Abstract
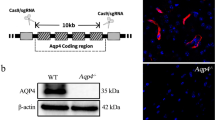
The pathological hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease (PD), a neurodegenerative disorder, are the selective loss of dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and the presence of α-synuclein (α-syn) aggregates in the form of Lewy bodies/Lewy neurites (LBs/LNs) in neurons. Recent studies have indicated that aquaporin 4 (AQP4), as a predominant water channel protein in the brain, is involved in the progression of Parkinson’s disease (PD). However, it remains unclear whether AQP4 expression affects α-syn pathology in Parkinson’s disease. In this study, we established a progressive PD model by subjecting AQP4 null (AQP4+/−) mice to bilateral intrastriatal injection of α-syn preformed fibrils (PFFs) and investigated the effect of decreased AQP4 expression on the development of PD. We found that decreased expression of AQP4 accelerated pathologic deposition of α-syn and facilitated the loss of dopamine neurons and behavioral disorders. Draining of macromolecules from the brain via the glymphatic pathway was slowed due to decreased AQP4 expression. Taken together, these findings indicate that decreased AQP4 expression may aggravate PD-like pathology, possibly via impairment of the glymphatic pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All relevant data supporting the findings of this study are either included within the article and its Supplementary Information files or are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- AQP4:
-
Water channel aquaporin 4
- WT:
-
Wild type
- SN:
-
Substantia nigra
- α-syn PFFs:
-
α-Syn-preformed fibrils
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- TH:
-
Tyrosine hydroxylase
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- TBI:
-
Traumatic brain injury
- ISF:
-
Interstitial fluid
- Mpi:
-
Months post-injection
- AQP4+/--PFFs:
-
α-Syn PFFs-injected AQP4+/- mice
- WT-PFFs:
-
WT mice treated with α-syn PFFs
- LBs/LNs:
-
Lewy-bodies/Lewy-neurites
- SNpc:
-
Substantia nigra pars compacta
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- M1,M2:
-
Motor cortex
- Pir:
-
Piriform cortex
- S1,S2:
-
Somatosensory cortex
- Cg1,Cg2:
-
Cingulate cortex
- DI,CI:
-
Insular cortex
- MPP + :
-
1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium
- MPTP:
-
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
References
Abdelmotilib H, Maltbie T, Delic V, Liu Z, Hu X, Fraser KB, Moehle MS, Stoyka L, Anabtawi N, Krendelchtchikova V, Volpicelli-Daley LA, West A (2017) α-Synuclein fibril-induced inclusion spread in rats and mice correlates with dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 105:84–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2017.05.014
Bloch O, Auguste KI, Manley GT, Verkman AS (2006) Accelerated progression of kaolin-induced hydrocephalus in aquaporin-4-deficient mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1527–1537. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600306
Boland B, Yu WH, Corti O, Mollereau B, Henriques A, Bezard E, Pastores GM, Rubinsztein DC, Nixon RA, Duchen MR, Mallucci GR, Kroemer G, Levine B, Eskelinen E-L, Mochel F, Spedding M, Louis C, Martin OR, Millan MJ (2018) Promoting the clearance of neurotoxic proteins in neurodegenerative disorders of ageing. Nat Rev Drug Discov 17:660–688. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2018.109
Brück D, Wenning GK, Stefanova N, Fellner L (2016) Glia and alpha-synuclein in neurodegeneration: a complex interaction. Neurobiol Dis 85:262–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.03.003
Da Mesquita S, Louveau A, Vaccari A, Smirnov I, Cornelison RC, Kingsmore KM, Contarino C, Onengut-Gumuscu S, Farber E, Raper D, Viar KE, Powell RD, Baker W, Dabhi N, Bai R, Cao R, Hu S, Rich SS, Munson JM, Lopes MB, Overall CC, Acton ST, Kipnis J (2018) Functional aspects of meningeal lymphatics in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 560:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0368-8
Danzer KM, Kranich LR, Ruf WP, Cagsal-Getkin O, Winslow AR, Zhu L, Vanderburg CR, McLean PJ (2012) Exosomal cell-to-cell transmission of alpha synuclein oligomers. Mol Neurodegener 7:42. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-7-42
Delenclos M, Trendafilova T, Mahesh D, Baine AM, Moussaud S, Yan IK, Patel T, McLean PJ (2017) Investigation of endocytic pathways for the internalization of exosome-associated oligomeric alpha-synuclein. Front Neurosci 11:172. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00172
Dickson DW (2018) Neuropathology of Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 46(Suppl 1):S30–S33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.07.033
