Abstract
Introduction
Non-coding RNAs have opened a new window in cancer biology. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), as a family of non-coding RNAs, play an important role in the gene regulation. The aberrant expression of these small molecules has been documented to involve in colorectal cancer (CRC) pathogenesis. This study aimed to examine the expression of miRNAs in CRC and to correlate their expression levels with histological markers (Ki-67 and CD34).
Materials and Methods
Tumor tissues and matched normal adjacent tissues were collected from 36 patients with newly diagnosed CRC. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of tumor tissues was performed for Ki-67 (proliferation) and CD34 (angiogenesis) markers, and the immunoexpression staining scores were obtained. A polyadenylation SYBER Green quantitative real-time PCR technique was used to quantify the expression of a panel of five CRC-related miRNAs (hsa-miR-21, 31, 20a, 133b, and 145). Histopathological (H) scores and miRNA expression levels were correlated with clinicopathological features including the degree of differentiation, staging, and lymphovascular invasion.
Results
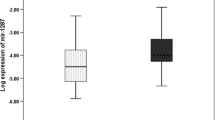
Our results showed the significant difference between the two groups for the expression level of hsa-miR-21, hsa-miR-31, hsa-miR-145, and miR-20a (P < 0.001), but not for hsa-miR-133b (P = 0.57). Further analysis revealed an inverse significant correlation between hsa-miR-145 and Ki-67 (r = − 0.942, P < 0.001). While a positive correlation was observed between hsa-miR-21 and Ki-67 (r = 0.920, P < 0.001), and hsa-miR-21 and CD34 (r = 0.981, P < 0.001). Also, a positive correlation between hsa-miR-31 and Ki-67 (r = 0.913, P < 0.001), hsa-miR-31 and CD34 (r = 0.798, P < 0.05), hsa-miR-20a and Ki-67 (r = 0.871, P < 0.001), and hsa-miR-20a and CD34 (r = 0.890, P < 0.001) was found.
Conclusion
Dysregulation of miRNAs and correlation with molecular histopathology indicate a biological role for miRNAs in various cellular processes including cell proliferation and angiogenesis in CRC development. On the other hand, the pattern of miRNA expression and its correlation with histological markers are potentially valuable to apply as diagnostic biomarkers for CRC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari A, et al. Modulation of transforming growth factor-β signaling transducers in colon adenocarcinoma cells induced by staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(1):909–14. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.4596.
Akbari A, Amanpour S, Muhammadnejad S, Ghahremani M, Ghaffari S, Dehpour A, et al. Evaluation of antitumor activity of a TGF-beta receptor I inhibitor (SD-208) on human colon adenocarcinoma. DARU J Pharm Sci. 2014;22(1):47. https://doi.org/10.1186/2008-2231-22-47.
Mobini GR, Ghahremani MH, Amanpour S, Dehpour AR, Akbari A, Hoseiniharouni SM, et al. Transforming growth factor beta-induced factor 2-linked X (TGIF2LX) regulates two morphogenesis genes, Nir1 and Nir2 in human colorectal. Acta Med Iran. 2016;54(5):302–7.
Agah S, Akbari A, Talebi A, Masoudi M, Sarveazad A, Mirzaei A, et al. Quantification of plasma cell-free circulating DNA at different stages of colorectal cancer. Cancer Investig. 2017;35(10):625–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/07357907.2017.1408814.
Akbari A, et al. Homeodomain protein transforming growth factor beta-induced factor 2 like, X-linked function in colon adenocarcinoma cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev: APJCP. 2017;18(8):2101.6.
Abastabar M, Akbari A, Akhtari J, Hedayati MT, Shokohi T, Mehrad-Majd H, et al. In vitro antitumor activity of patulin on cervical and colorectal cancer cell lines. MAZU-CMM. 2017;3(1):25–9.
Sagaert X. Prognostic biomarkers in colorectal cancer: where do we stand? Virchows Arch. 2014;464(3):379–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-013-1532-z.
Zaha DC. Significance of immunohistochemistry in breast cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 2014;5(3):382–92. https://doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v5.i3.382.
Espinosa CES, Slack FJ. Cancer issue: the role of microRNAs in cancer. Yale J Biol Med. 2006;79(3–4):131.
Zhou F, Li S, Meng HM, Qi LQ, Gu L. MicroRNA and histopathological characterization of pure mucinous breast carcinoma. Cancer Biol Med. 2013;10(1):22–7. https://doi.org/10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2013.01.004.
Fadakar P, Akbari A, Ghassemi F, Mobini GR, Mohebi M, Bolhassani M, et al. Evaluation of SD-208, a TGF-β-RI kinase inhibitor, as an anticancer agent in retinoblastoma. Acta Med Iran. 2016;54(6):352–8.
