Abstract
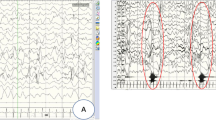
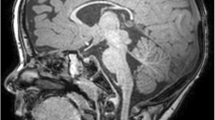
Mutations in the rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 9 gene (ARHGEF9) are present in patients with heterogeneous phenotypes including psychomotor developmental delay and variable degrees of epilepsy. Malfunction of collybistin (CB) encoded by ARHGEF9 leading to impaired clustering of gephyrin-dependent glycine receptors and γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAα) receptors is a crucial pathogenic mechanism. Here, we report on three patients with epilepsy and mental retardation. We studied three male patients with epilepsy and mild to moderate mental retardation. We conducted targeted panel sequencing of genes known to cause inherited disorders. In vitro studies and transcriptional experiments were performed to evaluate the functional and splicing effects of these variants on CB. Two novel missense variants (p.I294T and p.R357I) and one novel splicing variant (c.381+3A>G) in ARHGEF9 were identified in the three patients, respectively. In vitro studies confirmed that the two missense variants disrupted CB-mediated accumulation of gephyrin in submembrane microclusters. Transcriptional experiments of the splicing variant revealed the presence of aberrant transcripts leading to truncated protein product. Significance: Our cases and functional studies enrich our understanding of the phenotypic and genotypic spectrum of ARHGEF9.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alber M, Kalscheuer VM, Marco E, Sherr E, Lesca G, Till M, Gradek G, Wiesener A, Korenke C, Mercier S, Becker F, Yamamoto T, Scherer SW, Marshall CR, Walker S, Dutta UR, Dalal AB, Suckow V, Jamali P, Kahrizi K, Najmabadi H, Minassian BA (2017) ARHGEF9 disease: phenotype clarification and genotype-phenotype correlation. Neurol Genet 3:e148. https://doi.org/10.1212/NXG.0000000000000148
de Ligt J, Willemsen MH, van Bon BW, Kleefstra T, Yntema HG, Kroes T, Vulto-van Silfhout A, Koolen DA, de Vries P, Gilissen C, del Rosario M, Hoischen A, Scheffer H, de Vries BB, Brunner HG, Veltman JA, Vissers LE (2012) Diagnostic exome sequencing in persons with severe intellectual disability. N Engl J Med 367:1921–1929. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1206524
Grosskreutz Y, Hermann A, Kins S, Fuhrmann JC, Betz H, Kneussel M (2001) Identification of a gephyrin-binding motif in the GDP/GTP exchange factor collybistin. Biol Chem 382:1455–1462. https://doi.org/10.1515/BC.2001.179
Harvey K, Duguid IC, Alldred MJ, Beatty SE, Ward H, Keep NH, Lingenfelter SE, Pearce BR, Lundgren J, Owen MJ, Smart TG, Lüscher B, Rees MI, Harvey RJ (2004) The GDP-GTP exchange factor collybistin: an essential determinant of neuronal gephyrin clustering. J Neurosci 24:5816–5826. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1184-04.2004
Hu X, Li N, Xu Y, Li G, Yu T, Yao RE, Fu L, Wang J, Yin L, Yin Y, Wang Y, Jin X, Wang X, Wang J, Shen Y (2018) Proband-only medical exome sequencing as a cost-effective first-tier genetic diagnostic test for patients without prior molecular tests and clinical diagnosis in a developing country: the China experience. Genet Med 20:1045–1053. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2017.195
Jedlicka P, Papadopoulos T, Deller T, Betz H, Schwarzacher SW (2009) Increased network excitability and impaired induction of long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of collybistin-deficient mice in vivo. Mol Cell Neurosci 41:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2009.02.005
Kalscheuer VM, Musante L, Fang C et al (2009) A balanced chromosomal translocation disrupting ARHGEF9 is associated with epilepsy, anxiety, aggression, and mental retardation. Hum Mutat 30:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.20814
Kins S, Betz H, Kirsch J (2000) Collybistin, a newly identified brain-specific GEF, induces submembrane clustering of gephyrin. Nat Neurosci 3:22–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/71096
Klein KM, Pendziwiat M, Eilam A, Gilad R, Blatt I, Rosenow F, Kanaan M, Helbig I, Afawi Z; Israeli-Palestinian Epilepsy Family Consortium (2017) The phenotypic spectrum of ARHGEF9 includes intellectual disability, focal epilepsy and febrile seizures. J Neurol 264:1421–1425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-017-8539-3
Lionel AC, Vaags AK, Sato D, Gazzellone MJ, Mitchell EB, Chen HY, Costain G, Walker S, Egger G, Thiruvahindrapuram B, Merico D, Prasad A, Anagnostou E, Fombonne E, Zwaigenbaum L, Roberts W, Szatmari P, Fernandez BA, Georgieva L, Brzustowicz LM, Roetzer K, Kaschnitz W, Vincent JB, Windpassinger C, Marshall CR, Trifiletti RR, Kirmani S, Kirov G, Petek E, Hodge JC, Bassett AS, Scherer SW (2013) Rare exonic deletions implicate the synaptic organizer Gephyrin (GPHN) in risk for autism, schizophrenia and seizures. Hum Mol Genet 22:2055–2066. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt056
