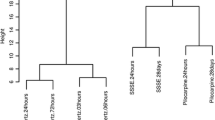
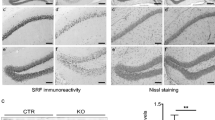
Abstract
Neuron-restrictive silencer factor (NRSF) and its isoforms are differentially regulated in rodent models of self-sustaining status epilepticus (SSSE). NRSF isoforms regulate genes associated with SSSE, including the proconvulsant tachykinins, brain-derived neurotrophic factor and multiple ion channels. NRSF isoforms may direct distinct gene expression patterns during SSSE, and the ratio of each isoform may be a causative factor in traumatic damage to the central nervous system. Here, we analysed global gene expression changes by microarray in human SK-N-AS neuroblastoma cells following the over-expression of NRSF and a truncated isoform, HZ4. We used bioinformatics software to analyse the microarray dataset and correlated these data with epilepsy candidate gene pathways. Findings were validated by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. We demonstrated that NRSF and HZ4 direct overlapping as well as distinct gene expression patterns, and that they differentially modulated gene expression patterns associated with epilepsy. Finally, we revealed that NRSF gene expression may be modulated by the anticonvulsant, phenytoin. We have interpreted our data to reflect altered gene expression directed by NRSF that might be relevant for SSSE.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora DK, Cosgrave AS, Howard MR, Bubb V, Quinn JP, Thippeswamy T (2007) Evidence of postnatal neurogenesis in dorsal root ganglion: role of nitric oxide and neuronal restrictive silencer transcription factor. J Mol Neurosci 32:97–107
Bassuk AG, Wallace RH, Buhr A et al (2008) A homozygous mutation in human PRICKLE1 causes an autosomal-recessive progressive myoclonus epilepsy-ataxia syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 83:572–581
Berkovic SF, Izzillo P, McMahon JM et al (2004) LGI1 mutations in temporal lobe epilepsies. Neurology 62:1115–1119
Bruce AW, Krejci A, Ooi L et al (2006) The transcriptional repressor REST is a critical regulator of the neurosecretory phenotype. J Neurochem 98:1828–1840
Cavalleri GL, Weale ME, Shianna KV et al (2007) Multicentre search for genetic susceptibility loci in sporadic epilepsy syndrome and seizure types: a case-control study. Lancet Neurol 6:970–980
Cheong A, Bingham AJ, Li J, Kumar B (2005) Downregulated REST transcription factor is a switch enabling critical potassium channel expression and cell proliferation. Mol Cell 20:45–52
Coulson JM, Edgson JL, Woll PJ, Quinn JP (2000) A splice variant of the neuron-restrictive silencer factor repressor is expressed in small cell lung cancer: a potential role in derepression of neuroendocrine genes and a useful clinical marker. Cancer Res 60:1840–1844
Crunelli V, Leresche N (2002) Childhood abscene epilepsy: genes, channels, neurons and networks. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:371–382
Drews VL, Shi K, de Haan G, Meisler MH (2007) Identification of evolutionarily conserved, functional noncoding elements in the promoter region of the sodium channel gene SCN8A. Mamm Genome 18:723–731
Everett K, Chioza B, Aicardi J et al (2007) Linkage and mutational analysis of CLCN2 in childhood absence epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 75:145–153
Fisher JL (2009) The anti‐convulsant stiripentol acts directly on the GABA(A) receptor as a positive allosteric modulator. Neuropharmacology. Jan;56(1):190‐7. Epub 2008 Jun 10
Gallanti A, Tonelli A, Cardin V, Bussone G, Bresolin N, Bassi MT (2008) A novel de novo nonsense mutation in ATP1A2 associated with sporadic hemiplegic migraine and epileptic seizures. J Neurol Sci 273:123–126
Garriga-Canut M, Schoenike B, Qazi R et al (2006) 2-Deoxy-D-glucose reduces epilepsy progression by NRSF-CtBP-dependent metabolic regulation of chromatin structure. Nat Neurosci 9:1382–1387
Gastaldi M, Robaglia-Schlupp A, Massacrier A, Planells R, Cau P (1998) mRNA coding for voltage-gated sodium channel beta2 subunit in rat central nervous system: cellular distribution and changes following kainate-induced seizures. Neurosci Lett 249:53–56
