Abstract
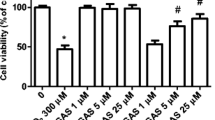
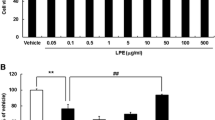
Magnolol, an orally available compound from Magnolia officinalis used widely in traditional herbal medicine against a variety of neuronal diseases, possesses potent antioxidant properties and protects the brain against oxidative damage. The aim of the work is to examine the protective mechanisms of magnolol on human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against apoptosis induced by the neurotoxin acrolein, which can cause neurodegenerative disorders by inducing oxidative stress. By investigating the effect of magnolol on neural cell damage induced by the neurotoxin acrolein, we found that magnolol pretreatment significantly attenuated acrolein-induced oxidative stress through inhibiting reactive oxygen species accumulation caused by intracellular glutathione depletion and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase activation. We next examined the signaling cascade(s) involved in magnolol-mediated antiapoptotic effects. The results showed that acrolein induced SH-SY5Y cell apoptosis by activating mitochondria/caspase and MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Our findings provide the first evidence that magnolol protects SH-SY5Y cells against acrolein-induced oxidative stress and prolongs SH-SY5Y cell survival through regulating JNK/mitochondria/caspase, PI3K/MEK/ERK, and PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 signaling pathways.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 3-NT:
-
3-Nitrotyrosine
- 4-HNE:
-
4-Hydroxynonenal
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- Akt:
-
Protein kinase B
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- FoxO:
-
O subfamily of forkhead transcription factors
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GSSG:
-
Disulfide oxidized glutathione
- HNE:
-
Hydroxynonenal
- JNK/SAPK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase
- MEK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- ΔΨm:
-
Mitochondrial membrane potential
References
Adams JD, Klaidman LK (1993) Acrolein-induced oxygen radical formation. Free Radic Biol Med 15:187–193
Akagi M, Tada T, Shirono A, Fukuyama Y, Nakade K, Zhai H, Yasui Y, Akagi R (2004) Neuroprotective effect of magnolol in the hippocampus of senescence-accelerated mice (SAMP1). Int Congr Ser 1260:405–408
Ansari MA, Joshi G, Huang Q, Opii WO, Abdul HM, Sultana R, Butterfield DA (2006) In vivo administration of D609 leads to protection of subsequently isolated gerbil brain mitochondria subjected to in vitro oxidative stress induced by amyloid beta-peptide and other oxidative stressors: relevance to Alzheimer’s disease and other oxidative stress-related neurodegenerative disorders. Free Radic Biol Med 41:1694–1703
Blanc A, Pandey N, Srivastava A (2003) Synchronous activation of ERK 1/2, p38mapk and PKB/Akt signaling by H2O2 in vascular smooth muscle cells: potential involvement in vascular disease. Int J Mol Med 11:229–234
Borchers MT, Carty MP, Leikauf GD (1999) Regulation of human airway mucins by acrolein and inflammatory mediators. Am J Physiol 276:549–555
Bowen PE, Borthakur G (2004) Postprandial lipid oxidation and cardiovascular disease risk. Curr Atheroscler Rep 6:477–484
Canas N, Valero T, Villarroya M, Montell E, Verges J, Garcia AG, Lopez MG (2007) Chondroitin sulfate protects SH-SY5Y cells from oxidative stress by inducing heme oxygenase-1 via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 323:946–953
Chang CP, Hsu YC, Lin MT (2003) Magnolol protects against cerebral ischaemic injury of rat heatstroke. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 30:387–392
Chauhan V, Chauhan A (2006) Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Pathophysiology 13:195–208
Fujita M, Itokawa H, Sashida Y (1972) Honokiol, a new phenolic compound isolated from the bark of Magnolia obovata Thunb. Chem Pharm Bull 20:212–213
Gunter TE, Pfeiffer DR (1990) Mechanisms by which mitochondria transport calcium. Am J Physiol 258:C755–C786
Hagen S, Clinton SB, Ruhi A, Jeremy PES, Roger FD, Catherine RE, Enrique C (2003) c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-mediated modulation of brain mitochondria function: new target proteins for JNK signalling in mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis. Biochem J 372:359–369
Haibo L, Jianmei G, Xixiang Y, ShuPeng W, Jianchun L (2007) Protective effect of magnolol on TBHP-induced injury in H460 cells partially via a p53 dependent mechanism. Arch Pharm Res (Seoul) 30:850–857
Heo SR, Han AM, Kwon YK, Joung I (2009) p62 protects SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells against H2O2-induced injury through the PDK1/Akt pathway. Neurosci Lett 450:45–50
Jin Y, Kim K, Kim Y, Ha Y, Kim H, Yun U, Bae K, Kim Y, Kang S, Seo H, Lee J, Chang K (2008) Anti-apoptotic effect of magnolol in myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury requires extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 pathways in rat in vivo. Exp Biol Med 233:1280–1288
Joshi G, Sultana R, Perluigi M, Butterfield DA (2005) In vivo protection of synaptosomes from oxidative stress mediated by Fe2+/H2O2 or 2,2-azobis-(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride by the glutathione mimetic tricyclodecan-9-yl-xanthogenate. Free Radic Biol Med 38:1023–1031
Kehrer JP, Biswal SS (2000) The molecular effects of acrolein. Toxicol Sci 57:6–15
Kutuk O, Basaga H (2007) Apoptosis signaling by 4-hydroxynonenal: a role for JNK-c-Jun/AP-1 pathway. Redox Rep 12:30–34
Lewitt PA (2000) New drugs for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacotherapy 20:26S–32S
