Abstract
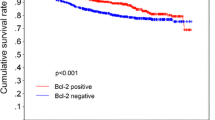
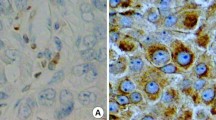
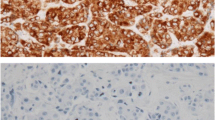
Many biomarkers for breast cancer prognosis have been proposed during the last two decades, among which HER2 and oestrogen receptors are of common use in routine clinical practice. However, in recent years, BCL2 has been recognized as an important prognostic parameter in human breast cancer, although its clinical utility is well established. The aim of this study was to examine the protein expression patterns of BCL2, HER2, oestrogen (ER) and progesterone receptors (PR) and to evaluate their correlation with survival and other prognostic parameters such as tumour size, histological grade and metastasis. We used a retrospective study including 84 Tunisian women with breast cancer. Immunohistochemistry was used to measure protein expression levels of several biomarkers. Association with conventional biopathological factors was analysed by SPSS (version13). The expression rates of BCL2, HER2, ER and PR were, respectively, 69, 62, 58.3 and 51.2%. In univariate analyses, BCL2 was highly correlated with both PR (P < 0.001) and ER (P = 0.006) and also with HER2 expression (P = 0.001). The triple negative profile showed a significant association with SBR (P = 0.016) and BCL2 expression (P = 0.02). In multivariate analyses, a significant association was maintained between BCL2 and both PR and ER (P = 0.02 and P = 0.004, respectively). Survival analysis showed that BCL2 expression was positively correlated with patients survival (P = 0.032). A Bayesian network analysis of all the variables confirmed the high value of BCL2 expression as a predictor of survival. As conclusion, BCL2 expression seems to be a very useful factor that should be in combination with HER2 and ER in breast cancer prognosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Callagy GM, Webber MJ, Pharoah PDP, Caldas C. Meta-analysis confirms BCL2 is an independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:153.
McDonnell TJ, Korsmeyer SJ. Progression from lymphoid hyperplasia to high-grade malignant lymphoma in mice transgenic for the t (14; 18). Nature. 1991;349:254–6.
McDonnell TJ, Troncoso P, Brisbay SM, Logothetis C, Chung LW, Hsieh JT, Tu SM, Campbell ML. Expression of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1992;52:6940–4.
Pietenpol JA, Papadopoulos N, Markowitz S, Willson JK, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Paradoxical inhibition of solid tumor cell growth by bcl2. Cancer Res. 1994;54:3714–7.
Van Slooten HJ, Clahsen PC, van Dierendonck JH, Duval C, Pallud C, Mandard AM, Delobelle-Deroide A, van de Velde CJ, van de Vijver MJ. Expression of Bcl-2 in node-negative breast cancer is associated with various prognostic factors, but does not predict response to onecourse of perioperative chemotherapy. Br J Cancer. 1996;74:78–85.
Linjawi A, Kontogiannea M, Halwani F, Edwardes M, Meterissian S. Prognostic significance of p53, bcl-2, and Bax expression in early breast cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 2004;198:83–90.
Lee KH, Im SA, Oh DY, Lee SH, Chie EK, Han W, Kim DW, Kim TY, Park IA, Noh DY, Heo DS, Ha SW, Bang YJ. Prognostic significance of bcl-2 expression in stage III breast cancer patients who had received doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel as adjuvant chemotherapy. BMC Cancer. 2007;7:63.
Nadler Y, Camp RL, Giltnane JM, Moeder C, Rimm DL, Kluger HM, Kluger Y. Expression patterns and prognostic value of Bag-1 and Bcl-2 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10:R35.
Bhargava V, Kell DL, Van de Rijn M, Warnke RA. Bcl-2 immunoreactivity in breast carcinoma correlates with hormone receptor positivity. Am J Pathol. 1994;145:535–40.
