Abstract
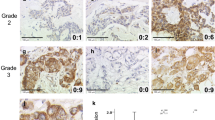
Cyclooxygenase is an enzyme that changes the immune response to malign cells and catalyzes prostaglandins that may have an impact on cell proliferation. The purpose of this study was to examine the relation between established clinicopathological parameters in breast carcinomas and COX-2 protein expression. COX-2, estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and c-erB-2 primary antibodies were assessed in the slides prepared from the paraffin blocks of 62 invasive ductal carcinoma cases. The relation between ER, PR, and c-erbB-2 positivity, histological grade, nuclear grade, lymphovascular invasion, tumor diameter, lymph node positivity, metastasis, and age were evaluated. The results were analyzed statistically. Cytoplasmic COX-2 expression was seen in 75.8% of all breast carcinomas. In both univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis, there was a positive correlation between COX-2 expression and negative ER status, respectively (P = 0.0173) (P = 0.016). There was any statistically significant relation between PR positivity, c-erbB-2 positivity, histological grade, nuclear grade, lymphovascular invasion, tumor diameter, lymph node positivity, metastasis, and age (P ≥ 0.05). Given that there was found a statistically significant relation between COX-2 expression and negative ER status, which is considered a poor prognostic parameter, suggests that COX-2 expression can have a place among the other prognostic parameters of breast carcinoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denkert C, Winzer KJ, Müler BM, et al. Elevated expression of cyclooxygenase-2 is a negative prognostic factor for disease free survival and overall survival in patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2003;97:2978–87.
Perrone G, Santini D, Vincenzi B, et al. COX-2 expression in DCIS: correlation with VEGF, HER-2/neu, prognostic molecular markers and clinicopathological features. Histopathology. 2005;46:561–8.
Fadden DW, Riggs DR, Jackson BJ, Cunningham C. Additive effect of COX-1 and COX-2 inhibition on breast cancer in vitro. Int J Oncol. 2006;29:1019–23.
Tan KB, Yong WP, Putti TC. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression: a potential prognostic and predictive marker for high-grade ductal carcinoma in situ of breast. Histopathology. 2004;44:24–8.
Soslow AS, Dannenberg AJ, Rush D, et al. COX-2 is expressed in human pulmonary, colonic, and mammary tumors. Cancer. 2000;89:2637–45.
Yiu GK, Toker A. NFAT induces breast cancer cell invasion by promoting the induction of cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:12210–7.
Gallicchio L, McSorley MA, Newschaffer CJ, et al. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, cyclooxygenase polymorphisms, and risk of developing breast carcinoma among women with benign breast disease. Cancer. 2006;106:1443–52.
Barnes N, Haywood P, Flint P, Knox WF, Bundred NJ. Survivin expression in in situ and invasive breast cancer relates to COX-2 expression and DCIS recurrence. Br J Cancer. 2006;94:253–8.
Howe LR, Chang SH, Tolle KC, et al. HER-2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis and angiogenesis are reduced in cyclooxygenase-2 knockout mice. Cancer Res. 2005;65:10113–9.
Howe LR. Cyclooxygenase/prostaglandin signaling and breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2007;9:210.
Nakopoulou L, Mylona E, Papadaki I, Kapranou A, Giannopoulou I. Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 is associated with a favorable prognostic phenotype in breast carcinoma. Pathobiology. 2005;72:241–9.
Watson J, Chuah SY. Techniques for primary culture of human breast cancer cells and measurement of their prostaglandin secretion. Clin Sci. 1992;83:347–52.
Fulton AM, Zhang SZ, Chong YC. Role of the prostaglandin E2 receptor in mammary tumor metastasis. Cancer Res. 1991;51:2047–50.
Liu XH, Rose DP. Differential expression and regulation of cyclooxygenase-1 in two human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1996;56:5125–7.
Rosai J. Rosai and Ackerman’s surgical pathology. In: Rosai J, editor. Breast. Philadelphia: Mosby Year Book; 2004. p. 1763–876.
Leo C, Faber S, Hentschel B, Höckel M, Horn LC. The status of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in ductal carcinoma in situ lesions and invasive breast cancer correlates to cyclooxygenase-2 expression in normal breast tissue. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2006;10:327–32.
Mohammad AM, Abdel HA, Abdel W, Ahmed AM, Wael T, Einman G. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and 12-lipoxygenase in human breast cancer and their relationship with HER-2/neu and hormonal receptors: impact on prognosis and therapy. Indian J Cancer. 2006;43:163–8.
Cho MH, Yoon JH, Jaegal YJ, et al. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in breast carcinogenesis and its relation to HER-2/neu and p53 protein expression in invasive ductal carcinoma. Breast. 2006;15:390–8.
Oliviera VM, Piato S, Silva ALG. Correlation of cyclooxygenase-2 and aromatase immunohistochemical expression in invasive ductal carcinoma, ductal carcinoma in situ, and adjacent normal epithelium. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;95:235–41.
Costa C, Soares R, Reis-Filho JS, Leitao D, Amendoiera I, Schmitt FC. Cyclo-oxygenase 2 expression is associated with angiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in human breast cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2002;55:429–34.
Ristimaki A, Sivula A, Lundin M, et al. Prognostic significance of elevated cyclooxygenase-2 expression in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62:632–5.
Nassar A, Radhakrishnan A, Cabrero IA, Cotsonis G, Cohen C. COX-2 expression in invasive breast cancer correlation with prognostic parameters and outcome. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2007;15:255–9.
Bundred NJ, Barnes NLP. Potential use of COX-2-aromatase inhibitor combinations in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2005;93:S10–5.
Witton CJ, Hawe SJK, Cooke TJ, Bartlett JM. Cyclooxygenase.2 (COX2) expression is associated with poor outcome in ER-negative, but not ER-positive, breast cancer. Histopathology. 2004;45:47–54.
Robertson FM, Mallery SR, Bergdall-Costell VK, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 directly induces MCF-7 breast tumor cells to develop into exponentially growing, highly angiogenic and regionally invasive human ductal carcinoma xenografts. Anticancer Res. 2007;27:719–27.
Roche-Nagle G, Connolly EM, Eng M, Bouchier-Hayes DJ, Harmey JH. Antimetastatic activity of a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. Br J Cancer. 2004;91:359–65.
Subbaramaiah K, Norton L, Gerald W, Dannenberg AJ. Cyclooxygenase-2: a target for the prevention and treatment of breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2001;8:97–114.
Boland GP, Butt IS, Prasad R, Knox WF, Bundred NJ. COX-2 expression is associated with an aggressive phenotype in ductal carcinoma in situ. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:423–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barısık, N.O., Keser, S.H., Gul, A.E. et al. The value of COX-2 expression in the prognostic parameters of invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Med Oncol 28, 703–708 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9503-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9503-6