Gillies S, Haddley K, Vasiliou S, Bubb VJ, Quinn JP (2009) The human neurokinin B gene, TAC3, and its promoter are regulated by neuron restrictive silencing factor (NRSF) transcription factor family. Neuropeptides 43:333–340
Gong HC, Hang J, Kohler W, Li L, Su TZ (2001) Tissue‐specific expression and gabapentinbinding properties of calcium channel alpha2delta subunit subtypes. J Membr Biol. Nov 1;184(1):35–43
Greco SJ, Smirnov SV, Murthy RG, Rameshwar P (2007) Synergy between the RE-1 silencer of transcription and NFkappaB in the repression of the neurotransmitter gene TAC1 in human mesenchymal stem cells. J Biol Chem 282:30039–30050
Gutierrez-Delicado E, Serratosa JM (2004) Genetics of the epilepsies. Curr Opin Neurol 17:147–153
Helbig I, Matigian NA, Vadlamudi L et al (2008) Gene expression analysis in absence epilepsy using a monozygotic twin design. Epilepsia 49:1546–1554
Hermann B, Jacoby A. (2009) The psychosocial impact of epilepsy in adults. Epilepsy Behav. Jun;15 Suppl 1:S11‐6. Epub 2009 Apr 18
Hermann BP, Hornbaker K, Rice DA, Sawadogo M, Heckert LL (2008) In vivo regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone receptor by the transcription factors upstream stimulatory factor 1 and upstream stimulatory factor 2 is cell specific. Endocrinology 149:5297–5306
Jiang FL, Tang YC, Chia SC, Jay TM, Tang FR (2007) Anticonvulsive effect of a selective mGluR8 agonist (S)‐3,4‐dicarboxyphenylglycine (S‐3,4‐DCPG) in the mouse pilocarpine model of status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2007 Apr;48(4):783–792. Epub 2007 Mar 13
Johnson DS, Mortazavi A, Myers RM, Wold B (2007) Genome-wide mapping of in vivo protein-DNA interactions. Science 316:1497–1502
Joshi I, Taylor CP (2006) Pregabalin action at a model synapse: binding to presynaptic calcium channel alpha2‐delta subunit reduces neurotransmission in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. Dec 28;553(1‐3):82–88. Epub 2006 Sep 23
Kalachikov S, Evgrafov O, Ross B et al (2002) Mutations in LGI1 cause autosomal-dominant partial epilepsy with auditory features. Nat Genet 30(3):335–341, Mar
Kaminski RM, Matagne A, Leclercq K et al (2008) SV2A protein is a broad-spectrum anticonvulsant target: functional correlation between protein binding and seizure protection in models of both partial and generalized epilepsy. Neuropharmacology 54:715–720
Kang SJ, Cho SH, Park K, Yi J, Yoo SJ, Shin KS (2008) Expression of Kir2.1 channels in astrocytes under pathophysiological conditions. Mol Cells. Feb 29;25(1):124–130
Kobayashi T, Hirai H, Iino M, et al (2009) Inhibitory effects of the antiepileptic drug ethosuximide on G protein‐activated inwardly rectifying K+ channels. Neuropharmacology. 2009 Feb;56(2):499‐506. Epub 2008 Oct 17
Kral T, Erdmann E, Sochivko D, Clusmann H, Schramm J, Dietrich D (2003) Down‐regulation of mGluR8 in pilocarpine epileptic rats. Synapse. 2003 Mar 15;47(4):278–284
Kuwahara K, Saito Y, Takano M et al (2003) NRSF regulates the fetal cardiac gene program and maintains normal cardiac structure and function. EMBO J 22:6310–6321
Lazarowski A, Czornyj L, Lubienieki F, Girardi E, Vazquez S, D’Giano C (2007) ABC transporters during epilepsy and mechanisms underlying multidrug resistance in refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia 48(Suppl 5):140–149
Lerner JT, Sankar R, Mazarati AM (2008) Galanin and epilepsy. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:1864–1871
Li S, Saragovi HU, Nedev H, Zhao C, Racine RJ, Fahnestock M (2005) Differential actions of nerve growth factor receptors TrkA and p75NTR in a rat model of epileptogenesis. Mol Cell Neurosci 29:162–172
Liu M, Hurn PD, Alkayed NJ (2004) Cytochrome P450 in neurological disease. Curr Drug Metab 5:225–234
Lohoff FW, Ferraro TN, Sander T et al (2005) No association between common variations in the human alpha 2 subunit gene (ATP1A2) of the sodium-potassium-transporting ATPase and idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Neurosci Lett 382:33–38
