Abstract
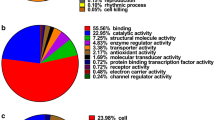
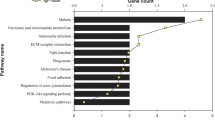
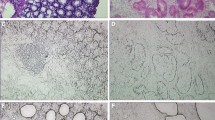
Early detection and rational therapy for gastric cancer are crucial. In this study we undertook comparative proteomics for identification of gastric carcinoma biomarkers using pooled laser capture microdissected GA cells and matched nonmalignant gastric mucosa epithelial cells. The method involved separation of total proteins by 1D SDS-PAGE, trypsin digestion, and postdigest 18O/16O labeling followed by nano-HPLC-MS/MS for peptide identification and relative quantification. A total of 78 differentially expressed proteins were identified, among these proteins, 42 proteins were up-regulated in GA and 36 proteins were down-regulated. Some differentially expressed proteins were further validated by western blot analysis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GA:
-
Gastric adenocarcinoma
- LCM:
-
Laser capture microdissection
- HPLC-MS/MS:
-
High performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry
- ESI-Q-TOF-MS:
-
Electrospray ionization quadrupole–time of flight mass spectrometry
References
Roder DM. The epidemiology of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2002;5(Suppl 1):5–11. doi:10.1007/s10120-002-0203-6.
Alberts SR, Cervantes A, van de Velde CJ. Gastric cancer: epidemiology, pathology and treatment. Ann Oncol. 2003;14(Suppl 2):ii31–6.
Henning GT, Schild SE, Stafford SL, et al. Results of irradiation or chemo irradiation following resection of gastric adenocarcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;46(3):589–98. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(99)00446-0.
Reymond MA, Schlegel W. Proteomics in cancer. Adv Clin Chem. 2007;44:103–42. doi:10.1016/S0065-2423(07)44004-5.
Bantscheff M, Schirle M, Sweetman G, et al. Quantitative mass spectrometry in proteomics: a critical review. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;389(4):1017–31. doi:10.1007/s00216-007-1486-6.
Sakai J, Kojima S, Yanagi K, Kanaoka M. 18O-labeling quantitative proteomics using an ion trap mass spectrometer. Proteomics. 2005;5(1):16–23. doi:10.1002/pmic.200300885.
Lassman ME, Rahbar A, Medintz IL, Ligler FS. Incorporation of (18)oxygen into peptide mixtures and analysis with multi-dimensional chromatography and mass-spectroscopy. Anal Lett. 2007;40(10):1864–78. doi:10.1080/00032710701384659.
Emmert-Buck MR, Bonner RF, Smith PD, et al. Laser capture microdissection. Science. 1996;274(5289):998–1001. doi:10.1126/science.274.5289.998.
Craven RA, Banks RE. Laser capture microdissection and proteomics: possibilities and limitation. Proteomics. 2001;1(10):1200–4. doi:10.1002/1615-9861(200110)1:10<1200::AID-PROT1200>3.0.CO;2-Q.
Lane CS, Wang Y, Betts R, et al. Comparative cytochrome P450 proteomics in the livers of immunodeficient mice using 18O stable isotope labeling. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007;6(6):953–62. doi:10.1074/mcp.M600296-MCP200.
Zeeberg BR, Feng W, Wang G, et al. GoMiner: a resource for biological interpretation of genomic and proteomic data. Genome Biol. 2003;4(4):R28. doi:10.1186/gb-2003-4-4-r28.
Zang L, Toy DP, Hancock WS, et al. Proteomic analysis of ductal carcinoma of the breast using laser capture microdissection, LC-MS, and O-16/O-18 isotopic labeling. J Proteome Res. 2004;3(3):604–12. doi:10.1021/pr034131l.
Hood BL, Darfler MM, Guiel TG, et al. Proteomic analysis of formalin-fixed prostate cancer tissue. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2005;4(11):1741–53. doi:10.1074/mcp.M500102-MCP200.
Lopez-Ferrer D, Ramos-Fernandez A, Martinez-Bartolome S, et al. Quantitative proteomics using (16)O/(18)O labeling and linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Proteomics. 2006;6(Suppl 1):S4–11. doi:10.1002/pmic.200500375.
Miyagi M, Rao KC. Proteolytic 18O-labeling strategies for quantitative proteomics. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2007;26(1):121–36. doi:10.1002/mas.20116.
Seow TK, Liang RC, Leow CK, Chung MC. Hepatocellular carcinoma: from bedside to proteomics. Proteomics. 2001;1(10):1249–63. doi:10.1002/1615-9861(200110)1:10<1249::AID-PROT1249>3.0.CO;2-1.
Bantscheff M, Dumpelfeld B, Kuster B. Femtomol sensitivity post-digest (18)O labeling for relative quantification of differential protein complex composition. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2004;18(8):869–76. doi:10.1002/rcm.1418.
Sun G, Anderson VE. A strategy for distinguishing modified peptides based on post-digestion 18O labeling and mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2005;19(19):2849–56. doi:10.1002/rcm.2133.
Fu Z, Kitagawa Y, Shen R, et al. Metastasis suppressor gene Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) is a novel prognostic marker in prostate cancer. Prostate. 2006;66(3):248–56. doi:10.1002/pros.20319.
Minoo P, Zlobec I, Baker K, et al. Loss of raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein expression is associated with tumor progression and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007;127(5):820–7. doi:10.1309/5D7MM22DAVGDT1R8.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (30000028, 30240056, 30370642), key research program from Science and Technology Committee of Hunan, China (04sk1006-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Z. ZhiQiang and L. MaoYu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ZhiQiang, Z., MaoYu, L., GuiYing, Z. et al. Identification of human gastric carcinoma biomarkers by differential protein expression analysis using 18O labeling and NanoLC-MS/MS coupled with laser capture microdissection. Med Oncol 27, 296–303 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-009-9208-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-009-9208-x