Bilalovic N, Vranic S, Hasanagic S, Basic H, Tatarevic A, Beslija S. The Bcl-2 protein: a prognostic indicator strongly related to ER and PR in breast cancer. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2004;4:5–12.
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:127–37.
McKean-Cowdin R, Kolonel LN, Press MF, Pike MC, Henderson BE. Germ-line HER-2 variant and breast cancer risk by stage of disease. Cancer Res. 2001;61:8393–4.
Tommasi S, Fedele V, Crapolicchio A, Bellizzi A, Paradiso A, Reshkin SJ. ErbB2 and the antimetastatic nm23/NDP kinase in regulating serum induced breast cancer invasion. Int J Mol Med. 2003;12:131–4.
Picard D, Bunone G, Liu JW, Donzw O. Steroid independent activation of steroid receptors in mammalian and yeast cells and in breast cancer. Biochem Soc Trans. 1997;25:597–602.
McGuire WL. Hormone receptors: their role in predicting prognosis and response to endocrine therapy. Semin Oncol. 1978;5:428–33.
Clarke R, Skaar T, Baumann K, Leonessa F, James M, Lippman J, Thompson EW, Freter C, Brunner N. Hormonol carcinogenesis in breast cancer: cellular and molecular studies of malignant progression. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1994;31:237–48.
Nicholson RI, McClelland RA, Gee JM, Manning DL, Cannon P, Robertson JF, Ellis IO, Blamey RW. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in breast cancer: association with response to endocrine therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1994;29:117–25.
Kreike B, van Kouwenhove M, Horlings H, Weigelt B, Peterse H, Bartelink H, van de Vijver MJ. Gene expression profiling and histopathological characterization of triple negative/basal-like breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res. 2007;R9:65.
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lønning PE, Børresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D. Molecular portraits of human breast tumors. Nature. 2000;406:747–52.
Cleator S, Heller W, Coombes RC. Triple-negative breast cancer: therapeutic options. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:235–44.
Grann VR, Troxel AB, Zojwalla NJ, Jacobson JS, Hershman D, Neugut AI. Hormone receptor status and survival in a population-based cohort of patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2005;103:2241–51.
Bloom HJ, Richardson WW. Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer: a study of 1,409 cases of which 359 have been followed for 15 years. Br J Cancer. 1957;11:359–77.
Khabir A, Ghorbel A, Daoud J, Frikha M, Drira MM, Laplanche A, Busson P, Jlidi R. Similar BCL-X but different BCL-2 levels in the two age groups of North African nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Cancer Detect Prev. 2003;27:250–5.
BenHassen H, Masmoudi F, Rebai A. Inference in signal transduction pathways with incomplete data: comparison between the EM algorithm and a new implicit algorithm. J Comput Biol. 2009;16:1227–40.
Bouchaala L, Masmoudi A, Rebai A. Improving algorithms for structure learning in Bayesian networks using a new implicit score. Expert Syst Appl. 2010;37:5470–5.
Sivridis E, Stamos C, Fiska A, Nikolettos N, Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A.c-erbB-2 and the “triple-state” in early breast carcinomas. Med Oncol 2009.
Hockenbery DM, Zutter M, Hickey W, Nahm M, Korsmeyer SJ. BCL2 protein is topographically restricted in tissues characterized by apoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1991;88:6961–5.
Chao DT, Korsmeyer SJ. BCL-2 family: regulators of cell death. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:395–419.
Luna-Moré S, Casquero S, Pérez-Mellado A, Rius F, Weill B, Gornemann I. Importance of estrogen receptors for the behavior of invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast. Review of 68 cases with follow-up of 54. Pathol Res Pract. 2000;196:35–9.
Wang S, Yang D, Lippman ME. Targeting Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL with non peptidic small-molecule antagonists. Semin Oncol. 2003;30:132–42.
Rehman S, Crow J, Revell PA. Bax protein expression in DCIS of the breast in relation to invasive ductal carcinoma and other molecular markers. Pathol Oncol Res. 2000;6:256–63.
