Abstract
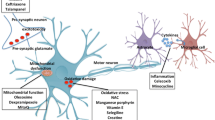
The 150-year-long search for treatments of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is still fueled by frustration over the shortcomings of available therapeutics. Contributing to the therapeutic limitations might be the targeting of a single aspect of this multifactorial-multisystemic disease. In an attempt to overcome this, we devised a novel multifactorial-cocktail treatment, using lentiviruses encoding: EAAT2, GDH2, and NRF2, that act synergistically to address the band and width of the effected excito-oxidative axis, reducing extracellular-glutamate and glutamate availability while improving the metabolic state and the anti-oxidant response. This strategy yielded particularly impressive results, as all three genes together but not separately prolonged survival in ALS mice by an average of 19–22 days. This was accompanied by improvement in every parameter evaluated, including body-weight loss, reflex score, neurologic score, and motor performance. We hope to provide a novel strategy to slow down disease progression and alleviate symptoms of patients suffering from ALS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azzouz M, Ralph G, Storkebaum E et al (2004) VEGF delivery with retrogradely transported lentivector prolongs survival in a mouse ALS model. Nature 429:413–417
Barber S, Shaw P (2010) Oxidative stress in ALS: key role in motor neuron injury and therapeutic target. Free Radic Biol Med 48:629–641
Bendotti C, Carri M (2004) Lessons from models of SOD1-linked familial ALS. Trends Mol Med 10:393–400
Benkler C, Ben Zur T, Barhum Y, Offen D (2013a) Altered astrocytic response to activation in SOD1(G93A) mice and its implications on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathogenesis. Glia 61:312–326
Benkler C, Offen D, Melamed E, et al. (2013b) Advances in predictive, preventive and personalised medicine, Chapter: Recent advances in ALS research: perspectives for personalized clinical application. Business Media Dordrecht
Bensimon G, Lacomblez L, Meininger V (1994) A controlled trial of riluzole in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. ALS/Riluzole Study Group. N Engl J Med 330:585–591
Bialer M (2012) Chemical properties of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:887–895
Boillée S, Vande Velde C, Cleveland D (2006) ALS: a disease of motor neurons and their nonneuronal neighbors. Neuron 52:39–59
Brambilla L, Martorana F, Rossi D (2013) Astrocyte signaling and neurodegeneration: new insights into CNS disorders. Prion 7:28–36
Calkins M, Vargas M, Johnson D, Johnson J (2010) Astrocyte-specific overexpression of Nrf2 protects striatal neurons from mitochondrial complex II inhibition. Toxicol Sci 115:557–568
Cashman N, Durham H, Blusztajn J et al (1992) Neuroblastoma x spinal cord (NSC) hybrid cell lines resemble developing motor neurons. Dev Dyn 194:209–221
Charles T, Swash M (2001) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: current understanding. J Neurosci Nurs 33:245–253
Coyle J, Puttfarcken P (1993) Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 262:689–695
Cozzolino M, Ferri A, Carri M (2008) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: from current developments in the laboratory to clinical implications. Antioxid Redox Signal 10:405–443
Cronin S, Berger S, Ding J et al (2008) A genome-wide association study of sporadic ALS in a homogenous Irish population. Hum Mol Genet 17:768–774
de Carvalho M, Pinto S, Costa J, Evangelista T, Ohana B, Pinto A (2010) A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of memantine for functional disability in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 11:456–460
Eggett C, Crosier S, Manning P et al (2000) Development and characterisation of a glutamate-sensitive motor neurone cell line. J Neurochem 74:1895–1902
Gordon P, Moore D, Miller R et al (2007) Efficacy of minocycline in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a phase III randomised trial. Lancet Neurol 6:1045–1053
Guo H, Lai L, Butchbach M et al (2003) Increased expression of the glial glutamate. Hum Mol Genet 12:2519–2532
Gurney M, Pu H, Chiu A et al (1994) Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science 264:1772–1775
Heath P, Shaw P (2002) Update on the glutamatergic neurotransmitter system and the role of excitotoxicity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 26:438–458
Howland D, Liu J, She Y et al (2002) Focal loss of the glutamate transporter EAAT2 in a transgenic rat model of SOD1 mutant-mediated amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:1604–1609
Hybertson B, Gao B, Bose S, McCord J (2011) Oxidative stress in health and disease: the therapeutic potential of Nrf2 activation. HYPERLINK “http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Hybertson+B%2C+Gao+B%2C+Bose+S.+and+McCord+J.+(2011)” \o “Molecular aspects of medicine.” Mol Aspects Med 32:234–246
Ilieva H, Polymenidou M, Cleveland D (2009) Non-cell autonomous toxicity in neurodegenerative disorders: ALS and beyond. J Cell Biol 187:761–772
Kaspar B, Llado J, Sherkat N, Rothstein J, Gage F (2003) Retrograde viral delivery of IGF-1 prolongs survival in a mouse ALS model. Science 301:839–842
Kruman I, Pedersen W, Springer J, Mattson M (1999) ALS-linked Cu/Zn-SOD mutation increases vulnerability of motor neurons to excitotoxicity by a mechanism involving increased oxidative stress and perturbed calcium homeostasis. Exp Neurol 160:28–39
Lacomblez L, Bensimon G, Leigh P, Guillet P, Meininger V (1996) Dose-ranging study of riluzole in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis/Riluzole Study Group II. Lancet 347:1425–1431
