Abstract
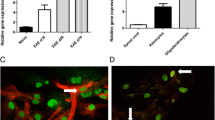
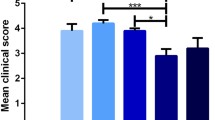
Ecto-5′-nucleotidase/cluster of differentiation 73 (CD73) (eN) is a 70-kDa glycoprotein expressed in several different mammalian tissues and cell types. It is the rate-limiting enzyme of the purine catabolic pathway, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of AMP to produce adenosine with known anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive actions. There is strong evidence for lymphocyte and endothelial cell eN having a role in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), but the role of eN in cell types within the central nervous system is less clear. We have previously shown that eN activity significantly increased in the lumbar spinal cord during EAE. The present study is aimed to explore molecular pattern of the eN upregulation over the course of the disease and cell type(s) accountable for the induction. EAE was induced in Dark Agouti (DA) rats by immunization with the spinal cord tissue homogenate and adjuvant. Animals were sacrificed 8, 15, and 28 days following immunization (D8, D15, and D28), i.e., at time points which corresponded to the presymptomatic, symptomatic, and postsymptomatic phases of the disease, respectively. Significant increase in eN activity and its upregulation at the gene and the protein levels were demonstrated at D15 and less prominently at D28 in comparison to control. Additionally, reactive astrocytes abundantly present in the lumbar spinal cord parenchyma were identified as principal cell type with significantly elevated eN expression. In all experimental groups, eN was expressed as a 71-kDa protein band of uniform abundance, whereas the overexpression of eN at D15 and D28 was associated with the expression of a second 75-kDa eN variant. The possible outcome of eN upregulation during EAE as a part of protective astrocyte repertoire contributing to the resolution of the disease is discussed.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- D:
-
Days after immunization
- EAE:
-
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- eN:
-
Ecto-5′-nucleotidase
- ENT:
-
Equilibrative nucleoside transporter
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- NTPDase:
-
Nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase
- Panx1:
-
pannexin 1
References
Airas L, Niemela J, Yegutkin GG, Jalkanen S (2007) Mechanism of action of IFN-β in the treatment of multiple sclerosis: a special reference to CD73 and adenosine. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1110:641–648
Aloisi F, Penna G, Cerase J, Menendez IB, Adorini L (1997) IL-12 production by central nervous system microglia is inhibited by astrocytes. J Immunol 159:1604–1612
Ascherio A, Munger KL (2007) Environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis. II. Noninfectious factors. Ann Neurol 61:504–513
Bjelobaba I, Parabucki A, Lavrnja I, Stojkov D, Dacic S, Pekovic S, Rakic L, Stojiljkovic M, Nedeljkovic N (2011) Dynamic changes in the expression pattern of ecto-5′-nucleotidase in the rat model of cortical stab injury. J Neurosci Res 89:862–873
Blazevski J, Petkovic F, Momcilovic M, Jevtic B, Miljkovic D, Mostarica-Stojkovic M (2013) High interleukin-10 expression within the central nervous system may be important for initiation of recovery of Dark Agouti rats from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunobiology 218:1192–1199
Bours MJ (2006) Adenosine 5′-triphosphate and adenosine as endogenous signaling molecules in immunity and inflammation. Pharmacol Ther 112:358–404
Braun N, Zhu Y, Krieglstein J, Culmsee C, Zimmermann H (1998) Upregulation of the enzyme chain hydrolyzing extracellular ATP after transient forebrain ischemia in the rat. J Neurosci 18:4891–4900
Brisevac D, Bjelobaba I, Bajic A, Clarner T, Stojiljkovic M, Beyer M, Andjus P, Kipp M, Nedeljkovic N (2012) Regulation of ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) in cultured cortical astrocytes by different inflammatory factors. Neurochem Int 61:681–688
Brück W (2005) The pathology of multiple sclerosis is the result of focal inflammatory demyelination with axonal damage. J Neurol 252S:v3–v9
Chen Y, Swanson RA (2003) Astrocytes and brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:137–149
Christensen LD (1996) No correlation between CD73 expression and ecto-5′-nucleotidase activity on blood mononuclear cells in vitro. Evidence of CD73 (ecto-5′-nucleotidase) on blood mononuclear cells with distinct antigenic properties. APMIS 10:126–134
Cuhna RA, Ribeiro JA (2000) ATP as a presynaptic modulator. Life Sci 68:119–137
