Abstract
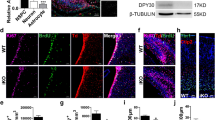
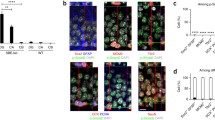
Transforming growth factor-β signaling through Smad3 inhibits cell proliferation in many cell types. As cell proliferation in the brain is an integral part of neurogenesis, we sought to determine the role of Smad3 in adult neurogenesis through examining processes and structures important to neurogenesis in adult Smad3 null mice. We find that there are fewer proliferating cells in neurogenic regions of adult Smad3 null mouse brains and reduced migration of neuronal precursor cells from the subventricular zone to the olfactory bulb. Alterations in astrocyte number and distribution within the rostral migratory stream of Smad3 null mice give rise to a smaller and more disorganized structure that may impact on neuronal precursor cell migration. However, the proportion of proliferating cells that become neurons is similar in wild type and Smad3 null mice. Our results suggest that signaling through Smad3 is needed to maintain the rate of cell division of neuronal precursors in the adult brain and hence the amount of neurogenesis, without altering neuronal cell fate.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman J (1969) Autoradiographic and histological studies of postnatal neurogenesis. IV. Cell proliferation and migration in the anterior forebrain, with special reference to persisting neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol 137:433–457
Altman J, Das GD (1965) Post-natal origin of microneurones in the rat brain. Nature 207:953–956
Andersson O, Reissmann E, Ibanez CF (2006) Growth differentiation factor 11 signals through the transforming growth factor-beta receptor ALK5 to regionalize the anterior-posterior axis. EMBO Rep 7:831–837
Arvidsson A, Collin T, Kirik D, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2002) Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med 8:963–970
Ashcroft GS, Yang X, Glick AB, Weinstein M, Letterio JL, Mizel DE, Anzano M, Greenwell-Wild T, Wahl SM, Deng C et al (1999) Mice lacking Smad3 show accelerated wound healing and an impaired local inflammatory response. Nat Cell Biol 1:260–266
Attisano L, Carcamo J, Ventura F, Weis FM, Massague J, Wrana JL (1993) Identification of human activin and TGF beta type I receptors that form heteromeric kinase complexes with type II receptors. Cell 75:671–680
Bakin AV, Safina A, Rinehart C, Daroqui C, Darbary H, Helfman DM (2004) A critical role of tropomyosins in TGF-beta regulation of the actin cytoskeleton and cell motility in epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell 15:4682–4694
Battista D, Ferrari CC, Gage FH, Pitossi FJ (2006) Neurogenic niche modulation by activated microglia: transforming growth factor beta increases neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus. Eur J NeuroSci 23:83–93
Belvindrah R, Rougon G, Chazal G (2002) Increased neurogenesis in adult mCD24-deficient mice. J Neurosci 22:3594–3607
Biebl M, Cooper CM, Winkler J, Kuhn HG (2000) Analysis of neurogenesis and programmed cell death reveals a self-renewing capacity in the adult rat brain. Neurosci Lett 291:17–20
Bottner M, Krieglstein K, Unsicker K (2000) The transforming growth factor-betas: structure, signaling, and roles in nervous system development and functions [in process citation]. J Neurochem 75:2227–2240
Bravo JA, Parra CS, Arancibia S, Andres S, Morales P, Herrera-Marschitz M, Herrera L, Lara HE, Fiedler JL (2006) Adrenalectomy promotes a permanent decrease of plasma corticoid levels and a transient increase of apoptosis and the expression of transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) in hippocampus: effect of a TGF-beta1 oligo-antisense. BMC Neurosci 7:40
Brionne TC, Tesseur I, Masliah E, Wyss-Coray T (2003) Loss of TGF-beta 1 leads to increased neuronal cell death and microgliosis in mouse brain. Neuron 40:1133–1145
