Abstract
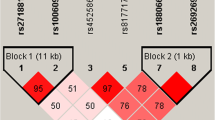
The tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) gene encodes a protein that acts downstream of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) pathway. TLRs activate inflammatory cascades and mediate inflammatory injury after cerebral ischemia. However, the role of TFAR6 gene polymorphisms in ischemic stroke (IS) remains unknown. This study aims to investigate the associations of TRAF6 gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to IS and IS-related quantitative traits in Southern Chinese Han population. A total of 816 IS cases and 816 age- and gender-matched controls were included. Two variants of the TRAF6 gene (rs5030411 and rs5030416) were genotyped using the Sequenom MassARRAY iPLEX platform. Our study showed that rs5030416 was significantly associated with increased susceptibility to IS in the additive model [ORadj 1.25(1.04–1.51), P adj = 0.019, P Bc = 0.038] and dominant model [ORadj 1.23(1.04–1.60), P adj = 0.021, P Bc = 0.042] after adjusting by age and sex and applying a Bonferroni correction. No significant association was found between rs5030411 and IS susceptibility (all P > 0.05). The haplotype rs5030416 (allele C)-rs5030411 (allele C) was significantly associated with IS susceptibility (P adj = 0.015). Moreover, a significant association of rs5030411 with TC levels in IS patients under the additive model [β 0.16(0.01–0.30), P adj = 0.034] and recessive model [β 0.45(0.12–0.78), P adj = 0.007] was observed after adjustment by age and sex. This association remained statistically significant under the recessive model (P Bc = 0.042) after Bonferroni correction. Our results suggest that TRAF6 gene polymorphisms may be involved in the pathogenesis of IS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4(7):499–511
Bak S, Gaist D, Sindrup SH, Skytthe A, Christensen K (2002) Genetic liability in stroke: a long-term follow-up study of Danish twins. Stroke 33(3):769–74
Bonita R (1992) Epidemiology of stroke. Lancet 339(8789):342–4
Bradley JR, Pober JS (2001) Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs). Oncogene 20(44):6482–91
Brass LM, Isaacsohn JL, Merikangas KR, Robinette CD (1992) A study of twins and stroke. Stroke 23(2):221–3
Cao Z, Xiong J, Takeuchi M, Kurama T, Goeddel DV (1996) TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1. Nature 383(6599):443–6
Caso JR, Pradillo JM, Hurtado O, Lorenzo P, Moro MA, Lizasoain I (2007) Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in brain damage and inflammation after experimental stroke. Circulation 115(12):1599–608
Cruchaga C, Kauwe JS, Harari O et al (2013) GWAS of cerebrospinal fluid tau levels identifies risk variants for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 78(2):256–68
Cui X, Chen H, Hou X, Wang S, Jayaram S, Zheng Z (2013) Polymorphism of the RAGE affects the serum inflammatory levels and risk of ischemic stroke in a Chinese population. Cell Physiol Biochem 32(4):986–96
Dichgans M (2007) Genetics of ischaemic stroke. Lancet Neurol 6(2):149–61
Dirnagl U, Iadecola C, Moskowitz MA (1999) Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci 22(9):391–7
Feigin VL, Lawes CM, Bennett DA, Anderson CS (2003) Stroke epidemiology: a review of population-based studies of incidence, prevalence, and case-fatality in the late 20th century. Lancet Neurol 2(1):43–53
Hachinski V (2002) Stroke: the next 30 years. Stroke 33(1):1–4
Hankey GJ (2006) Potential new risk factors for ischemic stroke: what is their potential? Stroke 37(8):2181–8
Hill-Burns EM, Wissemann WT, Hamza TH, Factor SA, Zabetian CP, Payami H (2014) Identification of a novel Parkinson’s disease locus via stratified genome-wide association study. BMC Genomics 15:118
Holliday EG, Maguire JM, Evans TJ et al (2012) Common variants at 6p21.1 are associated with large artery atherosclerotic stroke. Nat Genet 44(10):1147–51
Humphries SE, Morgan L (2004) Genetic risk factors for stroke and carotid atherosclerosis: insights into pathophysiology from candidate gene approaches. Lancet Neurol 3(4):227–35
Ishida T, Mizushima S, Azuma S et al (1996) Identification of TRAF6, a novel tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor protein that mediates signaling from an amino-terminal domain of the CD40 cytoplasmic region. J Biol Chem 271(46):28745–8
Jerrard-Dunne P, Cloud G, Hassan A, Markus HS (2003) Evaluating the genetic component of ischemic stroke subtypes: a family history study. Stroke 34(6):1364–9
Kim JS (2014) Stroke in Asia: a global disaster. Int J Stroke 9(7):856–7
