Abstract
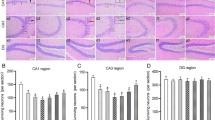
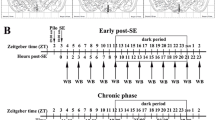
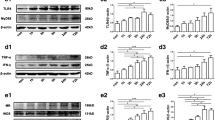
Recently, the role of inflammation has attracted great attention in the pathogenesis of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE), and microRNAs start to emerge as promising new players in MTLE pathogenesis. In this study, we investigated the dynamic expression patterns of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and microRNA-155 (miR-155) in the hippocampi of an immature rat model of status epilepticus (SE) and children with MTLE. The expressions of TNF-α and miR-155 were significantly upregulated in the seizure-related acute and chronic stages of MTLE in the immature rat model and also in children with MTLE. Modulation of TNF-α expression, either by stimulation using myeloid-related protein (MRP8) or lipopolysaccharide or inhibition using lenalidomide on astrocytes, leads to similar dynamic changes in miR-155 expression. Our study is the first to focus on the dynamic expression pattern of miR-155 in the immature rat of SE lithium-pilocarpine model and children with MTLE and to detect their relationship at the astrocyte level. TNF-α and miR-155, having similar expression patterns in the three stages of MTLE development, and their relationship at the astrocyte level may suggest a direct interactive relationship during MTLE development. Therefore, modulation of the TNF-α/miR-155 axis may be a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of MTLE.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akassoglou K, Probert L, Kontogeorgos G, Kollias G (1997) Astrocyte-specific but not neuron-specific transmembrane TNF triggers inflammation and degeneration in the central nervous system of transgenic mice. J Immunol 158:438–458
Amiri M, Bahrami F, Janahmadi M (2012) On the role of astrocytes in epilepsy: a functional modeling approach. Neurosci Res 72:172–180
Aronica E, Fluiter K, Iyer A, Zurolo E, Vreijling J, van Vliet EA et al (2010) Expression pattern of miR-146a, an inflammation-associated microRNA in experimental and human temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur J Neurosci 31:1100–1107
Bala S, Marcos M, Kodys K, Csak T, Catalano D, Mandrekar P et al (2011) Up-regulation of microRNA-155 in macrophages contributes to increased tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF{alpha}) production via increased mRNA half-life in alcoholic liver disease. J Biol Chem 286:1436–1444
Balosso S, Ravizza T, Perego C, Peschon J, Campbell IL, De Simoni MG et al (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits seizures in mice via p75 receptors. Ann Neurol 57:804–812
Balosso S, Ravizza T, Pierucci M, Calcagno E, Invernizzi R, Di Giovanni G et al (2009) Molecular and functional interactions between tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptors and the glutamatergic system in the mouse hippocampus: implications for seizure susceptibility. Neuroscience 161:293–300
Berg AT, Shinnar S, Levy SR, Testa FM (1999) Newly diagnosed epilepsy in children: presentation at diagnosis. Epilepsia 40:445–452
Bhattacharyya S, Balakathiresan NS, Dalgard C, Gutti U, Armistead D, Jozwik C et al (2011) Elevated miR-155 promotes inflammation in cystic fibrosis by driving hyper-expression of interleukin-8. J Biol Chem 286:11604–11615
Blümcke I, Pauli E, Clusmann H, Schramm J, Becker A, Elger C et al (2007) A new clinicopathological classification system for mesial temporal sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 113:235–244
Cascino GD (2009) Temporal lobe epilepsy is a progressive neurologic disorder time means neurons! Neurology 72:1718–1719
Ceppi M, Pereira PM, Dunand-Sauthier I, Barras E, Reith W, Santos MA et al (2009) MicroRNA-155 modulates the interleukin-1 signaling pathway in activated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:2735–2740
Damaye CA, Wu L, Peng J, He F, Zhang C, Lan Y et al (2011) An experimental study on dynamic morphological changes and expression pattern of GFAP and synapsin I in the hippocampus of MTLE models for immature rats. Int J Neurosci 121:575–588
de Lanerolle NC, Lee TS, Spencer DD (2010) Astrocytes and epilepsy. Neurotherapeutics 7:424–438
Dubé CM, Ravizza T, Hamamura M, Zha Q, Keebaugh A, Fok K et al (2010) Epileptogenesis provoked by prolonged experimental febrile seizures: mechanisms and biomarkers. J Neurosci 30:7484–7494
Galic MA, Riazi K, Heida JG, Mouihate A, Fournier NM, Spencer SJ et al (2008) Postnatal inflammation increases seizure susceptibility in adult rats. J Neurosci 28:6904–6913
Jung S, Yang H, Kim BS, Chu K, Lee SK, Jeon D (2012) The immunosuppressant cyclosporin A inhibits recurrent seizures in an experimental model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurosci Lett 529:133–138
Junker A, Krumbholz M, Eisele S, Mohan H, Augstein F, Bittner R et al (2009) MicroRNA profiling of multiple sclerosis lesions identifies modulators of the regulatory protein CD47. Brain 132:3342–3352
Kan AA, van Erp S, Derijck AA, de Wit M, Hessel EV, O’Duibhir E et al (2012) Genome-wide microRNA profiling of human temporal lobe epilepsy identifies modulators of the immune response. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:3127–3145
Kim VN (2005) MicroRNA biogenesis: coordinated cropping and dicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:376–385