Ding X, Zhou L, Jiang X, Liu H, Yao J, Zhang R, Liang D, Wang F, Ma M, Tang B, Wu E, Teng J, Wang X (2020) Propagation of Pathological α-Synuclein from the Urogenital Tract to the Brain Initiates MSA-like Syndrome. iScience 23:101166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.101166
Freundt EC, Maynard N, Clancy EK, Roy S, Bousset L, Sourigues Y, Covert M, Melki R, Kirkegaard K, Brahic M (2012) Neuron-to-neuron transmission of α-synuclein fibrils through axonal transport. Ann Neurol 72:517–524. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.23747
Froula JM, Castellana-Cruz M, Anabtawi NM, Camino JD, Chen SW, Thrasher DR, Freire J, Yazdi AA, Fleming S, Dobson CM, Kumita JR, Cremades N, Volpicelli-Daley LA (2019) Defining α-synuclein species responsible for Parkinson’s disease phenotypes in mice. J Biol Chem 294:10392–10406. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.007743
Havrda MC, Paolella BR, Ward NM, Holroyd KB (2013) Behavioral abnormalities and Parkinson’s-like histological changes resulting from Id2 inactivation in mice. Dis Model Mech 6:819–827. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.010041
Hoshi A, Tsunoda A, Tada M, Nishizawa M, Ugawa Y, Kakita A (2017) Expression of aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 4 in the temporal neocortex of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Brain Pathol 27:160–168. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12369
Huang F, Li Y-N, Yin F, Wu Y-T, Zhao D-X, Li Y, Zhang Y-F, Zhu Q-S (2015) Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits neuronal apoptosis and damage, enhances spinal aquaporin 4 expression and improves neurological deficits in rats with spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep 11:3565–3572. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3162
Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, Plogg BA, Peng W, Gundersen GA, Benveniste H, Vates GE, Deane R, Goldman SA, Nagelhus EA, Nedergaard M (2012) A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid β. Sci Trans Med 4:147ra111. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3003748
Jessen NA, Munk ASF, Lundgaard I, Nedergaard M (2015) The glymphatic system: a beginner’s guide. Neurochem Res 40:2583–2599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1581-6
Jones DR, Delenclos M, Baine AT, DeTure M, Murray ME, Dickson DW, McLean PJ (2015) Transmission of soluble and insoluble α-synuclein to mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 74:1158–1169. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0000000000000262
Kalia LV, Lang AE (2015) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 386:896–912. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61393-3
Kim S, Kwon S-H, Kam T-I, Panicker N, Karuppagounder SS, Lee S, Lee JH, Kim WR, Kook M, Foss CA, Shen C, Lee H, Kulkarni S, Pasricha PJ, Lee G, Pomper MG, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Ko HS (2019) Transneuronal propagation of pathologic α-synuclein from the gut to the brain models Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 103:627-641.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.05.035
Kohl Z, Ben Abdallah N, Vogelgsang J, Tischer L, Deusser J, Amato D, Anderson S, Müller CP, Riess O, Masliah E, Nuber S, Winkler J (2016) Severely impaired hippocampal neurogenesis associates with an early serotonergic deficit in a BAC α-synuclein transgenic rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 85:206–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.10.021
Kress BT, Iliff JJ, Xia M, Wang M, Wei HS, Zeppenfeld D, Xie L, Kang H, Xu Q, Liew JA, Plog BA, Ding F, Deane R, Nedergaard M (2014) Impairment of paravascular clearance pathways in the aging brain. Ann Neurol 76:845–861. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24271
Lan Y-L, Zhao J, Ma T, Li S (2016) The potential roles of aquaporin 4 in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 53:5300–5309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9446-1
Lee DJ, Hsu MS, Seldin MM, Arellano JL, Binder DK (2012) Decreased expression of the glial water channel aquaporin-4 in the intrahippocampal kainic acid model of epileptogenesis. Exp Neurol 235:246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.02.002
Lopes da Fonseca T, Villar-Piqué A, Outeiro TF (2015) The interplay between alpha-synuclein clearance and spreading. Biomolecules 5:435–471. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5020435
Loria F, Vargas JY, Bousset L, Syan S, Salles A, Melki R, Zurzolo C (2017) α-Synuclein transfer between neurons and astrocytes indicates that astrocytes play a role in degradation rather than in spreading. Acta Neuropathol 134:789–808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1746-2