Li Z, Pan-Pan Y, Xia-Jing T, Zhang Y-D (2009) Protective effect of magnolol against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in human lens epithelial cells. Am J Chin Med 37:785–796
Lin MH, Chao HT, Hong CY (1995) Magnolol protects human sperm motility against lipid peroxidation: a sperm head fixation method. Syst Biol Reprod Med 34:151–156
Liou JY, Chen YL, Loh SH, Chen PY, Hong CY, Chen J, Cheng TH, Liu JC (2009) Magnolol depresses urotensin-II-induced cell proliferation in rat cardiac fibroblasts. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 36:711–716
Liu-Snyder P, McNally H, Shi R, Borgens RB (2006) Acrolein-mediated mechanisms of neuronal death. J Neurosci Res 84:209–218
Lo Y-C, Teng C-M, Chen C-F, Chen C-C, Hong C-Y (1994) Magnolol and honokiol isolated from Magnolia officinalis protect rat heart mitochondria against lipid peroxidation. Biochem Pharmacol 47:549–553
Long C, Lei L, Jun Y, Yan L, Shile H (2009) Hydrogen peroxide-induced neuronal apoptosis is associated with inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A and 5, leading to activation of MAPK pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:1284–1295
Lovell MA, Xie C, Markesbery WR (2001) Acrolein is increased in Alzheimer’s disease brain and is toxic to primary hippocampal cultures. Neurobiol Aging 22:187–194
Luo J, Robinson JP, Shi R (2005) Acrolein-induced cell death in PC12 cells: role of mitochondria-mediated oxidative stress. Neurochem Int 47:449–457
Maiese K, Chong Z, Shang Y (2007) “Sly as a FOXO”: new paths with Forkhead signaling in the brain. Curr Neurovasc Res 4:295–302
Marco T, Maria P, Dirk-Jan S, Harold G, Nicolas A, Antoon J, Rainer B, Henk F (2007) Cigarette smoke irreversibly modifies glutathione in airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 293:L1156–L1162
Mohmmad AH, Butterfield DA (2007) Involvement of PI3K/PKG/ERK1/2 signaling pathways in cortical neurons to trigger protection by cotreatment of acetyl-l-carnitine and α-lipoic acid against HNE-mediated oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med 42:371–384
Nobuaki M, Kazuki T, Miho T, Touma K, Kaori N, Kana Y, Hideaki T, Kenichi T, Hideki O, Yuki K, Yumiko Y, Nobuyuki F, Yoshiyasu F, Masaaki A (2009) Magnolol and honokiol prevent learning and memory impairment and cholinergic deficit in SAMP8 mice. Brain Res 1305:108–117
Park CH, Kim MR, Han JM, Jeong TS, Sok DE (2009) Lysophosphatidylcholine exhibits selective cytotoxicity, accompanied by ROS formation, in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Lipids Health Dis 44:425–435
Perkinton M, Wood G, Crossthwaite A, Williams R (2002) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is a central mediator of NMDA receptor signalling to MAP kinase (Erk1/2). Akt/PKB and CREB in striatal neurones. J Neurochem 80:239–254
Pocernich CB, Butterfield DA (2003) Acrolein inhibits NADH-linked mitochondrial enzyme activity: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotoxicol Res 5:515–520
Pocernich CB, Cardin AL, Racine CL, Lauderback CM, Butterfield DA (2001) Glutathione elevation and its protective role in acrolein-induced protein damage in synaptosomal membranes: relevance to brain lipid peroxidation in neurodegenerative disease. Neurochem Int 39:141–149
Pugazhenthi S, Phansalkar K, Audesirk G, West A, Cabell L (2006) Differential regulation of c-Jun and CREB by acrolein and 4-hydroxynonenal. Free Radic Biol Med 40:21–34
Rajagopalan S, Kurz S, Munzel T, Tarpey M, Freeman BA, Griendling KK, Harrison DG (1996) Angiotensin II-mediated hypertension in the rat increases vascular superoxide production via membrane NADH/NADPH oxidase activation. Contribution to alterations of vasomotor tone. J Clin Invest 97:1916–1923
Ramassamy C (2006) Emerging role of polyphenolic compounds in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: a review of their intracellular targets. Eur J Pharmacol 545:51–64
Tietze F (1969) Enzymic method for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione: applications to mammalian blood and other tissues. Anal Biochem 106:207–212
Tsai TH, Chou CJ, Chen CF (1996) Pharmacokinetics and brain distribution of magnolol in the rat after intravenous bolus injection. J Pharm Pharmacol 48:57–59
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MTD, Mazur M, Telser J (2007) Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:44–84
Yi-Rong C, Anju S, Tse-Hua T (2001) Down-regulation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) phosphatase M3/6 and activation of JNK by hydrogen peroxide and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate. Oncogene Res 20:367–374
Zhao DL, Zou LB, Lin S, Shi JG, Zhu HB (2007) Anti-apoptotic effect of esculin on dopamine-induced cytotoxicity in the human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line. Neuropharmacology 53:724–732
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China National “12.5” Foundation (no. 2011BAJ07B04) and the Open Foundation (SKLODSCUKF2012-04) from the State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Sichuan University for the financial support and National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 20972105 and 20772087) and Sichuan Province Foundation (no. 2008SZ0024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Liqun Dong and Shu Zhou contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 11.7 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, L., Zhou, S., Yang, X. et al. Magnolol Protects Against Oxidative Stress-Mediated Neural Cell Damage by Modulating Mitochondrial Dysfunction and PI3K/Akt Signaling. J Mol Neurosci 50, 469–481 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-9964-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-9964-0