Abstract
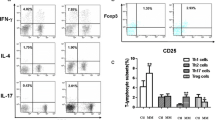
The imbalance in Th17/Treg cell-related responses plays an important role in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis (MS). The development of Th17- and Treg cells is regulated by specific transcription factors—RORγt and RORα—and FOXP3, respectively. The aim was to determine the expression of RORγt, RORα, and FOXP3 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from MS patients following in vitro stimulation. The PBMCs from 22 MS patients and 20 healthy subjects were cultured in the presence of 10 μg/ml MOG, 10 μg/ml PHA, or without stimulation. The PBMCs were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h, and then the messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of RORγt, RORα, and FOXP3 was determined by real-time PCR. The expression of RORγt and RORα was increased in non-stimulated, MOG-stimulated, and PHA-stimulated PBMCs from MS patients in comparison with same cultures from the healthy group (P < 0.01, P < 0.01, and P < 0.02 for RORγt; P < 0.001, P < 0.001, and P < 0.05, for RORα, respectively). The FOXP3 expression in non-stimulated PBMCs from MS patients was significantly lower than that in equal culture from healthy subjects (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences between healthy subjects and MS patients regarding the expression of FOXP3 mRNA by MOG-stimulated and PHA-stimulated PBMCs. These results showed an imbalance in Th17/Treg cells at transcription factor levels with a deviation toward Th17 cell in MS. The correction of Th17/Treg balance at transcription levels should be considered to design novel therapeutic strategies for MS treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu R, Hatton RD, Weaver CT (2013) The Th17 family: flexibility follows function. Immunol Rev 252:89–103
Becher B, Segal BM (2011) T(H)17 cytokines in autoimmune neuro-inflammation. Curr Opin Immunol 23:707–712
Bedoya SK, Lam B, Lau K, Larkin J 3rd (2013) Th17 cells in immunity and autoimmunity. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:986789
Buc M (2013) Role of regulatory T cells in pathogenesis and biological therapy of multiple sclerosis. Mediators Inflamm 2013:963748
Chen YC, Yang X, Miao L, Liu ZG, Li W, Zhao ZX, Sun XJ, Jiang GX, Chen SD, Cheng Q (2012) Serum level of interleukin-6 in Chinese patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 249:109–111
Edstrom M, Mellergard J, Mjosberg J, Jenmalm M, Vrethem M, Press R, Dahle C, Ernerudh J (2011) Transcriptional characteristics of CD4+ T cells in multiple sclerosis: relative lack of suppressive populations in blood. Mult Scler 17:57–66
Floss DM, Schroder J, Franke M, Scheller J (2015) Insights into IL-23 biology: from structure to function. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 26:569–578
Ichiyama K, Yoshida H, Wakabayashi Y, Chinen T, Saeki K, Nakaya M, Takaesu G, Hori S, Yoshimura A, Kobayashi T (2008) Foxp3 inhibits RORgammat-mediated IL-17A mRNA transcription through direct interaction with RORgammat. J Biol Chem 283:17003–17008
Ivanova EA, Orekhov AN (2015) T helper lymphocyte subsets and plasticity in autoimmunity and cancer: an overview. Biomed Res Int 2015:327470
Jafarzadeh A, Bagherzadeh S, Ebrahimi HA, Hajghani H, Bazrafshani MR, Khosravimashizi A, Nemati M, Gadari F, Sabahi A, Iranmanesh F, Mohammadi MM, Daneshvar H (2014a) Higher circulating levels of chemokine CCL20 in patients with multiple sclerosis: evaluation of the influences of chemokine gene polymorphism, gender, treatment and disease pattern. J Mol Neurosci 53:500–505
Jafarzadeh A, Ebrahimi HA, Bagherzadeh S, Zarkesh F, Iranmanesh F, Najafzadeh A, Khosravimashizi A, Nemati M, Sabahi A, Hajghani H, Daneshvar H, Mohammadi MM (2014b) Lower serum levels of Th2-related chemokine CCL22 in women patients with multiple sclerosis: a comparison between patients and healthy women. Inflammation 37:604–610
Jafarzadeh A, Jamali M, Mahdavi R, Ebrahimi HA, Hajghani H, Khosravimashizi A, Nemati M, Najafipour H, Sheikhi A, Mohammadi MM, Daneshvar H (2015) Circulating levels of interleukin-35 in patients with multiple sclerosis: evaluation of the influences of FOXP3 gene polymorphism and treatment program. J Mol Neurosci 55:891–897