Lu JJ, Zhang YH, Pan H et al (2004) Case-control study and transmission/disequilibrium tests of the genes encoding GABRA5 and GABRB3 in a Chinese population affected by childhood absence epilepsy. Chin Med J (Engl) 117:1497–1501
Lynch BA, Lambeng N, Nocka K et al (2004) The synaptic vesicle protein SV2A is the binding site for the antiepileptic drug levetiracetam. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9861–9866
Magin A, Lietz M, Cibelli G, Thiel G (2002) RE-1 silencing transcription factor-4 (REST4) is neither a transcriptional repressor nor a de-repressor. Neurochem Int 40:195–202
Meldrum BS, Chapman AG. (1999) Basic mechanisms of gabitril (tiagabine) and future potential developments. Epilepsia. 40 Suppl 9:S2‐6. Review
Mistrik P, Mader R, Michalakis S, Weidinger M, Pfeifer A, Biel M (2005) The murine HCN3 gene encodes a hyperpolarization-activated cation channel with slow kinetics and unique response to cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem 280:27056–27061
Miyajima F, Quinn JP, Horan M et al (2008) Additive effect of BDNF and REST polymorphisms is associated with improved general cognitive ability. Genes Brain Behav 7:714–719
Mosher CM, Tai G, Rettie AE (2009) CYP2C9 amino acid residues influencing phenytoin turnover and metabolite regio- and stereochemistry. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. Jun; 329(3):938–944. Epub 2009 Mar 3
Niemeyer MI, Yusef YR, Cornejo I, Flores CA, Sepúlveda FV, Cid LP (2004) Functional evaluation of human ClC-2 chloride channel mutations associated with idiopathic generalized epilepsies. Physiol Genomics 19:74–83
Ooi L, Wood I (2007) Chromatin crosstalk in development and disease: lessons from REST. Nat Rev Genet 8:544–554
Palm K, Belluardo N, Metsis M, Timmusk T (1998) Neuronal expression of zinc finger transcription factor REST/NRSF/XBR gene. J Neurosci 18:1280–1296
Perucca E (2006) Clinically relevant drug interactions with antiepileptic drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol 61:246–255
Powell KL, Ng C, O’Brien TJ et al (2008) Decreases in HCN mRNA expression in the hippocampus after kindling and status epilepticus in adult rats. Epilepsia 49:1686–1695
Quinn JP, Bubb VJ, Marshall-Jones ZV, Coulson JM (2002) Neuron restrictive silencer factor as a modulator of neuropeptide gene expression. Regul Pept 108:135–141
Roberts DS, Raol YH, Bandyopadhyay S et al (2005) Egr3 stimulation of GABRA4 promoter activity as a mechanism for seizure-induced up-regulation of GABA(A) receptor alpha4 subunit expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11894–11899
Roopra A, Sharling L, Wood IC et al (2000) Transcriptional repression by neuron-restrictive silencer factor is mediated via the Sin3-histone deacetylase complex. Mol Cell Biol 20:2147–2157
Rudy B, Chow A, Lau D, et al (1999) Contributions of Kv3 channels to neuronal excitability. Ann N Y Acad Sci. Apr 30;868:304–343
Schousboe A, Sarup A, Larsson OM, White HS (2004) GABA transporters as drug targets for modulation of GABAergic activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Oct 15;68(8):1557–1563
Schroder RL, Jespersen T, Christophersen P, Strobaek D, Jensen BS, Olesen SP (2001) KCNQ4 channel activation by BMS-204352 and retigabine. Neuropharmacology 40:888–898
Seo T, Nakada N, Ueda N et al (2006) Effect of CYP3A5*3 on carbamazepine pharmacokinetics in Japanese patients with epilepsy. Clin Pharmacol Ther 79:509–510
Shimojo M, Paquette AJ, Anderson DJ, Hersh LB (1999) Protein kinase A regulates cholinergic gene expression in PC12 cells: REST4 silences the silencing activity of neuron-restrictive silencer factor/REST. Mol Cell Biol 19:6788–6795
Singh SK, Kagalwala MN, Parker-Thornburg J, Adams H, Majumder S (2008) REST maintains self-renewal and pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. Nature 453:223–227
Spencer EM, Chandler KE, Haddley K et al (2006) Regulation and role of REST and REST4 variants in modulation of gene expression in in vivo and in vitro in epilepsy models. Neurobiol Dis 24:41–52
