Abstract
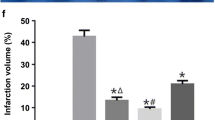
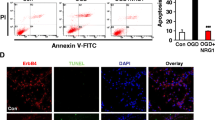
The aim is to investigate the effect of neuregulin-1β (NRG-1β) on the neuronal apoptosis and the expressions of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT3) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in rats following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. The animal models of middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R) were established by an intraluminal filament method from left external–internal carotid artery in 100 cases of adult healthy male Wister rats. NRG-1β was administered from the internal carotid artery (ICA) into MCA in the treatment group. The neuronal apoptosis was detected by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transference-mediated biotinylated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick-end labeling technique. The expression alternations of STAT3 and GFAP proteins were determined by fluorescent labeling analysis and Western blotting assay. Ischemic cerebral injury could induce neuronal apoptosis. Furthermore, with the duration of ischemia, the amount of apoptotic cells increased in the control group. These apoptotic cells distributed in various brain regions, especially the cortex, striatum, and hippocampus, while only a small amount of apoptotic cells could be observed in the treatment group, and there were significant differences compared with that in the control group (P < 0.01). The expressions of STAT3 and GFAP proteins in brain tissue gradually increased in the control group with the duration of ischemia. And NRG-1β could elevate the expressional level of STAT3 and GFAP proteins in contrast to the control group (P < 0.05). NRG-1β may play a neuroprotective role in cerebral ischemic insult by activating JAK/STAT signal transduction pathway, promoting the astrocyte gumnosis and regulating the anti-apoptosis mechanism in neurocytes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baliga, R. R., Pimental, D. R., Zhao, Y. Y., et al. (1999). NRG-1-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Role of PI-3-kinase, p70(S6K), and MEK-MAPK-RSK. The American Journal of Physiology, 277(5Pt 2), H2026–H2037.
Currie, R. W., Ellison, J. A., White, R. F., et al. (2000). Benign focal ischemic preconditioning induces neuronal Hsp70 and prolonged astrogliosis with expression of Hsp27. Brain Research, 863(1–2), 169–181.
Guo, Y. L., & Gao, Y. M. (2002). The time relationships between apoptosis of neuron and endotheliocyte with the expression of Bcl-2 and Bax after focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats. Acta Anatomica Sinica, 33(2), 151–156.
Guo, Y. L., Wang, L., Gao, X. Y., et al. (2005). Gene expression of nerve cell proliferation associated factor following cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats. Chinese Journal of Anatomy, 28(5), 538–541.
Justicia, C., Gabriel, C., & Planas, A. M. (2000). Activation of the JAK/STAT pathway following transient focal cerebral ischemia signal through JAK1 and STAT3 in astrocytes. Glia, 30(3), 253–270.
Li, B. S., Ma, W., Jaffe, H., et al. (2003). Cyclin-dependent kinase-5 is involved in neuregulin dependent activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt activity mediating neuronal survival. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278(37), 35702–35709.
Liu, D., Smith, C. L., Barone, F. C., et al. (1999). Astrocytic demise precedes delayed neuronal death in focal ischemic rat brain. Brain Research—Molecular Brain Research, 68(1), 29–41.
Nie, Y. X., Wu, X. L., & Guo, M. (2006). The expressions of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT3)in cortex in rats after focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 26(11), 1522–1524.
Rohrbach, S., Yan, X., Weinberg, E. O., et al. (1999). Neuregulin in cardiac hypertrophy in rats with aortic stenosis. Differential expression of erbB2 and erbB4 receptors. Circulation, 100(4), 407–412.
Strǒmberg, H., Svensson, S. P., & Hermanson, O. (2000). Distribution of the transcription factor signal transducer and activator of transcription3 in the rat central nervous system and dorsal root ganglia. Brain Research, 853(1), 105–114.
Suzuki, S., Tanaka, K., Nogawa, S., et al. (2001). Phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (Stat3) after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Experimental Neurology, 170(1), 63–71.
Suzuki, S., Yamashita, T., Tanaka, K., et al. (2005). Activation of cytokine signaling through leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR)/gp130 attenuates ischemic brain injury in rats. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 25(6), 685–693.
Wang, X. M., Feng, J. C., & Rao, M. L. (2001). Protection of reactive astrocyte on ischemic neurons. Journal of Apoplexy and Nervous Diseases, 18(1), 63–65.
Wen, T. C., Peng, H., Hata, R., et al. (2001). Induction of phosphorylated-STAT3 following focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Neuroscience Letters, 303(3), 153–156.
Xu, Z., & Ford, B. D. (2005). Upregulation of erbB receptors in rat brain after middle cerebral arterial occlusion. Neuroscience Letters, 375(3), 181–186.
Xu, Z., Jiang, J., Ford, G., et al. (2004). Neuregulin-1 is neuroprotective and attenuates inflammatory responses induced by ischemic stroke. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 322(2), 440–446.
Yanamoto, H., Mizuta, I., Nagata, I., et al. (2000). Infarct tolerance accompanied enhanced BDNF-like immunoreactivity in neuronal nuclei. Brain Research, 877(2), 331–344.
Yu, H., & Jove, R. (2004). The STATs of cancer—new molecular targets come of age. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 4(2), 97–105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Natural Science Fund of Shandong Province (Y2004C04).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Zhang, R., Guo, Yl. et al. Effect of Neuregulin on Apoptosis and Expressions of STAT3 and GFAP in Rats Following Cerebral Ischemic Reperfusion. J Mol Neurosci 37, 67–73 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9121-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9121-3