Buckwalter MS, Yamane M, Coleman BS, Ormerod BK, Chin JT, Palmer T, Wyss-Coray T (2006) Chronically increased transforming growth factor-beta1 strongly inhibits hippocampal neurogenesis in aged mice. Am J Pathol 169:154–164
Close JL, Gumuscu B, Reh TA (2005) Retinal neurons regulate proliferation of postnatal progenitors and Muller glia in the rat retina via TGF beta signaling. Development 132:3015–3026
Constam DB, Schmid P, Aguzzi A, Schachner M, Fontana A (1994) Transient production of TGF-beta 2 by postnatal cerebellar neurons and its effect on neuroblast proliferation. Eur J NeuroSci 6:766–778
Curtis MA, Penney EB, Pearson AG, van Roon-Mom WM, Butterworth NJ, Dragunow M, Connor B, Faull RL (2003) Increased cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult human Huntington's disease brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9023–9027
D'Antonio M, Droggiti A, Feltri ML, Roes J, Wrabetz L, Mirsky R, Jessen KR (2006) TGFbeta type II receptor signaling controls Schwann cell death and proliferation in developing nerves. J Neurosci 26:8417–8427
Datto MB, Frederick JP, Pan L, Borton AJ, Zhuang Y, Wang XF (1999) Targeted disruption of Smad3 reveals an essential role in transforming growth factor beta-mediated signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol 19:2495–2504
Derynck R, Zhang Y, Feng XH (1998) Smads: transcriptional activators of TGF-beta responses. Cell 95:737–740
Doetsch F, Alvarez-Buylla A (1996) Network of tangential pathways for neuronal migration in adult mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:14895–14900
Duan X, Kang E, Liu CY, Ming GL, Song H (2008) Development of neural stem cell in the adult brain. Curr Opin Neurobiol 18:108–115
Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, Gage FH (1998) Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med 4:1313–1317
Fee DB, Sewell DL, Andresen K, Jacques TJ, Piaskowski S, Barger BA, Hart MN, Fabry Z (2004) Traumatic brain injury increases TGF beta RII expression on endothelial cells. Brain Res 1012:52–59
Feng XH, Derynck R (2005) Specificity and versatility in tgf-beta signaling through Smads. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:659–693
Fink SP, Mikkola D, Willson JK, Markowitz S (2003) TGF-beta-induced nuclear localization of Smad2 and Smad3 in Smad4 null cancer cell lines. Oncogene 22:1317–1323
Gagelin C, Pierre M, Gavaret JM, Toru-Delbauffe D (1995) Rapid TGF beta 1 effects on actin cytoskeleton of astrocytes: comparison with other factors and implications for cell motility. Glia 13:283–293
Garcia-Campmany L, Marti E (2007) The TGFbeta intracellular effector Smad3 regulates neuronal differentiation and cell fate specification in the developing spinal cord. Development 134:65–75
Getchell ML, Boggess MA, Pruden SJ 2nd, Little SS, Buch S, Getchell TV (2002) Expression of TGF-beta type II receptors in the olfactory epithelium and their regulation in TGF-alpha transgenic mice. Brain Res 945:232–241
Gomes FC, Sousa Vde O, Romao L (2005) Emerging roles for TGF-beta1 in nervous system development. Int J Dev Neurosci 23:413–424
Gould E, Tanapat P (1997) Lesion-induced proliferation of neuronal progenitors in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. Neuroscience 80:427–436
Gould E, Tanapat P, McEwen BS, Flugge G, Fuchs E (1998) Proliferation of granule cell precursors in the dentate gyrus of adult monkeys is diminished by stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:3168–3171
Goumans MJ, Valdimarsdottir G, Itoh S, Rosendahl A, Sideras P, ten Dijke P (2002) Balancing the activation state of the endothelium via two distinct TGF-beta type I receptors. Embo J 21:1743–1753
Hagedorn L, Floris J, Suter U, Sommer L (2000) Autonomic neurogenesis and apoptosis are alternative fates of progenitor cell communities induced by TGFbeta. Dev Biol 228:57–72
Hagg T (2007) Endogenous regulators of adult CNS neurogenesis. Curr Pharm Des 13:1829–1840