Cunha RA, Brendel P, Zimmermann H, Ribeiro JA (2000) Immunologically distinct isoforms of ecto-5′-nucleotidase in nerve terminals of different areas of the rat hippocampus. J Neurochem 74:334–338
Dong Y, Benveniste EN (2001) Immune function of astrocytes. Glia 36:180–190
Eltzschig HK, Sitkovsky MV, Robson SC (2012) Purinergic signaling during inflammation. N Engl J Med 367:2322–2333
Eng LF, Gerstl B, Vanderhaeghen JJ (1970) A study of proteins in old multiple sclerosis plaques. Trans Am Soc Neurochem 1:42
Farina C, Aloisi F, Meinl E (2007) Astrocytes are active players in cerebral innate immunity. Trends Immunol 28:138–145
Fiebich BL, Akter S, Akundi RS (2014) The two-hit hypothesis for neuroinflammation: role of exogenous ATP in modulating inflammation in the brain. Front Cell Neurosci 8(260):1–11. doi:10.3389/fncel.2014.00260
Fini C, Amoresano A, Andolfo A, D’Auria S, Floridi A, Paolini S, Pucci P (2000) Mass spectrometry study of ecto-5′-nucleotidase from bull seminal plasma. Eur J Biochem 267:4978–4987
Franke H, Verkhratsky A, Burnstock G, Illes P (2012) Pathophysiology of astroglial purinergic signalling. Purinergic Signal 8:629–657
Garcia Redondo PA, Nakamura CV, de Souza W, Morgado–Díaz JA (2004) Differential expression of sialic acid and N-acetyl galactosamine residues on the cell surface of intestinal epithelial cells according to normal or metastatic potential. J Histochem Cytochem 52:629–640
Garcıa-Ayllon MS, Campoy FJ, Vidal CJ, Munoz-Delgado E (2001) Identification of inactive ecto-5′-nucleotidase in normal mouse muscle and its increased activity in dystrophic Lama2 dy mice. J Neurosci Res 66:656–665
Gray EG, Whittaker VP (1962) The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat 96:79–88
Grkovic I, Bjelobaba I, Nedeljkovic N, Mitrovic N, Drakulic D, Stanojlovic M, Horvat A (2014) Developmental increase in ecto-5′-nucleotidase activity overlaps with appearance of two immunologically distinct enzyme isoforms in rat hippocampal synaptic plasma membranes. J Mol Neurosci 54:109–118
Henttinen T, Jalkanen S, Yegutkin GG (2003) Adherent leukocytes prevent adenosine formation and impair endothelial barrier function by ecto-5′-nucleotidase/CD73-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 278:24888–24895
Hide I, Tanaka M, Inoue A, Nakajima K, Kohsaka S, Inoue K, Nakata Y (2000) Extracellular ATP triggers tumor necrosis factor-alpha release from rat microglia. J Neurochem 75:965–972
Hostenbach S, Cambron M, D’haeseleer M, Kooijman R, De Keyser J (2014) Astrocyte loss and astrogliosis in neuroinflammatory disorders. Neurosci Lett 565:39–41
Ingram G, Loveless S, Howell OW, Hakobyan S, Dancey B, Harris CL, Robertson NP, Neal JW, Morgan BP (2014) Complement activation in multiple sclerosis plaques: an immunohistochemical analysis. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2:53
John GR, Lee SC, Song X, Rivieccio M, Brosnan CF (2005) IL-1-regulated responses in astrocytes: relevance to injury and recovery. Glia 49:161–176
Jun S, Ochoa-Reparaz J, Zlotkowska D, Hoyt T, Pascual DW (2012) Bystander-mediated stimulation of proteolipid protein-specific regulatory T (Treg) cells confers protection against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) via TFG-β. J Neuroimmunol 245:39–47
Keegan BM, Noseworthy JH (2002) Multiple sclerosis. Annu Rev Med 53:285–302
Kobie JJ, Shah PR, Yang L, Rebhahn JA, Fowell DJ, Mosmann TR (2006) T regulatory and primed uncommitted CD4 T cells express CD73, which suppresses effector CD4 T cells by converting 5′-adenosine monophosphate to adenosine. J Immunol 177:6780–6786
Lassmann H, Bruck W, Lucchinetti CF (2007) The immunopathology of multiple sclerosis: an overview. Brain Pathol 17:210–218
Lavrnja I, Bjelobaba I, Stojiljkovic M, Pekovic S, Mostatica-Stojkovic M, Stosic-Grujicic S, Nedeljkovic N (2009) Time-course changes in ectonucleotidase activities during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurochem Int 55:193–198
Lavrnja I, Savic D, Bjelobaba I, Dacic S, Bozic I, Parabucki A, Nedeljkovic N, Pekovic S, Rakic L, Stojiljkovic M (2012) The effect of ribavirin on reactive astrogliosis in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Pharmacol Sci 119:221–232
Liedtke W, Edelmann W, Chiu FC, Kucherlapati R, Raine CS (1998) Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice lacking glial fibrillary acidic protein is characterized by a more severe clinical course and an infiltrative central nervous system lesion. Am J Pathol 152:251–259
Matute C (2011) Glutamate and ATP signalling in white matter pathology. J Anat 219:53–64
Mills JH, Thompson LF, Mueller C, Waickman AT, Jalkanen S, Niemela J, Airas L, Bynoe MS (2008) CD73 is required for efficient entry of lymphocytes into the central nervous system during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. PNAS 105:9325–9330
