function. In this study, we for the first time found that miR-153 was downregulated in As2O3-induced drug-resistant K562 cells. In the CD34+ K562 subpopulation, which is characteristic of leukemia stem cell and resembles the drug-resistant subgroup, miR-153 expression level was also much lower than that in the bulk. Forced expression of miR-153 only in K562 cells has no significant effects on cell growth and apoptosis. However, when cells were additionally treated with As2O3, significant greater apoptosis was observed in the miR-153 overexpressed group. Our data here suggest that strategies increasing the endogenous miR-153 might hold promise for an alternative adjuvant therapy of leukemia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rowley JD. Letter: a new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature. 1973;243:290–3.
Holyoake DT. Recent advances in the molecular and cellular biology of chronic myeloid leukaemia: lessons to be learned from the laboratory. Br J Haematol. 2001;113:11–23.
Calabretta B, Perrotti D. The biology of CML blast crisis. Blood. 2004;103:4010–22.
Goldman JM, Melo JV. Chronic myeloid leukemia–advances in biology and new approaches to treatment. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1451–64.
Yin T, Wu YL, Sun HP, Sun GL, Du YZ, Wang KK, Zhang J, Chen GQ, Chen SJ, Chen Z. Combined effects of As4S4 and imatinib on chronic myeloid leukemia cells and BCR-ABL oncoprotein. Blood. 2004;104:4219–25.
Gu J, Zhu X, Li Y, Dong D, Yao J, Lin C, Huang K, Hu H, Fei J. miRNA-21 regulates arsenic-induced anti-leukemia activity in myelogenous cell lines. Med Oncol. Feb 9 [Epub ahead of print].
Gao SM, Chen C, Wu J, Tan Y, Yu K, Xing CY, Ye A, Yin L, Jiang L. Synergistic apoptosis induction in leukemic cells by miR-15a/16-1 and arsenic trioxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;403:203–8.
Zhang QY, Mao JH, Liu P, Huang QH, Lu J, Xie YY, Weng L, Zhang Y, Chen Q, Chen SJ, Chen Z. A systems biology understanding of the synergistic effects of arsenic sulfide and Imatinib in BCR/ABL-associated leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:3378–83.
Holtz MS, Forman SJ, Bhatia R. Non proliferating CML CD34 + progenitors are resistant to apoptosis induced by a wide range of proapoptotic stimuli. Leukemia. 2005;19:1034–41.
Bartel DP. Micro RNAs: genomics. biogenes mech funct Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Hammond SM. MicroRNAs as oncogenes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006;16:4–9.
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature. 2007;449:682–8.
Fabbri M, Garzon R, Cimmino A, Liu Z, Zanesi N, Callegari E, Liu S, Alder H, Costinean S, Fernandez-Cymering C, Volinia S, Guler G, Morrison CD, Chan KK, Marcucci G, Calin GA, Huebner K, Croce CM. MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A and 3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:15805–10.
Xu J, Liao X, Wong C. Downregulations of B-cell lymphoma 2 and myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1 by microRNA 153 induce apoptosis in a glioblastoma cell line DBTRG-05MG. Int J Cancer. 2009;126:1029–35.
Liu L, Chen R, Huang S, Wu Y, Li G, Liu Q, Yin D, Liang Y. Knockdown of SOD1 sensitizes the CD34 + CML cells to imatinib therapy. Med Oncol. 2010 Apr 21 [Epub ahead of print].
Chen Y, Peng C, Sullivan C, Li D, Li S. Critical molecular pathways in cancer stem cells of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2010;24:1545–54.
Naka K, Hoshii T, Hirao A. Novel therapeutic approach to eradicate tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistant chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:1577–81.
Hochhaus A, Schenk T, Erben P, Ernst T, La Rosee P, Muller MC. Cause and management of therapy resistance. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2009;22:367–79.
Thomadaki H, Scorilas A. BCL2 family of apoptosis-related genes: functions and clinical implications in cancer. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2006;43:1–67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Chen, R., Huang, S. et al. miR-153 sensitized the K562 cells to As2O3-induced apoptosis. Med Oncol 29, 243–247 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9807-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9807-6