He W, Cao T, Smith DA, Myers TE, Wang XJ (2001) Smads mediate signaling of the TGFbeta superfamily in normal keratinocytes but are lost during skin chemical carcinogenesis. Oncogene 20:471–483
Heldin CH, Miyazono K, ten Dijke P (1997) TGF-beta signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins. Nature 390:465–471
Hinds JW (1968) Autoradiographic study of histogenesis in the mouse olfactory bulb. I. Time of origin of neurons and neuroglia. J Comp Neurol 134:287–304
Hunter KE, Sporn MB, Davies AM (1993) Transforming growth factor-betas inhibit mitogen-stimulated proliferation of astrocytes. Glia 7:203–211
Ishinaga H, Jono H, Lim JH, Komatsu K, Xu X, Lee J, Woo CH, Xu H, Feng XH, Chen LF et al (2009) Synergistic induction of nuclear factor-kappaB by transforming growth factor-beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha is mediated by protein kinase A-dependent RelA acetylation. Biochem J 417:583–591
Jankovski A, Sotelo C (1996) Subventricular zone-olfactory bulb migratory pathway in the adult mouse: cellular composition and specificity as determined by heterochronic and heterotopic transplantation. J Comp Neurol 371:376–396
Jin K, Sun Y, Xie L, Peel A, Mao XO, Batteur S, Greenberg DA (2003) Directed migration of neuronal precursors into the ischemic cerebral cortex and striatum. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:171–189
Kano MR, Bae Y, Iwata C, Morishita Y, Yashiro M, Oka M, Fujii T, Komuro A, Kiyono K, Kaminishi M et al (2007) Improvement of cancer-targeting therapy, using nanocarriers for intractable solid tumors by inhibition of TGF-beta signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3460–3465
Kempermann G, Jessberger S, Steiner B, Kronenberg G (2004) Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus. Trends Neurosci 27:447–452
Keshamouni VG, Jagtap P, Michailidis G, Strahler JR, Kuick R, Reka AK, Papoulias P, Krishnapuram R, Srirangam A, Standiford TJ et al (2009) Temporal quantitative proteomics by iTRAQ 2D-LC-MS/MS and corresponding mRNA expression analysis identify post-transcriptional modulation of actin-cytoskeleton regulators during TGF-beta-Induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Proteome Res 8:35–47
Kim SG, Kim HA, Jong HS, Park JH, Kim NK, Hong SH, Kim TY, Bang YJ (2005) The endogenous ratio of Smad2 and Smad3 influences the cytostatic function of Smad3. Mol Biol Cell 16:4672–4683
Kretschmer A, Moepert K, Dames S, Sternberger M, Kaufmann J, Klippel A (2003) Differential regulation of TGF-beta signaling through Smad2, Smad3 and Smad4. Oncogene 22:6748–6763
Krieglstein K, Farkas L, Unsicker K (1998a) TGF-beta regulates the survival of ciliary ganglionic neurons synergistically with ciliary neurotrophic factor and neurotrophins. J Neurobiol 37:563–572
Krieglstein K, Henheik P, Farkas L, Jaszai J, Galter D, Krohn K, Unsicker K (1998b) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor requires transforming growth factor-beta for exerting its full neurotrophic potential on peripheral and CNS neurons. J Neurosci 18:9822–9834
Kumar A, Novoselov V, Celeste AJ, Wolfman NM, ten Dijke P, Kuehn MR (2001) Nodal signaling uses activin and transforming growth factor-beta receptor-regulated Smads. J Biol Chem 276:656–661
Labbe E, Silvestri C, Hoodless PA, Wrana JL, Attisano L (1998) Smad2 and Smad3 positively and negatively regulate TGF beta-dependent transcription through the forkhead DNA-binding protein FAST2. Mol Cell 2:109–120
Lagna G, Hata A, Hemmati-Brivanlou A, Massague J (1996) Partnership between DPC4 and SMAD proteins in TGF-beta signalling pathways. Nature 383:832–836
Liao CW, Fan CK, Kao TC, Ji DD, Su KE, Lin YH, Cho WL (2008) Brain injury-associated biomarkers of TGF-beta1, S100B, GFAP, NF-L, tTG, AbetaPP, and tau were concomitantly enhanced and the UPS was impaired during acute brain injury caused by Toxocara canis in mice. BMC Infect Dis 8:84
Lois C, Alvarez-Buylla A (1993) Proliferating subventricular zone cells in the adult mammalian forebrain can differentiate into neurons and glia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:2074–2077