Mastorodemos V, Zaganas I, Spanaki C, Bessa M, Plaitakis A (2005) Molecular basis of human glutamate dehydrogenase regulation under changing energy demands. HYPERLINK “http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Mastorodemos+V%2C+Zaganas+I%2C+Spanaki+C%2C+Bessa+M.+and+Plaitakis+A.+(2005)” \o “Journal of neuroscience research.” J Neurosci Res 79:65–73
Matusica D, Fenech M, Rogers M, Rush R (2008) Characterization and use of the NSC-34 cell line for study of neurotrophin receptor trafficking. J Neurosci Res 86:553–565
Nagai M, Re D, Nagata T et al (2007) Astrocytes expressing ALS-linked mutated SOD1 release factors selectively toxic to motor neurons. Nat Neurosci 10:615–622
Oliveira A, Pereira R (2009) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): three letters that change the people’s life. For ever. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 67:750–782
Orrell R, Lane R, Ross M (2007) Antioxidant treatment for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neuron disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD002829
Palmada M, Centelles J (1998) Excitatory amino acid neurotransmission. Pathways for metabolism, storage and reuptake of glutamate in brain. Front Biosci 20(3):d701–d718
Pekny M, Nilsson M (2005) Astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis. Glia 50:427–434
Plaitakis A, Zaganas I (2001) Regulation of human glutamate dehydrogenases: implications for glutamate, ammonia and energy metabolism in brain. J Neurosci Res 66:899–908
Polymenidou M, Cleveland D (2011) The seeds of neurodegeneration: prion-like spreading in ALS. Cell 147:498–508
Ralph G, Radcliffe P, Day D et al (2005) Silencing mutant SOD1 using RNAi protects against neurodegeneration and extends survival in an ALS model. Nat Med 11:429–433
Rosen D, Siddique T, Patterson D et al (1993) Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 362:59–62
Rothstein J (2009) Current hypotheses for the underlying biology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 65(Suppl 1):S3–S9
Rothstein J, Van Kammen M, Levey A, Martin L, Kuncl R (1995) Selective loss of glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 38:73–84
Rothstein J, Dykes-Hoberg M, Pardo C et al (1996) Knockout of glutamate transporters reveals a major role for astroglial transport in excitotoxicity and clearance of glutamate. Neuron 16:675–686
Rothstein J, Patel S, Regan M et al (2005) Beta-lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nature 433:73–77
Spanaki C, Zaganas I, Kleopa K, Plaitakis A (2010) Human GLUD2 glutamate dehydrogenase is expressed in neural and testicular supporting cells. J Biol Chem 285:16748–16756
Suzuki M, McHugh J, Tork C et al (2008) Direct muscle delivery of GDNF with human mesenchymal stem cells improves motor neuron survival and function in a rat model of familial ALS. Mol Ther 16:2002–2010
Turner B, Talbot K (2008) Transgenics, toxicity and therapeutics in rodent models of mutant SOD-1-mediated familial ALS. Prog Neurobiol 85:94–134
Van Damme P, Dewil M, Robberecht W, Van Den Bosch L (2005) Excitotoxicity and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurodegener Dis 2:147–159
Van Den Bosch L, Robberecht W (2008) Crosstalk between astrocytes and motor neurons: what is the message? Exp Neurol 211:1–6
Vargas M, Johnson J (2009) The Nrf2-ARE cytoprotective pathway in astrocytes. Expert Rev Mol Med 11:e17
Vargas M, Pehar M, Cassina P, Beckman J, Barbeito L (2006) Increased glutathione biosynthesis by Nrf2 activation in astrocytes prevents p75NTR-dependent motor neuron apoptosis. J Neurochem 97:687–696
Vargas M, Johnson D, Sirkis D, Messing A, Johnson J (2008) Nrf2 activation in astrocytes protects against neurodegeneration in mouse models of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci 28:13574–13581
Wan L, Sharma K, Grisotti G, Roos R (2009) The effect of mutant SOD1 dismutase activity on non-cell autonomous degeneration in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol Dis 35:234–240
Wang L, Lu Y, Muramatsu S et al (2002) Neuroprotective effects of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor mediated by an adeno-associated virus vector in a transgenic animal model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci 22:6920–6928
Weishaupt J, Bartels C, Pölking E et al (2006) Reduced oxidative damage in ALS by high-dose enteral melatonin treatment. J Pineal Res 41:313–323
Wong P, Pardo C, Borchelt D et al (1995) An adverse property of a familial ALS-linked SOD1 mutation causes motor neuron disease characterized by vacuolar degeneration of mitochondria. Neuron 14:1105–1116
Xiao S, McLean J, Robertson J (2006) Neuronal intermediate filaments and ALS: a new look at an old question. Biochim Biophys Acta 1762:1001–1012
Yamanaka K, Chun S, Boillee S et al (2008) Astrocytes as determinants of disease progression in inherited amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Neurosci 11:251–253
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The study was partially supported by Prize4life.
Conflict of Interest
D. O. is a consultant in Brainstorm Cell Therapeutics, Israel. C.B and D.O. have registered a patent on this issue. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Animal Care
The experiments were performed in accordance with local and international regulations, and were approved by the Tel Aviv University Ethical Committee. Every effort was made to reduce the number of animals used and to minimize their suffering.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benkler, C., Barhum, Y., Ben-Zur, T. et al. Multifactorial Gene Therapy Enhancing the Glutamate Uptake System and Reducing Oxidative Stress Delays Symptom Onset and Prolongs Survival in the SOD1-G93A ALS Mouse Model. J Mol Neurosci 58, 46–58 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0695-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0695-2