Mills JH, Alabanza LM, Mahamed DA, Bynoe MS (2012) Extracellular adenosine signaling induces CX3CL1 expression in the brain to promote experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroinflammation 9:193
Misumi Y, Ogata S, Hirose S, Ikehara Y (1990) Primary structure of rat liver 5′-nucleotidase deduced from the cDNA. Presence of the COOH-terminal hydrophobic domain for possible posttranslational modification by glycophospholipid. J Biol Chem 265:2178–2183
Morote-Garcia JC, Sanchez Del Campo LF, Campoy FJ, Vidal CJ, Munoz-Delgado E (2006) The increased ecto-5′-nucleotidase activity in muscle, heart and liver of laminin alpha2-deficient mice is not caused by an elevation in the mRNA content. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 38:1092–1101
Nair A, Frederick TJ, Miller SD (2008) Astrocytes in multiple sclerosis: a product of their environment. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:2702–2720
Navarro JM, Olmo N, Lopez-Conejo MT, Lizarbe MA (1998) Ecto-5′-nucleotidase from a human colon adenocarcinoma cell line. Correlation between enzyme activity and levels in intact cells. Mol Cell Biochem 187:121–131
Nedeljkovic N, Bjelobaba I, Subasic S, Lavrnja I, Pekovic S, Stojkov D, Vjestica A, Rakic L, Stojiljkovic M (2006) Upregulation of ectonucleotidase activity after cortical stab injury in rat. Cell Biol Int 30:541–546
Niemela J, Ifergan I, Yegutkin GG, Jalkanen S, Prat A, Airas L (2008) IFN-b regulates CD73 and adenosine expression at the blood–brain barrier. Eur J Immunol 38:2718–2726
Niino M, Fukazawa T, Kikuchi S, Sasaki H (2007) Recent advances in genetic analysis of multiple sclerosis: genetic associations and therapeutic implications. Expert Rev Neurother 7:1175–1188
Roth J, Zuber C, Park S, Jang I, Lee Y, Kysela KG, Le Fourn V, Santimaria R, Guhl B, Cho JW (2010) Protein N-glycosylation, protein folding, and protein quality control. Mol Cells 30:497–506
Serhan CN, Savill J (2005) Resolution of inflammation: the beginning programs the end. Nat Immunol 6:1191–1197
Thompson LF, Takedachi M, Ebisuno Y, Tanaka T, Miyasaka M, Mills JH, Bynoe MS (2008) Regulation of leukocyte migration across endothelial barriers by ecto-5′-nucleotidase-generated adenosine. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 27:755–760
Virgilio FD, Ceruti S, Bramanti P, Abbracchio MP (2009) Purinergic signalling in inflammation of the central nervous system. Trends Neurosci 32:79–87
Vogel M, Kowalewski HJ, Zimmermann H, Janetzko A, Margolis RU, Wollny HE (1991) Association of the HNK-1 epitope with 5′-nucleotidase from Torpedo marmorata (electric ray) electric organ. Biochem J 278:199–202
Voskuhl RR, Peterson S, Song B, Ao Y, Morales LBJ, Tiwari-Woodruff S, Sofroniew MV (2009) Reactive astrocytes form scar-like perivascular barriers to leukocytes during adaptive immune inflammation of the CNS. J Neurosci 29:11511–11522
Wada I, Himeno M, Furuno K, Kato K (1986) Biosynthesis and intracellular transport of rat liver 5′-nucleotidase. J Biol Chem 261:2222–2227
Warford J, Jones QR, Nichols M, Sullivan V, Rupasinghe HP, Robertson GS (2014) The flavonoid-enriched fraction AF4 suppresses neuroinflammation and promotes restorative gene expression in a mouse model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 268:71–83
Zhang Q, Cui F, Fang L, Hong J, Zheng B, Zhang JZ (2013) TNF-α impairs differentiation and function of TGF-β-induced Treg cells in autoimmune diseases through Akt and Smad3 signaling pathway. J Mol Cell Biol 5:85–98
Zimmermann H (1992) 5′-Nucleotidase—molecular structure and functional aspects. Biochem J 285:345–365
Zimmermann H (2000) Extracellular metabolism of ATP and other nucleotides. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 362:299–309
Zimmermann H, Braun N (1999) Ecto-nucleotidases: molecular structures, catalytic properties, and functional roles in the nervous system. Prog Brain Res 120:371–385
Zimmermann H, Zebisch M, Strater N (2012) Cellular functions and molecular structure of ecto-nucleotidases. Purinergic Signal 8:437–502
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia, Project No. III41014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Irena Lavrnja and Danijela Laketa contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lavrnja, I., Laketa, D., Savic, D. et al. Expression of a Second Ecto-5′-Nucleotidase Variant Besides the Usual Protein in Symptomatic Phase of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J Mol Neurosci 55, 898–911 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0445-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0445-x