Lois C, Alvarez-Buylla A (1994) Long-distance neuronal migration in the adult mammalian brain. Science 264:1145–1148
Luskin MB (1993) Restricted proliferation and migration of postnatally generated neurons derived from the forebrain subventricular zone. Neuron 11:173–189
Ma M, Ma Y, Yi X, Guo R, Zhu W, Fan X, Xu G, Frey WH 2nd, Liu X (2008) Intranasal delivery of transforming growth factor-beta1 in mice after stroke reduces infarct volume and increases neurogenesis in the subventricular zone. BMC Neurosci 9:117
Makwana M, Jones LL, Cuthill D, Heuer H, Bohatschek M, Hristova M, Friedrichsen S, Ormsby I, Bueringer D, Koppius A et al (2007) Endogenous transforming growth factor beta 1 suppresses inflammation and promotes survival in adult CNS. J Neurosci 27:11201–11213
Marzella PL, Gillespie LN, Clark GM, Bartlett PF, Kilpatrick TJ (1999) The neurotrophins act synergistically with LIF and members of the TGF-beta superfamily to promote the survival of spiral ganglia neurons in vitro. Hear Res 138:73–80
Massague J (2003) Integration of Smad and MAPK pathways: a link and a linker revisited. Genes Dev 17:2993–2997
Massague J, Seoane J, Wotton D (2005) Smad transcription factors. Genes Dev 19:2783–2810
Matsuura I, Denissova NG, Wang G, He D, Long J, Liu F (2004) Cyclin-dependent kinases regulate the antiproliferative function of Smads. Nature 430:226–231
McKinnon RD, Piras G, Ida JA Jr, Dubois-Dalcq M (1993) A role for TGF-beta in oligodendrocyte differentiation. J Cell Biol 121:1397–1407
Miller MW (2003) Expression of transforming growth factor-beta in developing rat cerebral cortex: effects of prenatal exposure to ethanol. J Comp Neurol 460:410–424
Miller MW, Luo J (2002) Effects of ethanol and transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta) on neuronal proliferation and nCAM expression. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:1281–1285
Misumi S, Kim TS, Jung CG, Masuda T, Urakawa S, Isobe Y, Furuyama F, Nishino H, Hida H (2008) Enhanced neurogenesis from neural progenitor cells with G1/S-phase cell cycle arrest is mediated by transforming growth factor beta1. Eur J NeuroSci 28:1049–1059
Moreno-Lopez B, Romero-Grimaldi C, Noval JA, Murillo-Carretero M, Matarredona ER, Estrada C (2004) Nitric oxide is a physiological inhibitor of neurogenesis in the adult mouse subventricular zone and olfactory bulb. J Neurosci 24:85–95
Moustakas A, Stournaras C (1999) Regulation of actin organisation by TGF-beta in H-ras-transformed fibroblasts. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 8):1169–1179
Moustakas A, Pardali K, Gaal A, Heldin CH (2002) Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling in regulation of cell growth and differentiation. Immunol Lett 82:85–91
Newman MP, Feron F, Mackay-Sim A (2000) Growth factor regulation of neurogenesis in adult olfactory epithelium. Neuroscience 99:343–350
Oh SP, Seki T, Goss KA, Imamura T, Yi Y, Donahoe PK, Li L, Miyazono K, ten Dijke P, Kim S et al (2000) Activin receptor-like kinase 1 modulates transforming growth factor-beta 1 signaling in the regulation of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:2626–2631
Satoh M, Sugino H, Yoshida T (2000) Activin promotes astrocytic differentiation of a multipotent neural stem cell line and an astrocyte progenitor cell line from murine central nervous system. Neurosci Lett 284:143–146
Saunier EF, Akhurst RJ (2006) TGF beta inhibition for cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 6:565–578
Semple-Rowland SL, Mahatme A, Popovich PG, Green DA, Hassler G Jr, Stokes BT, Streit WJ (1995) Analysis of TGF-beta 1 gene expression in contused rat spinal cord using quantitative RT-PCR. J Neurotrauma 12:1003–1014
Shimizu A, Kato M, Nakao A, Imamura T, ten DijkeP H, CH KM, Shimada S, Miyazono K (1998) Identification of receptors and Smad proteins involved in activin signalling in a human epidermal keratinocyte cell line. Genes Cells 3:125–134