Kucher BM, Neary JT (2005) Bi-functional effects of ATP/P2 receptor activation on tumor necrosis factor-alpha release in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated astrocytes. J Neurochem 92:525–235
Liu DZ, Tian Y, Ander BP, Xu H, Stamova BS, Zhan X et al (2010) Brain and blood microRNA expression profiling of ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, and kainate seizures. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:92–101
Maroso M, Balosso S, Ravizza T, Liu J, Bianchi ME, Vezzani A (2011) Interleukin-1 type 1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signalling in epilepsy: the importance of IL-1beta and high-mobility group box 1. J Intern Med 270:319–326
O’Connell RM, Kahn D, Gibson WS, Round JL, Scholz RL, Chaudhuri AA et al (2010) MicroRNA-155 promotes autoimmune inflammation by enhancing inflammatory T cell development. Immunity 33:607–619
Omran A, Elimam D, Shalaby S, Peng J, Yin F (2012a) MicroRNAs: a light into the “black box” of neuropediatric diseases? Neuromolecular Med 14:244–261
Omran A, Peng J, Zhang C, Xiang QL, Xue J, Gan N et al (2012b) Interleukin-1ß and microRNA-146a in an immature rat model and children with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 53:1215–1224
Omran A, Elimam D, Webster K, Shehadeh L, Yin F (2013) MicroRNAs: a new piece in the paediatric cardiovascular disease puzzle. Cardiol Young. doi:10.1017/S1047951113000048
Pedersen IM, Otero D, Kao E, Miletic AV, Hother C, Ralfkiaer E et al (2009) Onco-miR-155 targets SHIP1 to promote TNF alpha-dependent growth of B cell lymphomas. EMBO Mol Med 1:288–295
Peng J, Omran A, Ashhab MU, Kong H, Gan N, He F et al (2013) Expression patterns of miR-124, miR-134, miR-132, and miR-21 in an immature rat model and children with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. J Mol Neurosci. doi:10.1007/s12031-013-9953-3
Plata-Salamán CR, Ilyin SE, Turrin NP, Gayle D, Flynn MC, Romanovitch AE et al (2000) Kindling modulates the IL-1beta system, TNF alpha, TGF-beta1 and neuropeptide mRNAs in specific brain regions. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 75:248–258
Racine RJ (1972) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32:281–294
Ravizza T, Rizzi M, Perego C, Richichi C, Velísková J, Moshé SL et al (2005) Inflammatory response and glia activation in developing rat hippocampus after status epilepticus. Epilepsia 46:113–117
Ravizza T, Gagliardi B, Noé F, Boer K, Aronica E, Vezzani A (2008) Innate and adaptive immunity during epileptogenesis and spontaneous seizures: evidence from experimental models and human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 29:142–160
Ravizza T, Balosso S, Vezzani A (2011) Inflammation and prevention of epileptogenesis. Neurosci Lett 497:223–230
Risbud RM, Lee C, Porter BE (2011) Neurotrophin-3 mRNA a putative target of miR21 following status epilepticus. Brain Res 1424:53–59
Shandra AA, Godlevsky LS, Vastyanov RS, Oleinik AA, Konovalenko VL, Rapoport EN et al (2002) The role of TNF-alpha in amygdala kindled rats. Neurosci Res 42:147–153
Sinha S, Patil SA, Jayalekshmy V, Satishchandra P (2008) Do cytokines have any role in epilepsy? Epilepsy Res 82:171–176
Tarassishin L, Loudig O, Bauman A, Shafit-Zagardo B, Suh HS, Lee SC (2011) Interferon regulatory factor 3 inhibits astrocyte inflammatory gene expression through suppression of the proinflammatory miR-155 and miR-155*. Glia 59:1911–1922
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Cimino A, Costinean S, Dumitru CD, Adair B et al (2007) Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J Immunol 179:5082–5089
Vezzani A, Granata T (2005) Brain inflammation in epilepsy: experimental and clinical evidence. Epilepsia 46:1724–1743
Vezzani A, Moneta D, Richichi C, Aliprandi M, Burrows SJ, Ravizza T et al (2002) Functional role of inflammatory cytokines and antiinflammatory molecules in seizures and epileptogenesis. Epilepsia 43:30–35
Vogl T, Tenbrock K, Ludwig S, Leukert N, Ehrhardt C, van Zoelen MA et al (2007) Mrp8 and Mrp14 are endogenous activators of Toll-like receptor 4, promoting lethal, endotoxin-induced shock. Nat Med 13:1042–1049
Zimmer LA, Ennis M, Shipley MT (1997) Soman-induced seizures rapidly activate astrocytes and microglia in discrete brain regions. J Comp Neurol 378:482–492
Acknowledgments
This work was kindly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 30872790, 30901631, 81171226, and 81100846) and the Scientific and Technological Department of Hunan Province (2011FJ3163). We are most grateful to Dr. Lixin Zhang (Department of Ophthalmology, Xiangya Hospital, China), Dr. Zeng Lei (Department of Spinal Surgery, Xiangya Hospital, China), and Yasmin Majeed, Central South University, for their kind help during the preparation of this work.
Conflict of Interest
None of the authors have any conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashhab, M.U., Omran, A., Kong, H. et al. Expressions of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha and MicroRNA-155 in Immature Rat Model of Status Epilepticus and Children with Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. J Mol Neurosci 51, 950–958 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0013-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0013-9