Cho WC. MicroRNAs: potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis, prognosis and targets for therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42(8):1273–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2009.12.014.
Berger F, Reiser MF. Micro-RNAs as potential new molecular biomarkers in oncology: have they reached relevance for the clinical imaging sciences. Theranostics. 2013;3(12):943–52. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.7445.
Akbari A, Ghahremani MH, Mobini GR, Abastabar M, Akhtari J, Bolhassani M, et al. Down-regulation of miR-135b in colon adenocarcinoma induced by a TGF-β receptor I kinase inhibitor (SD-208). Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015;18(9):856–61.
Akbari A, et al. Evaluation of antitumor activity of a TGF-beta receptor I inhibitor (SD-208) on human colon adenocarcinoma. DARU J Pharm Sci. 2014;22(1):1.
Akbari, A., et al. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B down-regulates the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling transducers in human glioblastoma. Jundishapur J Microbiol, 2016. 9(5).
Karimi A, Majidzadeh-A K, Madjd Z, et al. Effect of copper sulfate on expression of endogenous L1 retrotransposons in HepG2 cells (hepatocellular carcinoma). Biol Trace Elem Res. 2015;165:131–4.
Faghihloo E, Akbari A, Adjaminezhad-Fard F, Mokhtari-Azad T. Transcriptional regulation of E-cadherin and oncoprotein E7 by valproic acid in HPV positive cell lines. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016;19(6):601–7.
Mirzaei A, Madjd Z, Kadijani AA, Tavakoli-Yaraki M, Modarresi MH, Verdi J, et al. Evaluation of circulating cellular DCLK1 protein, as the most promising colorectal cancer stem cell marker, using immunoassay based methods. Cancer Biomark. 2016;17(3):301–11. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-160642.
Mirzaei A, Madjd Z, Amini Kadijani A, Alinaghi S, Akbari A, et al. Cancer stem cell’s potential clinical implications. Int J Cancer Manag. 2017;10(1):e5897. https://doi.org/10.17795/ijcp-5897.
Compton CC. Colorectal carcinoma: diagnostic, prognostic, and molecular features. Mod Pathol. 2003;16(4):376–88. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.MP.0000062859.46942.93.
De Mattos-Arruda L, Cortes J, Santarpia L, Vivancos A, Tabernero J, Reis-Filho JS, et al. Circulating tumour cells and cell-free DNA as tools for managing breast cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013;10(7):377–89. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.80.
Llombart-Bosch, A., et al., Cancer: clinical background and key challenges, in Cancer systems biology, bioinformatics and medicine. 2011, Springer. p. 29–93.
Molina R, Filella X, Augé JM, Fuentes R, Bover I, Rifa J, et al. Tumor markers (CEA, CA 125, CYFRA 21-1, SCC and NSE) in patients with non-small cell lung cancer as an aid in histological diagnosis and prognosis. Tumor Biol. 2003;24(4):209–18. https://doi.org/10.1159/000074432.
Choi WW, et al. Angiogenic and lymphangiogenic microvessel density in breast carcinoma: correlation with clinicopathologic parameters and VEGF-family gene expression. Mod Pathol. 2005;18(1):143–52. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.3800253.
Reddy KB. MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2015;15(1):38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-015-0185-1.
zur Hausen H. The role of microRNAs in human cancer. Int J Cancer. 2008;122(5):ix–x.
Schuster C, Budczies J, Faber C, Kirchner T, Hlubek F. MicroRNA expression profiling of specific cells in complex archival tissue stained by immunohistochemistry. Lab Investig. 2011;91(1):157–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2010.134.
Zhao D, Tu Y, Wan L, Bu L, Huang T, Sun X, et al. In vivo monitoring of angiogenesis inhibition via down-regulation of mir-21 in a VEGFR2-luc murine breast cancer model using bioluminescent imaging. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e71472. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071472.
Landskroner-Eiger S, Moneke I, Sessa WC. miRNAs as modulators of angiogenesis. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med. 2013;3(2):a006643. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a006643.
Buscaglia LEB, Li Y. Apoptosis and the target genes of miR-21. Chin J Cancer. 2011;30(6):371–80. https://doi.org/10.5732/cjc.30.0371.
Zhu S, Wu H, Wu F, Nie D, Sheng S, Mo YY. MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res. 2008;18(3):350–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.24.
Liu X, Cheng Y, Zhang S, Lin Y, Yang J, Zhang C. A necessary role of miR-221 and miR-222 in vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia. Circ Res. 2009;104(4):476–87. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.185363.
Cheng Y, Zhang C. MicroRNA-21 in cardiovascular disease. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010;3(3):251–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-010-9169-7.
Asangani I, et al. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27(15):2128–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210856.