Li Y, Cui LL, Li QQ et al (2014) Association between ADAM17 promoter polymorphisms and ischemic stroke in a Chinese population. J Atheroscler Thromb 21(8):878–93
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K et al (2012) Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380(9859):2095–128
Lu JX, Lu ZQ, Zhang SL, Zhi J, Chen ZP, Wang WX (2014) Polymorphism in Integrin ITGA2 is Associated with Ischemic Stroke and Altered Serum Cholesterol in Chinese Individuals. Balkan Med J 31(1):55–9
Luo S, Wang F, Li Z, Deng J (2013) Effect of the +781C/T polymorphism in the interleukin-8 gene on atherosclerotic cerebral infarction, and its interaction with smoking and drinking. PLoS One 8(11):e80246
Markus HS, Labrum R, Bevan S et al (2006) Genetic and acquired inflammatory conditions are synergistically associated with early carotid atherosclerosis. Stroke 37(9):2253–9
Markus HS (2011) Stroke genetics. Hum Mol Genet 20(R2):R124–31
Miyahara T, Koyama H, Miyata T et al (2004) Inflammatory signaling pathway containing TRAF6 contributes to neointimal formation via diverse mechanisms. Cardiovasc Res 64(1):154–64
Moghimpour Bijani F, Vallejo JG, Rezaei N (2012) Toll-like receptor signaling pathways in cardiovascular diseases: challenges and opportunities. Int Rev Immunol 31(5):379–95
Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R et al (2012) Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380(9859):2197–223
Muzio M, Natoli G, Saccani S, Levrero M, Mantovani A (1998) The human toll signaling pathway: divergence of nuclear factor kappaB and JNK/SAPK activation upstream of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6). J Exp Med 187(12):2097–101
Namjou B, Choi CB, Harley IT et al (2012) Evaluation of TRAF6 in a large multiancestral lupus cohort. Arthritis Rheum 64(6):1960–9
Sacco RL, Ellenberg JH, Mohr JP et al (1989) Infarcts of undetermined cause: the NINCDS Stroke Data Bank. Ann Neurol 25(4):382–90
Song HY, Regnier CH, Kirschning CJ, Goeddel DV, Rothe M (1997) Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated kinase cascades: bifurcation of nuclear factor-kappaB and c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK/SAPK) pathways at TNF receptor-associated factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(18):9792–6
Song Y, Long Y, Long L, Zhang N, Liu Y (2014) Polymorphism Ala54Thr of fatty acid-binding protein 2 gene is not associated with stroke risk in Han population of Hunan China. Med Sci Monit 20:1751–7
Traylor M, Farrall M, Holliday EG et al (2012) Genetic risk factors for ischaemic stroke and its subtypes (the METASTROKE collaboration): a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol 11(11):951–62
Vasiliadis AV, Zikic M (2014) Current status of stroke epidemiology in Greece: a panorama. Neurol Neurochir Pol 48(6):449–457
Wang YC, Lin S, Yang QW (2011) Toll-like receptors in cerebral ischemic inflammatory injury. J Neuroinflammation 8:134
Wu D, Lee YC, Liu HC et al (2013) Identification of TLR downstream pathways in stroke patients. Clin Biochem 46(12):1058–64
Wu H, Arron JR (2003) TRAF6, a molecular bridge spanning adaptive immunity, innate immunity and osteoimmunology. Bioessays 25(11):1096–105
Xue H, Wang H, Song X et al (2009) Phosphodiesterase 4D gene polymorphism is associated with ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke. Clin Sci (Lond) 116(4):335–40
Ye H, Arron JR, Lamothe B et al (2002) Distinct molecular mechanism for initiating TRAF6 signalling. Nature 418(6896):443–7
Yuan P, Liu Z, Liu M, Huang J, Li X, Zhou X (2013) Up-regulated tumor necrosis factor-associated factor 6 level is correlated with apoptosis in the rat cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Neurol Sci 34(7):1133–8
Zhao N, Liu X, Wang Y et al (2012) Association of inflammatory gene polymorphisms with ischemic stroke in a Chinese Han population. J Neuroinflammation 9:162
Acknowledgments
Our study is supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81473670 and 81260594), the Guangxi National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2013GXNSFAA019145), and the Scientific Research Foundation of the Guangxi Health Department (Grant No. 2012047).
Conflict of Interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Li Su, Ziwen Chen, and Yan Yan were the first coauthors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 41 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, L., Chen, Z., Yan, Y. et al. Association Between TRAF6 Gene Polymorphisms and Susceptibility of Ischemic Stroke in Southern Chinese Han Population. J Mol Neurosci 57, 386–392 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0580-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0580-z