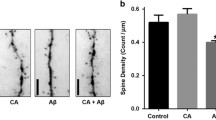
Abstract
We set out to identify NAP (davunetide) analogs, providing neuroprotection and reducing tau pathology, specifically addressing protection against protein misfolding. NAP (NAPVSIPQ, intranasal formulation AL-108) is a drug candidate that (1) had a statistically significant impact on two measures, namely digit span and delayed-match-to-sample, tests of verbal recall and visual working memory, respectively, in patient population of mild cognitive impairment [preceding Alzheimer’s disease (AD)] and (2) protected functional activities of daily living in schizophrenia patients. Previous preclinical studies have shown that stabilization of NAP by replacement of all l-amino acids by d-amino acids resulted in an active peptide, d-NAP. Other NAP mimetics are now explored. A new NAP analog was designed that included replacement of the proline residues by alpha-aminoisobutyric acid to enhance β-sheet breaker characteristics, thereby reducing protein misfolding. Three lines of investigations were chosen: (1) protection against the AD-associated amyloid β (1-42), Aβ1-42, peptide toxicity in cell cultures; (2) inhibition of AD-associated tau aggregation in vitro; and (3) cognitive protection in a mouse model of deficiencies of the NAP parent protein, activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP), exhibiting tau pathology and neurodegeneration. NAP alpha-aminoisobutyric acid (IsoNAP) protected neurons against AD-associated Aβ1-42-toxicity, inhibited the aggregation of the tau-derived peptide VQIVYK (important for the aggregation of tau into paired helical filaments, which form the tangles found in AD and related disorders), and protected cognitive functions in a model of ADNP deficiency. With AD being the major tauopathy, novel NAP derivatives that reduce tauopathy and provide neuroprotection as well as cognitive protection are of scientific and clinical interest.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashur-Fabian O, Segal-Ruder Y, Skutelsky E, Brenneman DE, Steingart RA, Giladi E, Gozes I (2003) The neuroprotective peptide NAP inhibits the aggregation of the beta-amyloid peptide. Peptides 24:1413–1423
Bassan M, Zamostiano R, Davidson A, Pinhasov A, Giladi E, Perl O, Bassan H, Blat C, Gibney G, Glazner G, Brenneman DE, Gozes I (1999) Complete sequence of a novel protein containing a femtomolar-activity-dependent neuroprotective peptide. J Neurochem 72:1283–1293
Bour A, Grootendorst J, Vogel E, Kelche C, Dodart JC, Bales K, Moreau PH, Sullivan PM, Mathis C (2008) Middle-aged human apoE4 targeted-replacement mice show retention deficits on a wide range of spatial memory tasks. Behav Brain Res 193:174–182
Brandeis R, Brandys Y, Yehuda S (1989) The use of the Morris water maze in the study of memory and learning. Int J Neurosci 48:29–69
Brenneman DE, Spong CY, Hauser JM, Abebe D, Pinhasov A, Golian T, Gozes I (2004) Protective peptides that are orally active and mechanistically nonchiral. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309:1190–1197
Divinski I, Mittelman L, Gozes I (2004) A femtomolar acting octapeptide interacts with tubulin and protects astrocytes against zinc intoxication. J Biol Chem 279:28531–28538
Friedhoff P, Schneider A, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (1998) Rapid assembly of Alzheimer-like paired helical filaments from microtubule-associated protein tau monitored by fluorescence in solution. Biochemistry 37:10223–10230
Furman S, Hill JM, Vulih I, Zaltzman R, Hauser JM, Brenneman DE, Gozes I (2005) Sexual dimorphism of activity-dependent neuroprotective protein in the mouse arcuate nucleus. Neurosci Lett 373:73–78
Gilead S, Gazit E (2004) Inhibition of amyloid fibril formation by peptide analogues modified with alpha-aminoisobutyric acid. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 43:4041–4044