Sierra A, Castellsague X, Escobedo A, Lloveras B, Garcia-Ramirez M, Moreno A, Fabra A. Bcl2 with loss of apoptosis allows accumulation of genetic alterations: a pathway to metastatic progression in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2000;89:142–7.
Fernandez Y, Gu B, Martinez A, Torregrosa A, Sierra A. Inhibition of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells: role in tumor progression to the metastatic state. Int J Cancer. 2002;101:317–26.
Gasparini G, Barbareschi M, Doglioni C, Palma PD, Mauri FA, Boracchi P, Bevilacqua P, Caffo O, Morelli L, Verderio P, Pezzella F, Harris AL. Expression of bcl-2 protein predicts efficacy of adjuvant treatments in operable node-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1995;1:189–98.
Tsutsui S, Yasuda K, Suzuki K, Takeuchi H, Nishizaki T, Higashi H, Sf Era. Bcl-2 protein expression is associated with p27 and p53 protein expressions and MIB-1 counts in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2006;6:187.
Elledge RM, Green S, Howes L, Clark GM, Berardo M, Allred DC, Pugh R, Ciocca D, Radvin P, O’sullivan J, Rivkin S, Martino S, Osborne CK. bcl-2, p53, and response to tamoxifen in estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: a southwest oncology group study. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:1916–22.
Yang Q, Sakurai T, Jing X, Utsunomiya H, Shan L, Nakamura Y, Nakamura M, Oura S, Suzuma T, Yoshimura G, Umemura T, Kokawa Y, Nakudo K. Expression of Bcl2, but not Bax, correlates with estrogen receptor status and tumour proliferation in invasive breast carcinoma. Pathol Int. 1999;49:775–80.
Kyndi M, Sorensen FB, Knudsen H, Alsner J, Overgaard M, Nielsen HM, Overgaard J. Impact of BCL2 and p53 on postmastectomy radiotherapy response in high-risk breast cancer. A subgroup analysis of DBCG82 b&c. Acta Oncol. 2008;47:608–17.
Kroger N, Langosch KM, Riethdorf S, Schmoor C, Schumacher M, Zander AR, Loning T. Prognostic and predictive effects of immunohistochemical factors in high-risk primary breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(1):159–68.
Masmoudi Y, Chabchoub H, Hanafi S, Rebai A. A Mathematical Programming based Procedure for Breast Cancer Classification. J Math Model Algorithms. 2010; in press.
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM, Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P, Narod SA. Triple negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:4429–34.
Rakha EA, EL-Sayed ME, Grenn AR, Lee AH, Robertson JF. Ellis IO: prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer. 2007;109:25–32.
Livasy CA, Karaca G, Nanda R, Tretiakova MS, Olopade OI, Moore DT, Perou CM. Phenotypic evaluation of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 2006;19:264–71.
Fulford LG, Easton DF, Reis-Filho JS, Sofronis A, Gillett CE, Lakhani SR, Hanby A. Specific morphological features predictive for the basal phenotype in grade 3 invasive ductal carcinoma of breast. Histopathology. 2006;49:22–34.
William J, Irvin Jr, Lisa A. Carey: what is triple-negative breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44:2799–805.
Rolland P, Spendlove I, Madjd Z, Rakha EA, Patel P, Ellis IO, Durrant L. The p53 positive Bcl-2 negative phenotype is an independent marker of prognosis in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:1311–7.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mrs Raoudha Abdelnadher for the technical assistance and all of the clinicians and pathologists at Habib BOURGUIBA Hospital, who performed diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. We thank Dr Sami Baccouche for his valuable discussion and advices during this study. We also thank Mrs Salma Hamsa, for English editing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kallel-Bayoudh, I., Hassen, H.B., Khabir, A. et al. Bcl-2 expression and triple negative profile in breast carcinoma. Med Oncol 28 (Suppl 1), 55–61 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9694-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9694-x