Slaby O, Svoboda M, Fabian P, Smerdova T, Knoflickova D, Bednarikova M, et al. Altered expression of miR-21, miR-31, miR-143 and miR-145 is related to clinicopathologic features of colorectal cancer. Oncology. 2007;72(5–6):397–402. https://doi.org/10.1159/000113489.
Qi L, Bart J, Tan LP, Platteel I, Sluis T, Huitema S, et al. Expression of miR-21 and its targets (PTEN, PDCD4, TM1) in flat epithelial atypia of the breast in relation to ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2009;9(1):163. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-9-163.
Liu L-Z, Li C, Chen Q, Jing Y, Carpenter R, Jiang Y, et al. MiR-21 induced angiogenesis through AKT and ERK activation and HIF-1α expression. PLoS One. 2011;6(4):e19139. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019139.
Forsythe JA, Jiang BH, Iyer NV, Agani F, Leung SW, Koos RD, et al. Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16(9):4604–13. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.16.9.4604.
Breier G, Albrecht U, Sterrer S, Risau W. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor during embryonic angiogenesis and endothelial cell differentiation. Development. 1992;114(2):521–32.
Plate KH, Breier G, Weich HA, Risau W. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature. 1992;359(6398):845–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/359845a0.
Harris VK, Coticchia CM, Kagan BL, Ahmad S, Wellstein A, Riegel AT. Induction of the angiogenic modulator fibroblast growth factor-binding protein by epidermal growth factor is mediated through both MEK/ERK and p38 signal transduction pathways. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(15):10802–11. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.15.10802.
Song MS, Salmena L, Pandolfi PP. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(5):283–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3330.
Xia C, Meng Q, Cao Z, Shi X, Jiang BH. Regulation of angiogenesis and tumor growth by p110 alpha and AKT1 via VEGF expression. J Cell Physiol. 2006;209(1):56–66. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.20707.
Wang S, Olson EN. AngiomiRs—key regulators of angiogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009;19(3):205–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2009.04.002.
Cheng D, Zhao S, Tang H, Zhang D, Sun H, Yu F, et al. MicroRNA-20a-5p promotes colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by downregulating Smad4. Oncotarget. 2016;7(29):45199–213. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9900.
Zhang GJ, et al. miR-20a is an independent prognostic factor in colorectal cancer and is involved in cell metastasis. Mol Med Rep. 2014;10(1):283–91. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.2144.
Dews M, Homayouni A, Yu D, Murphy D, Sevignani C, Wentzel E, et al. Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a Myc-activated microRNA cluster. Nat Genet. 2006;38(9):1060–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1855.
Suárez Y, et al. Dicer-dependent endothelial microRNAs are necessary for postnatal angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2008;105(37):14082–7. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804597105.
Kuhnert F, Kuo CJ. miR-17-92 angiogenesis micromanagement. Blood. 2010;115(23):4631–2. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-03-276428.
Wong H-KA, Fatimy RE, Onodera C, Wei Z, Yi M, Mohan A, et al. The cancer genome atlas analysis predicts microRNA for targeting cancer growth and vascularization in glioblastoma. Mol Ther. 2015;23(7):1234–47. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2015.72.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65(16):7065–70. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1783.
Michael MZ, O' Connor SM, van Holst Pellekaan NG, Young GP, James RJ. Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Note: Susan M. O'Connor and Nicholas G. van Holst Pellekaan contributed equally to this work. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1(12):882–91.
Takagi T, Iio A, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T, Tanigawa N, Akao Y. Decreased expression of microRNA-143 and-145 in human gastric cancers. Oncology. 2009;77(1):12–21. https://doi.org/10.1159/000218166.
Liu L-Z, Hu XW, Xia C, He J, Zhou Q, Shi X, et al. Reactive oxygen species regulate epidermal growth factor-induced vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression through activation of AKT and P70S6K1 in human ovarian cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;41(10):1521–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.08.003.
Xu Q, Liu LZ, Qian X, Chen Q, Jiang Y, Li D, et al. MiR-145 directly targets p70S6K1 in cancer cells to inhibit tumor growth and angiogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(2):761–74. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr730.
Yu Z, Tozeren A, Pestell RG. Function of miRNAs in tumor cell proliferation, in microRNA in cancer. 2013, Springer. p. 13–27.
Zhou Q, Liu LZ, Fu B, Hu X, Shi X, Fang J, et al. Reactive oxygen species regulate insulin-induced VEGF and HIF-1α expression through the activation of p70S6K1 in human prostate cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2006;28(1):28–37. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgl085.
Funding
This study was funded by the Iran University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. 26649).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This project was approved by the ethical and research committee (IR.IUMS.REC 1394.26649).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emami, S.S., Akbari, A., Zare, AA. et al. MicroRNA Expression Levels and Histopathological Features of Colorectal Cancer. J Gastrointest Canc 50, 276–284 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-018-0055-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-018-0055-x