Gold M, Lorenzl S, Stewart AJ, Morimoto BH, Williams DR, Gozes I (2012) Critical appraisal of the role of davunetide in the treatment of progressive supranuclear palsy. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 8:85–93
Gozes I (2010) Davunetide (NAP) pharmacology: neuroprotection and tau. In: Martinez A (ed) Emerging drugs and targets for Alzheimer’s disease, vol 3. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 108–128
Gozes I (2011) NAP (davunetide) provides functional and structural neuroprotection. Curr Pharm Des 17:1040–1044
Gozes I, Baas PW (2013) Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) and davunetide (NAP). In: Kastin AJ (ed) Handbook of biologically active peptide (Illana Gozes editor of section XVIII, pp 1611–1653), 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 1611–1618
Gozes I, Divinski I, Piltzer I (2008) NAP and d-SAL: neuroprotection against beta amyloid peptide (1–42). Curr Alzheimer Res 9(Suppl 3):S3
Gozes I, Giladi E, Pinhasov A, Bardea A, Brenneman DE (2000) Activity-dependent neurotrophic factor: intranasal administration of femtomolar-acting peptides improve performance in a water maze. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293:1091–1098
Gozes I, Morimoto BH, Tiong J, Fox A, Sutherland K, Dangoor D, Holser-Cochav M, Vered K, Newton P, Aisen PS, Matsuoka Y, van Dyck CH, Thal L (2005) NAP: research and development of a peptide derived from activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP). CNS Drug Rev 11:353–368
Idan-Feldman A, Ostritsky R, Gozes I (2012) Tau and caspase 3 as targets for neuroprotection. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2012:493670
Jarskog LF, Dong Z, Kangarlu A, Colibazzi T, Girgis RR, Kegeles LS, Barch DM, Buchanan RW, Csernansky JG, Goff DC, Harms MP, Javitt DC, Keefe RS, McEvoy JP, McMahon RP, Marder SR, Peterson BS, Lieberman JA (2013) Effects of davunetide on N-acetylaspartate and choline in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in patients with schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:1245–1252
Javitt DC, Buchanan RW, Keefe RS, Kern R, McMahon RP, Green MF, Lieberman J, Goff DC, Csernansky JG, McEvoy JP, Jarskog F, Seidman LJ, Gold JM, Kimhy D, Nolan KS, Barch DS, Ball MP, Robinson J, Marder SR (2012) Effect of the neuroprotective peptide davunetide (AL-108) on cognition and functional capacity in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 136:25–31
Jouroukhin Y, Ostritsky R, Assaf Y, Pelled G, Giladi E, Gozes I (2013) NAP (davunetide) modifies disease progression in a mouse model of severe neurodegeneration: protection against impairments in axonal transport. Neurobiol Dis 56C:79–94
Jouroukhin Y, Ostritsky R, Gozes I (2012) d-NAP prophylactic treatment in the SOD mutant mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: review of discovery and treatment of tauopathy. J Mol Neurosci 48:597–602
Leker RR, Shohami E, Constantini S (2002) Experimental models of head trauma. Acta Neurochir Suppl 83:49–54
Matsuoka Y, Gray AJ, Hirata-Fukae C, Minami SS, Waterhouse EG, Mattson MP, LaFerla FM, Gozes I, Aisen PS (2007) Intranasal NAP administration reduces accumulation of amyloid peptide and tau hyperphosphorylation in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease at early pathological stage. J Mol Neurosci 31:165–170
Matsuoka Y, Jouroukhin Y, Gray AJ, Ma L, Hirata-Fukae C, Li HF, Feng L, Lecanu L, Walker BR, Planel E, Arancio O, Gozes I, Aisen PS (2008) A neuronal microtubule-interacting agent, NAPVSIPQ, reduces tau pathology and enhances cognitive function in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 325:146–153
Merenlender-Wagner A, Pikman R, Giladi E, Andrieux A, Gozes I (2010) NAP (davunetide) enhances cognitive behavior in the STOP heterozygous mouse—a microtubule-deficient model of schizophrenia. Peptides 31:1368–1373