Luk KC, Kehm V, Carroll J, Zhang B, O’Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2012) Pathological α-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science 338:949–953. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1227157
Ma T, Yang B, Gillespie A, Carlson EJ, Epstein CJ, Verkman AS (1997) Generation and phenotype of a transgenic knockout mouse lacking the mercurial-insensitive water channel aquaporin-4. J Clin Invest 100:957–962. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI231
Mack JM, Moura TM, Lanznaster D, Bobinski F, Massari CM, Sampaio TB, Schmitz AE, Souza LF, Walz R, Tasca CI, Poli A, Doty RL, Dafre AL, Prediger RD (2018) Intranasal administration of sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate induces motor deficits and dopaminergic dysfunction in mice. Neurotoxicology 66:107–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2018.03.011
Mao X, Ou MT, Karuppagounder SS, Kam T-I, Yin X, Xiong Y, Ge P, Umanah GE, Brahmachari S, Shin J-H, Kang HC, Zhang J, Xu J, Chen R, Park H, Andrabi SA, Kang SU, Gonçalves RA, Liang Y, Zhang S, Qi C, Lam S, Keiler JA, Tyson J, Kim D, Panicker N, Yun SP, Workman CJ, Vignali DAA, Dawson VL, Ko HS, Dawson TM (2016) Pathological α-synuclein transmission initiated by binding lymphocyte-activation gene 3. Science 353https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aah3374
Mestre H, Hablitz LM, Xavier AL, Feng W, Zou W, Pu T, Monai H, Murlidharan G, Castellanos Rivera RM, Simon MJ, Pike MM, Plá V, Du T, Kress BT, Wang X, Plog BA, Thrane AS, Lundgaard I, Abe Y, Yasui M, Thomas JH, Xiao M, Hirase H, Asokan A, Iliff JJ, Nedergaard M (2018) Aquaporin-4-dependent glymphatic solute transport in the rodent brain. eLife 7. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40070
Murad F, Leitman D, Waldman S, Chang CH, Hirata M, Kohse K (1988) Effects of nitrovasodilators, endothelium-dependent vasodilators, and atrial peptides on cGMP. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 53(Pt 2):1005–1009. https://doi.org/10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.115
Nagelhus EA, Ottersen OP (2013) Physiological roles of aquaporin-4 in brain. Physiol Rev 93:1543–1562. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00011.2013
Parnetti L, Gaetani L, Eusebi P, Paciotti S, Hansson O, El-Agnaf O, Mollenhauer B, Blennow K, Calabresi P (2019) CSF and blood biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 18:573–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30024-9
Patterson JR, Duffy MF, Kemp CJ, Howe JW, Collier TJ, Stoll AC, Miller KM, Patel P, Levine N, Moore DJ, Luk KC, Fleming SM, Kanaan NM, Paumier KL, El-Agnaf OMA, Sortwell CE (2019) Time course and magnitude of alpha-synuclein inclusion formation and nigrostriatal degeneration in the rat model of synucleinopathy triggered by intrastriatal α-synuclein preformed fibrils. Neurobiol Dis 130:104525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104525
Paumier KL, Luk KC, Manfredsson FP, Kanaan NM, Lipton JW, Collier TJ, Steece-Collier K, Kemp CJ, Celano S, Schulz E, Sandoval IM, Fleming S, Dirr E, Polinski NK, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Sortwell CE (2015) Intrastriatal injection of pre-formed mouse α-synuclein fibrils into rats triggers α-synuclein pathology and bilateral nigrostriatal degeneration. Neurobiol Dis 82:185–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.06.003
Prydz A, Stahl K, Zahl S, Skauli N, Skare Ø, Ottersen OP, Amiry-Moghaddam M (2020) Pro-Inflammatory Role of AQP4 in Mice Subjected to Intrastriatal Injections of the Parkinsonogenic. Toxin MPP Cells 9https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112418
Rainey-Smith SR, Mazzucchelli GN, Villemagne VL, Brown BM, Porter T, Weinborn M, Bucks RS, Milicic L, Sohrabi HR, Taddei K, Ames D, Maruff P, Masters CL, Rowe CC, Salvado O, Martins RN, Laws SM (2018) Genetic variation in Aquaporin-4 moderates the relationship between sleep and brain Aβ-amyloid burden. Transl Psychiatry 8:47. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-018-0094-x
Rasmussen MK, Mestre H, Nedergaard M (2018) The glymphatic pathway in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol 17:1016–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30318-1
Sacino AN, Brooks M, Thomas MA, McKinney AB, Lee S, Regenhardt RW, McGarvey NH, Ayers JI, Notterpek L, Borchelt DR, Golde TE, Giasson BI (2014) Intramuscular injection of α-synuclein induces CNS α-synuclein pathology and a rapid-onset motor phenotype in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:10732–10737. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1321785111
Shiotsuki H, Yoshimi K, Shimo Y, Funayama M, Takamatsu Y, Ikeda K, Takahashi R, Kitazawa S, Hattori N (2010) A rotarod test for evaluation of motor skill learning. J Neurosci Methods 189:180–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.03.026
