Abstract
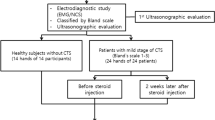
Very few data are available on the structural and functional effects of corticosteroids on peripheral nerve fibers. This paper is addressed to verify possible changes in the functional properties of myelinated Aβ fibers of the median nerve in carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) after a local injection of triamcinolone acetate. Thirteen subjects affected by mild CTS and 13 controls were selected. Clinical, electrophysiological, and ultrasonographic (cross sectional area: CSA) data of the median nerve were quantified at 0 (pre-injection), and 1 month after triamcinolone injection at wrist. We analyzed the input–output curves constructed by plotting the response amplitude as a function of stimulus intensity. After corticosteroid injection, all patients experienced symptom relief, the median nerve CSA decreased, and the plateau value of the input–output curve was significant higher than before the treatment. Pre injection, we observed a significant inverse correlation between median nerve CSA and plateau value of the input–output curve, which remained significant even after the corticosteroid injection. The Aβ fibers with higher electrical threshold undergo conduction recovery after local corticosteroid injection. In CTS, combined mechanisms might contribute to resolution of symptoms: anti-edema/anti-inflammatory action and direct effect on the electrical properties of the nerve fibers.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
American academy of neurology, and American academy of physical medicine and rehabilitation (2002) Practice parameter for electrodiagnostic studies in carpal tunnel syndrome: summary statement. American Association of electrodiagnostic medicine. Muscle Nerve 25:918–922
Cartwright MS, White DL, Demar S et al (2011) Median nerve changes following steroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 44:25–29
Clatworthy AL, Illich PA, Castro GA, Walters ET (1995) Role of peri-axonal inflammation in the development of thermal hyperalgesia and guarding behavior in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett 184:5–8
Devor M, Govrin-Lippmann R, Raber P (1985) Corticosteroids suppress ectopic neural discharge originating in experimental neuromas. Pain 22:127–137
Djouhri L, Lawson SN (2004) A beta-fiber nociceptive primary afferent neurons: a review of incidence and properties in relation to other afferent A-fiber neurons in mammals. Brain Res Rev 46:131–145
Freeland AE, Tucci MA, Barbieri RA, Angel MF, Nick TG (2002) Biochemical evaluation of serum and flexor tenosynovium in carpal tunnel syndrome. Microsurgery 22:378–385
Ginanneschi F, Mondelli M, Dominici F, Rossi A (2006) Changes in motor axon recruitment in the median nerve in mild carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin Neurophysiol 117:2467–2477
Grassi W, Farina A, Filippucci E, Cervini C (2002) Intralesional therapy in carpal tunnel syndrome: a sonographic-guided approach. Clin Exp Rheumatol 20:73–76
Johansson A, Bennett GJ (1997) Effect of local methylprednisolone on pain in a nerve injury model. A pilot study. Reg Anesth 22:59–65
Johansson A, Hao J, Sjölund B (1990) Local corticosteroid application blocks transmission in normal nociceptive C-fibres. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 34:335–338
Kingery WS (1997) A critical review of controlled clinical trials for peripheral neuropathic pain and complex regional pain syndromes. Pain 73:123–139
Kingery WS, Castellote JM, Maze M (1999) Methylprednisolone prevents the development of autotomy and neuropathic edema in rats, but has no effect on nociceptive thresholds. Pain 80:555–566
Levine DW, Simmons BP, Koris MJ et al (1993) A self administered questionnaire for the assessment of severity of symptoms and functional status in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am 75:1585–1592
Lussier D, Huskey AG, Portenoy RK (2004) Adjuvant analgesics in cancer pain management. Oncologist 9:571–591
Marshall S, Tardif G, Ashworth N (2007) Local corticosteroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. CD001554
Mondelli M, Filippou G, Aretini A, Frediani B, Reale F (2008) Ultrasonography before and after surgery in carpal tunnel syndrome and relationship with clinical and electrophysiological findings. A new outcome predictor? Scand J Rheumatol 37:219–224
Morisaki S, Nishi M, Fujiwara H, Oda R, Kawata M, Kubo T (2010) Endogenous glucocorticoids improve myelination via Schwann cells after peripheral nerve injury: an in vivo study using a crush injury model. Glia 58:954–963
Padua R, Padua L, Romanini E, Aulisa L, Lupparelli S, Sanguinetti C (1998) Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire Italian version. Ital J Orthop Traumatol 24:123–129
Press WH, Flannery BP, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT (1986) Numerical recipes Cambridge. Cambridge University Press, UK
Takeda K, Sawamura S, Sekiyama H, Tamai H, Hanaoka K (2004) Effect of methylprednisolone on neuropathic pain and spinal glial activation in rats. Anesthesiology 100:1249–1257
Truini A, Padua L, Biasiotta A et al (2009) Differential involvement of A-delta and A-beta fibres in neuropathic pain related to carpal tunnel syndrome. Pain 14:105–109
Wareham D (2004) Postherpetic neuralgia. Clin Evid 12:1182–1193
Werner RA, Andary M (2002) Carpal tunnel syndrome: pathophysiology and clinical neurophysiology. Clin Neurophysiol 113:1373–1381
Zhu YF, Henry JL (2012) Excitability of Ab sensory neurons is altered in an animal model of peripheral neuropathy. BMC Neurosci 30:13–15
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ginanneschi, F., Filippou, G., Bonifazi, M. et al. Effects of Local Corticosteroid Injection on Electrical Properties of Aβ-Fibers in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. J Mol Neurosci 52, 525–530 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0107-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0107-4