Morimoto BH, de Lannoy I, Fox AW, Gozes I, Stewart AJ (2009) Davunetide: pharmacokinetics and distribution to brain after intravenous or intranasal administration to rat. Chimica Oggi/Chemistry Today 27:16–20
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
Oz S, Ivashko-Pachima Y, Gozes I (2012) The ADNP derived peptide, NAP modulates the tubulin pool: implication for neurotrophic and neuroprotective activities. PLoS One 7:e51458
Perez M, Santa-Maria I, Tortosa E, Cuadros R, Del Valle M, Hernandez F, Moreno FJ, Avila J (2007) The role of the VQIVYK peptide in tau protein phosphorylation. J Neurochem 103:1447–1460
Pinhasov A, Mandel S, Torchinsky A, Giladi E, Pittel Z, Goldsweig AM, Servoss SJ, Brenneman DE, Gozes I (2003) Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein: a novel gene essential for brain formation. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 144:83–90
Quraishe S, Cowan CM, Mudher A (2013) NAP (davunetide) rescues neuronal dysfunction in a Drosophila model of tauopathy. Mol Psychiatry 18:834–842
Shiryaev N, Jouroukhin Y, Giladi E, Polyzoidou E, Grigoriadis NC, Rosenmann H, Gozes I (2009) NAP protects memory, increases soluble tau and reduces tau hyperphosphorylation in a tauopathy model. Neurobiol Dis 34:381–388
Shiryaev N, Pikman R, Giladi E, Gozes I (2011) Protection against tauopathy by the drug candidates NAP (davunetide) and D-SAL: biochemical, cellular and behavioral aspects. Curr Pharm Des 17:2603–2612
Sudo H, Baas PW (2011) Strategies for diminishing katanin-based loss of microtubules in tauopathic neurodegenerative diseases. Hum Mol Genet 20:763–778
von Bergen M, Friedhoff P, Biernat J, Heberle J, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (2000) Assembly of tau protein into Alzheimer paired helical filaments depends on a local sequence motif ((306)VQIVYK(311)) forming beta structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:5129–5134
Vulih-Shultzman I, Pinhasov A, Mandel S, Grigoriadis N, Touloumi O, Pittel Z, Gozes I (2007) Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein snippet NAP reduces tau hyperphosphorylation and enhances learning in a novel transgenic mouse model. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 323:438–449
Wilkemeyer MF, Chen SY, Menkari CE, Brenneman DE, Sulik KK, Charness ME (2003) Differential effects of ethanol antagonism and neuroprotection in peptide fragment NAPVSIPQ prevention of ethanol-induced developmental toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:8543–8548
Zemlyak I, Furman S, Brenneman DE, Gozes I (2000) A novel peptide prevents death in enriched neuronal cultures. Regul Pept 96:39–43
Acknowledgments
Professor Gozes’ laboratory is supported by the AMN Foundation, CFTAU Montreal Circle of Friends and the Adams family, Adams Super Center for Brain Studies, and Lily and Avraham Gildor Chair for the Investigation of Growth Factors at Tel Aviv University. Initial studies in this research were also partially supported by Allon Therapeutics Inc. Yulie Schirer and Anat Idan-Feldman performed this work as part of their graduate studies in the Dr. Miriam and Sheldon G. Adelson Graduate School of Medicine associated with the Sackler Faculty of Medicine at Tel Aviv University. Merav David was an undergraduate student at the combined medicine–biology program of Tel Aviv University. Professor Gozes is currently a Humboldt Award recipient and a fellow at the Hanse-Wissenschaftenskolleg, Germany. IsoNAP is under patent protection, Ramot at Tel Aviv University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gozes, I., Schirer, Y., Idan-Feldman, A. et al. NAP Alpha-Aminoisobutyric Acid (IsoNAP). J Mol Neurosci 52, 1–9 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0103-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0103-8