Splawski I, Shen J, Timothy KW, et al (2000) Spectrum of mutations in long‐QT syndrome genes. KVLQT1, HERG, SCN5A, KCNE1, and KCNE2. Circulation. Sep 5;102(10):1178–1185
Steinlein OK (2008) Genetic disorders caused by mutated acetylcholine receptors. Life Sci. 2007 May 30;80(24–25):2186–2190. Epub 2007 Mar 19
Stillitano F, Lonardo G, Zicha S et al (2008) Molecular basis of funny current (If) in normal and failing human heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 45:289–299
Sun YM, Greenway DJ, Johnson R et al (2005) Distinct profiles of REST interactions with its target genes at different stages of neuronal development. Mol Biol Cell 16:5630–5638
Tabuchi A, Yamada T, Sasagawa S, Naruse Y, Mori N, Tsuda M (2002) REST4-mediated modulation of REST/NRSF-silencing function during BDNF gene promoter activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:415–420
Tapia-Ramirez J, Eggen BJ, Peral-Rubio MJ, Toledo-Aral JJ, Mandel G (1997) A single zinc finger motif in the silencing factor REST represses the neural-specific type II sodium channel promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:1177–1182
Tate SK, Depondt C, Sisodiya SM et al (2005) Genetic predictors of the maximum doses patients receive during clinical use of the anti-epileptic drugs carbamazepine and phenytoin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5507–5512
Thiry A, Dogne JM, Supuran CT, Masereel B (2007) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors as anticonvulsant agents. Curr Top Med Chem 7:855–864
Timmusk T, Palm K, Lendahl U, Metsis M (1999) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in vivo is under the control of neuron-restrictive silencer element. J Biol Chem 274:1078–1084
Unsain N, Nuñez N, Anastasía A, Mascó DH (2008) Status epilepticus induces a TrkB to p75 neurotrophin receptor switch and increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor interaction with p75 neurotrophin receptor: an initial event in neuronal injury induction. Neuroscience 154:978–993
Van Gelder RN, von Zastrow ME, Yool A, Dement WC, Barchas JD, Eberwine JH (1990) Amplified RNA synthesized from limited quantities of heterogeneous cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1663–1667
Varghese A, Tenbroek EM, Coles J Jr, Sigg DC (2006) Endogenous channels in HEK cells and potential roles in HCN ionic current measurements. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 90:26–37
Warrington J (2000) Large-scale genomic analysis using Affymetrix GeneChip(R) probe arrays. In: Schena M (ed) Microarray biochip technology. Eaton Publishing, Natick, pp 119–148
Yang Y, Li Y, Lv Y et al (2008) NRSF silencing induces neuronal differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res 314:2257–2265
Zachrisson O, Lindefors N, Brene S (1998) A tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonist, CP-122, 721–1, attenuates kainic acid-induced seizure activity. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 60:291–295
Zahn RK, Tolner EA, Derst C, Gruber C, Veh RW, Heinemann U (2008) Reduced ictogenic potential of 4‐aminopyridine in the perirhinal and entorhinal cortex of kainate‐treated chronic epileptic rats. Neurobiol Dis. Feb;29(2):186–200. Epub 2007 Sep 4
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Dr. Graeme Sills for critical review of this manuscript. We confirm that we have read the journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines. We wish to thank the MRC for studentship funding for SG and the BBSRC for funding for KH, SV, VJB and JPQ.
Conflicts of interest
None of the authors has any conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gillies, S.G., Haddley, K., Vasiliou, S.A. et al. Distinct Gene Expression Profiles Directed by the Isoforms of the Transcription Factor Neuron-Restrictive Silencer Factor in Human SK-N-AS Neuroblastoma Cells. J Mol Neurosci 44, 77–90 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-010-9420-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-010-9420-3