Stoyka LE, Arrant AE, Thrasher DR, Russell DL, Freire J, Mahoney CL, Narayanan A, Dib AG, Standaert DG, Volpicelli-Daley LA (2020) Behavioral defects associated with amygdala and cortical dysfunction in mice with seeded α-synuclein inclusions. Neurobiol Dis 134:104708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104708
Tarasoff-Conway JM, Carare RO, Osorio RS, Glodzik L, Butler T, Fieremans E, Axel L, Rusinek H, Nicholson C, Zlokovic BV, Frangione B, Blennow K, Ménard J, Zetterberg H, Wisniewski T, de Leon MJ (2015) Clearance systems in the brain-implications for Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 11:457–470. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2015.119
Thenral ST, Vanisree AJ (2012) Peripheral assessment of the genes AQP4, PBP and TH in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Res 37:512–515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0637-5
Thomsen MB, Ferreira SA, Schacht AC, Jacobsen J, Simonsen M, Betzer C, Jensen PH, Brooks DJ, Landau AM, Romero-Ramos M (2021) PET imaging reveals early and progressive dopaminergic deficits after intra-striatal injection of preformed alpha-synuclein fibrils in rats. Neurobiol Dis 149:105229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2020.105229
Uemura N, Yagi H, Uemura MT, Hatanaka Y, Yamakado H, Takahashi R (2018) Inoculation of α-synuclein preformed fibrils into the mouse gastrointestinal tract induces Lewy body-like aggregates in the brainstem via the vagus nerve. Mol Neurodegener 13:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-018-0257-5
Volpicelli-Daley LA, Luk KC, Patel TP, Tanik SA, Riddle DM, Stieber A, Meaney DF, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2011) Exogenous α-synuclein fibrils induce Lewy body pathology leading to synaptic dysfunction and neuron death. Neuron 72:57–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.08.033
Wang L-Y, Yu X, Li X-X, Zhao Y-N, Wang C-Y, Wang Z-Y, He Z-Y (2019) Catalpol exerts a neuroprotective effect in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 11:316. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2019.00316
Wang X-J, Ma M-M, Zhou L-B, Jiang X-Y, Hao M-M, Teng RKF, Wu E, Tang B-S, Li J-Y, Teng J-F, Ding X-B (2020) Autonomic ganglionic injection of α-synuclein fibrils as a model of pure autonomic failure α-synucleinopathy. Nat Commun 11:934. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14189-9
Xie L, Kang H, Xu Q, Chen MJ, Liao Y, Thiyagarajan M, O’Donnell J, Christensen DJ, Nicholson C, Iliff JJ, Takano T, Deane R, Nedergaard M (2013) Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science 342:373–377. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241224
Xue X, Zhang W, Zhu J, Chen X, Zhou S, Xu Z, Hu G, Su C (2019) Aquaporin-4 deficiency reduces TGF-β1 in mouse midbrains and exacerbates pathology in experimental Parkinson’s disease. J Cell Mol Med 23:2568–2582. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14147
Zhang J, Yang B, Sun H, Zhou Y, Liu M, Ding J, Fang F, Fan Y, Hu G (2016) Aquaporin-4 deficiency diminishes the differential degeneration of midbrain dopaminergic neurons in experimental Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 614:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2015.12.057
Zou W, Pu T, Feng W, Lu M, Zheng Y, Du R, Xiao M, Hu G (2019a) Blocking meningeal lymphatic drainage aggravates Parkinson’s disease-like pathology in mice overexpressing mutated α-synuclein. Transl Neurodegener 8:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-019-0147-y
Zou S, Lan Y-L, Wang H, Zhang B, Sun Y-G (2019b) The potential roles of aquaporin 4 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurol Sci 40:1541–1549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-03877-5
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Springer Nature for the expert linguistic services provided.
Funding
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81671267).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Huili Cui, Hanliu and Danhao Xia.ChiQin. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Huili Cui, Haiyan Tian, Xinhui Zheng, and Wenkang Wang and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
All experimental performances were in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The research projects were approved by the Institutional Ethics Committees of the Zhengzhou University.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, H., Wang, W., Zheng, X. et al. Decreased AQP4 Expression Aggravates ɑ-Synuclein Pathology in Parkinson’s Disease Mice, Possibly via Impaired Glymphatic Clearance. J Mol Neurosci 71, 2500–2513 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01836-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01836-4