Jamshidian A, Kazemi M, Shaygannejad V, Salehi M (2015) The effect of plasma exchange on the expression of FOXP3 and RORC2 in relapsed multiple sclerosis patients. Iran J Immunol 12:311–318
Kostic M, Dzopalic T, Zivanovic S, Zivkovic N, Cvetanovic A, Stojanovic I, Vojinovic S, Marjanovic G, Savic V, Colic M (2014) IL-17 and glutamate excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Scand J Immunol 79:181–186
Kostic M, Stojanovic I, Marjanovic G, Zivkovic N, Cvetanovic A (2015) Deleterious versus protective autoimmunity in multiple sclerosis. Cell Immunol 296:122–132
Lin ZW, Wu LX, Xie Y, Ou X, Tian PK, Liu XP, Min J, Wang J, Chen RF, Chen YJ, Liu C, Ye H, Ou QJ (2015) The expression levels of transcription factors T-bet, GATA-3, RORgammat and FOXP3 in peripheral blood lymphocyte (PBL) of patients with liver cancer and their significance. Int J Med Sci 12:7–16
Mahad DH, Trapp BD, Lassmann H (2015) Pathological mechanisms in progressive multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 14:183–193
Martinez NE, Sato F, Omura S, Kawai E, Takahashi S, Yoh K, Tsunoda I (2014) RORgammat, but not T-bet, overexpression exacerbates an autoimmune model for multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 276:142–149
McDonald WI, Compston A, Edan G, Goodkin D, Hartung HP, Lublin FD, McFarland HF, Paty DW, Polman CH, Reingold SC, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Sibley W, Thompson A, van den Noort S, Weinshenker BY, Wolinsky JS (2001) Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 50:121–127
Mirshafiey A, Asghari B, Ghalamfarsa G, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Azizi G (2014) The significance of matrix metalloproteinases in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of multiple sclerosis. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J 14:e13–e25
Murphy KM, Stockinger B (2010) Effector T cell plasticity: flexibility in the face of changing circumstances. Nat Immunol 11:674–680
Nie J, Li YY, Zheng SG, Tsun A, Li B (2015) FOXP3(+) treg cells and gender bias in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol 6:493
Noack M, Miossec P (2014) Th17 and regulatory T cell balance in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun Rev 13:668–677
Raphael I, Nalawade S, Eagar TN, Forsthuber TG (2015) T cell subsets and their signature cytokines in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine 74:5–17
Rathore JS, Wang Y (2016) Protective role of Th17 cells in pulmonary infection. Vaccine 34:1504–1514
Rodriguez-Perea AL, Arcia ED, Rueda CM and Velilla PA (2016) Phenotypic characterization of regulatory T cells in humans and rodents. Clin Ex Immunol doi: 10.1111/cei.12804. in press.
Shichita T, Sugiyama Y, Ooboshi H, Sugimori H, Nakagawa R, Takada I, Iwaki T, Okada Y, Iida M, Cua DJ, Iwakura Y, Yoshimura A (2009) Pivotal role of cerebral interleukin-17-producing gammadeltaT cells in the delayed phase of ischemic brain injury. Nat Med 15:946–950
Volpe E, Battistini L, Borsellino G (2015) Advances in T helper 17 cell biology: pathogenic role and potential therapy in multiple sclerosis. Mediators Inflamm 2015:475158
Wang X, Ma C, Wu J, Zhu J (2013) Roles of T helper 17 cells and interleukin-17 in neuroautoimmune diseases with emphasis on multiple sclerosis and Guillain-Barre syndrome as well as their animal models. J Neurosci Res 91:871–881
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Gu W, He L, Sun B (2014) Th1/Th2 cell’s function in immune system. Adv Exp Med Biol 841:45–65
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Neurology Research Center, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Etesam, Z., Nemati, M., Ebrahimizadeh, MA. et al. Altered Expression of Specific Transcription Factors of Th17 (RORγt, RORα) and Treg Lymphocytes (FOXP3) by Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. J Mol Neurosci 60, 94–101 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0789-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0789-5