Siegenthaler JA, Miller MW (2005) Transforming growth factor beta 1 promotes cell cycle exit through the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 in the developing cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 25:8627–8636
Silva R, Lu J, Wu Y, Martins L, Almeida OF, Sousa N (2006) Mapping cellular gains and losses in the postnatal dentate gyrus: implications for psychiatric disorders. Exp Neurol 200:321–331
Snyder EY, Yoon C, Flax JD, Macklis JD (1997) Multipotent neural precursors can differentiate toward replacement of neurons undergoing targeted apoptotic degeneration in adult mouse neocortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:11663–11668
Song HJ, Stevens CF, Gage FH (2002) Neural stem cells from adult hippocampus develop essential properties of functional CNS neurons. Nat Neurosci 5:438–445
Suh H, Consiglio A, Ray J, Sawai T, D'Amour KA, Gage FH (2007) In vivo fate analysis reveals the multipotent and self-renewal capacities of Sox2+ neural stem cells in the adult hippocampus. Cell Stem Cell 1:515–528
ten Dijke P, Hill CS (2004) New insights into TGF-beta-Smad signalling. Trends Biochem Sci 29:265–273
Ten Dijke P, Goumans MJ, Itoh F, Itoh S (2002) Regulation of cell proliferation by Smad proteins. J Cell Physiol 191:1–16
Thored P, Wood J, Arvidsson A, Cammenga J, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2007) Long-term neuroblast migration along blood vessels in an area with transient angiogenesis and increased vascularization after stroke. Stroke 38:3032–3039
Unsicker K, Strelau J (2000) Functions of transforming growth factor-beta isoforms in the nervous system. Cues based on localization and experimental in vitro and in vivo evidence. Eur J Biochem 267:6972–6975
Unsicker K, Flanders KC, Cissel DS, Lafyatis R, Sporn MB (1991) Transforming growth factor beta isoforms in the adult rat central and peripheral nervous system. Neuroscience 44:613–625
Vardouli L, Moustakas A, Stournaras C (2005) LIM-kinase 2 and cofilin phosphorylation mediate actin cytoskeleton reorganization induced by transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem 280:11448–11457
Wachs FP, Winner B, Couillard-Despres S, Schiller T, Aigner R, Winkler J, Bogdahn U, Aigner L (2006) Transforming growth factor-beta1 is a negative modulator of adult neurogenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:358–370
Wrana JL, Attisano L, Carcamo J, Zentella A, Doody J, Laiho M, Wang XF, Massague J (1992) TGF beta signals through a heteromeric protein kinase receptor complex. Cell 71:1003–1014
Yang X, Letterio JJ, Lechleider RJ, Chen L, Hayman R, Gu H, Roberts AB, Deng C (1999) Targeted disruption of SMAD3 results in impaired mucosal immunity and diminished T cell responsiveness to TGF-beta. Embo J 18:1280–1291
Zhao C, Deng W, Gage FH (2008) Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell 132:645–660
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Chuxia Deng (NIH) for supplying the Smad3 null mice and are grateful for the encouragement and support we received from Dr. Anita Roberts when first starting this project. We thank Helina Moges and Matthew Adams for significant technical assistance and past and present members of the Symes lab for their helpful comments and suggestions. This work was supported by a translational research grant from the Defense Brain and Spinal Cord Injury Program (AJS). The opinions and assertions contained herein are the private opinions of the authors and are not to be construed as reflecting the views of the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, the US Department of Defense, or the Government of the USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Symes, A.J. Smad3 Deficiency Reduces Neurogenesis in Adult Mice. J Mol Neurosci 41, 383–396 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-010-9329-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-010-9329-x