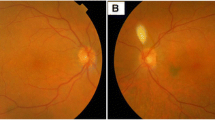
Abstract
To report a clinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical findings in a case of primary extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of the uvea associated with massive diffuse extraocular episcleral extension and focal infiltration of the optic nerve and meninges, clinically presented as longstanding uveitis masquerade syndrome. Interventional case reports with histopathological correlation. We describe a 80-year-old male patient with a 3-year history of chronic recurrent hypertensive (pan) uveitis associated with ocular pain, unresponsive to topical and systemic anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, antibiotic/antiviral and antiglaucomatous therapy. Because the eye was not salvageable with conservative treatment, enucleation of blind and painful eye was performed. Findings from histopathological and immunohistochemistry examination of the enucleated eye showed an extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of the uveal tract with massive epibulbar extension and optic nerve and meningeal penetration. During almost 3 years of clinical course and 6 months after the enucleation, there were no systemic manifestations of lymphoma, and patient has not required subsequent treatment. Primary lymphoproliferative lesions of the uvea, comprising the iris, ciliary body and choroid are very rare, associated with epibulbar extension extremely and with optic nerve and menigeal penetration exceptionally. Despite its rarity, primary lymphoma of the uvea should be included in the differential diagnosis particularly in older patients with longstanding recurrent uveitis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. (eds). World health organization classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon: IARC Press; 2008.
Coupland SE, Damato B. Lymphomas involving the eye and the ocular adnexa. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2006;17(6):523–31.
Coutinho AB, et al. Extranodal B-cell lymphoma of the uvea: a case report. Can J Ophthalmol. 2005;40(5):623–6.
Sjö LD. Ophthalmic lymphoma: epidemiology and pathogenesis. Acta Ophthalmologica. 2009;87(Thesis 1):1–20.
Ben-Ezra D, Sahel JA, Harris NL, Hemo I, Albert DM. Uveal lymphoid infiltrates: immunohistochemical evidence for a lymphoid neoplasia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1989;73(10):846–51.
Chan CC, Buggage RR, Nussenblatt RB. Intraocular lymphoma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2002;13(6):411–8.
Cockerham GC, Hidayat AA, Bijwaard KE, Sheng ZM. Re-evaluation of “reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the uvea”: an immunohistochemical and molecular analysis of 10 cases. Ophthalmology. 2000;107(1):151–8.
Coupland SE, Heimann H, Bechrakis NE. Primary intraocular lymphoma: a review of the clinical, histopathological and molecular biological features. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2004;240:901–13.
Coupland SE, et al. Extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphomas of the uvea: an analysis of 13 cases. J Pathol. 2002;197(3):333–40.
Coupland SE, Joussen A, Anastassiou G, Stein H. Diagnosis of a primary uveal extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma by chorioretinal biopsy: case report. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005;243(5):482–6.
Fuller ML, Sweetenham J, Schoenfield L, Singh AD. Uveal lymphoma: a variant of ocular adnexal lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008;49(12):2393–7.
Garcia-Alvarez C, et al. Uveal lymphoma with extraocular involvement. Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica 2006; 84 (Suppl 239):70.
Grossniklaus HE, et al. Uveal lymphoid infiltration: report of four cases and clinicopathologic review. Ophthalmology. 1998;105:1265–73.
Holz FG, Boehmer HV, Mechtersheimer G, Ott G, Völcker HE. Uveal non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with epibulbar extension simulating choroidal effusion syndrome. Retina. 1999;19(4):343–6.
Jahnke K, et al. Intraocular lymphoma 2000–2005: a results of a retrospective multicentre trial. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006;244:663–9.
Coupland SE, Damato B. Understanding intraocular lymphomas. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2008;36(6):564–78.
Coupland SE, Damato B. Molecular pathology of intraocular lymphomas. Expert Rev Ophthalmol. 2008;3(5):543–51.
Waheed NK, Foster CS. Masquerade syndromes: malignancies in diagnosis and treatment of uveitis. Foster CS and Vitale AT. WB Saunders Company 2002, pp. 503–527.
Zamiri P, Boyd SH, Lightman S. Uveitis in the elderly: is it easy to identify the masquerade? Br J Ophthalmol. 1997;81(10):827–31.
Sagaert X, De Wolf-Peeters C, Noels H, Baens M. The pathogenesis of MALT lymphomas: where do we stand? Leukemia. 2007;21:389–96.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rašić, D.M., Stanković, Z., Terzić, T. et al. Primary extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of the uvea associated with massive diffuse epibulbar extension and focal infiltration of the optic nerve and meninges, clinically presented as uveitis masquerade syndrome: a case report. Med Oncol 27, 1010–1016 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-009-9325-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-009-9325-6