Long P, May MM, James VM, Grannò S, Johnson JP, Tarpey P, Stevenson RE, Harvey K, Schwartz CE, Harvey RJ (2016) Missense mutation R338W in ARHGEF9 in a family with X-linked intellectual disability with variable macrocephaly and macro-orchidism. Front Mol Neurosci 8:83. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2015.00083
Machado CO, Griesi-Oliveira K, Rosenberg C, Kok F, Martins S, Passos-Bueno MR, Sertie AL (2016) Collybistin binds and inhibits mTORC1 signaling: a potential novel mechanism contributing to intellectual disability and autism. Eur J Hum Genet 24:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2015.69
Papadopoulos T, Schemm R, Grubmüller H, Brose N (2015) Lipid binding defects and perturbed synaptogenic activity of a Collybistin R290H mutant that causes epilepsy and intellectual disability. J Biol Chem 290:8256–8270. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.633024
Papadopoulos T, Soykan T (2011) The role of collybistin in gephyrin clustering at inhibitory synapses: facts and open questions. Front Cell Neurosci 5:11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2011.00011
Poulopoulos A, Aramuni G, Meyer G, Soykan T, Hoon M, Papadopoulos T, Zhang M, Paarmann I, Fuchs C, Harvey K, Jedlicka P, Schwarzacher SW, Betz H, Harvey RJ, Brose N, Zhang W, Varoqueaux F (2009) Neuroligin 2 drives postsynaptic assembly at perisomatic inhibitory synapses through gephyrin and collybistin. Neuron 63:628–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2009.08.023
Reddy-Alla S, Schmitt B, Birkenfeld J, Eulenburg V, Dutertre S, Böhringer C, Götz M, Betz H, Papadopoulos T (2010) PH-domain-driven targeting of collybistin but not Cdc42 activation is required for synaptic gephyrin clustering. Eur J Neurosci 31:1173–1184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07149.x
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2089
Stenson PD, Ball EV, Mort M, Phillips AD, Shiel JA, Thomas NS, Abeysinghe S, Krawczak M, Cooper DN (2003) Human gene mutation database (HGMD): 2003 update. Hum Mutat 21:577–581. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.10212
Soykan T, Schneeberger D, Tria G, Buechner C, Bader N, Svergun D, Tessmer I, Poulopoulos A, Papadopoulos T, Varoqueaux F, Schindelin H, Brose N (2014) A conformational switch in collybistin determines the differentiation of inhibitory postsynapses. EMBO J 33:2113–2133. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201488143
Stelzer G, Plaschkes I, Oz-Levi D et al (2016) VarElect: the phenotype-based variation prioritizer of the GeneCards Suite. BMC Genomics 17 Suppl 2:444. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2722-2
Xiang S, Kim EY, Connelly JJ, Nassar N, Kirsch J, Winking J, Schwarz G, Schindelin H (2006) The crystal structure of Cdc42 in complex with collybistin II, a gephyrin-interacting guanine nucleotide exchange factor. J Mol Biol 359:35–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.03.019
Acknowledgments
We thank all the members of the family for their participation in this study.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81873984, 181772303), the Project of Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission (Grant No. 16ZR1421700), the young talents training program of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (Grant No. 2018YQ24), “Shuguang Program” of Shanghai Education Development Foundation and Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. 18SG14), and the Project of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission-Gaofeng Clinical Medicine (Grant No. 20152529).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee at Shanghai Children’s Medical Center (SCMCIRB-Y2019021) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the parents of all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key Points
•Three novel variants in ARHGEF9 were identified in three patients with epilepsy and mental retardation.
•The two missense variants in ARHGEF9 disrupted collybistin-mediated accumulation of gephyrin in submembrane microclusters.
•The splicing variant in ARHGEF9 resulted in various aberrant ARHGEF9 transcripts.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, R., Zhang, Y., Liu, J. et al. Clinical and Molecular Characterization of Three Novel ARHGEF9 Mutations in Patients with Developmental Delay and Epilepsy. J Mol Neurosci 70, 908–915 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01465-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01465-y