Abstract
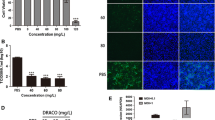
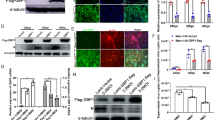
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) causes a series of inflammatory reactions in sites of infection, companied by the upregulation of key inflammatory factor TNFα. TNFα, which serves as a “master regulator” of inflammatory cytokine production, is mainly produced by macrophages at the early infection stage. Here, we showed that porcine alveolar macrophages produced a great amount of soluble TNFα upon PRRSV infection. Furthermore, we found that TNFα had great anti-PRRSV effect. Next, by using inhibitor and genetic modification methods, we addressed that porcine TNFα production was mediated by ADAM17. Lastly, we proved that the 78Arg–Ser–Ser motif of porcine TNFα contained the essential information for efficient cleavage. Taken together, our findings provide the direct evidence that ADAM17 cleaves porcine TNFα, which represents a new view for identifying potential therapeutic targets in anti-PRRSV therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benfield DA, Nelson E, Collins JE, Harris L, Goyal SM, Robison D, Christianson WT, Morrison RB, Gorcyca D, Chladek D. Characterization of swine infertility and respiratory syndrome (SIRS) virus (isolate ATCC VR-2332). J Vet Diagn Invest. 1992;4(2):127–33.
Cavanagh D. Nidovirales: a new order comprising Coronaviridae and Arteriviridae. Arch Virol. 1997;142(3):629–33.
Meulenberg JJ, Hulst MM, de Meijer EJ, Moonen PL, den Besten A, de Kluyver EP, Wensvoort G, Moormann RJ. Lelystad virus, the causative agent of porcine epidemic abortion and respiratory syndrome (PEARS), is related to LDV and EAV. Virology. 1993;192(1):62–72. doi:10.1006/viro.1993.1008.
Nelsen CJ, Murtaugh MP, Faaberg KS. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus comparison: divergent evolution on two continents. J Virol. 1999;73(1):270–80.
Zhou L, Chen S, Zhang J, Zeng J, Guo X, Ge X, Zhang D, Yang H. Molecular variation analysis of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in China. Virus Res. 2009;145(1):97–105. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2009.06.014.
Tian K, Yu X, Zhao T, Feng Y, Cao Z, Wang C, Hu Y, Chen X, Hu D, Tian X, Liu D, Zhang S, Deng X, Ding Y, Yang L, Zhang Y, Xiao H, Qiao M, Wang B, Hou L, Wang X, Yang X, Kang L, Sun M, Jin P, Wang S, Kitamura Y, Yan J, Gao GF. Emergence of fatal PRRSV variants: unparalleled outbreaks of atypical PRRS in China and molecular dissection of the unique hallmark. PLoS ONE. 2007;2(6):e526. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000526.
Li Y, Wang X, Bo K, Wang X, Tang B, Yang B, Jiang W, Jiang P. Emergence of a highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in the Mid-Eastern region of China. Vet J. 2007;174(3):577–84. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.07.032.
Duan X, Nauwynck HJ, Pensaert MB. Effects of origin and state of differentiation and activation of monocytes/macrophages on their susceptibility to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV). Arch Virol. 1997;142(12):2483–97.
Thanawongnuwech R, Thacker B, Halbur P, Thacker EL. Increased production of proinflammatory cytokines following infection with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004;11(5):901–8. doi:10.1128/cdli.11.5.901-908.2004.
Guo B, Lager KM, Henningson JN, Miller LC, Schlink SN, Kappes MA, Kehrli ME Jr, Brockmeier SL, Nicholson TL, Yang HC, Faaberg KS. Experimental infection of United States swine with a Chinese highly pathogenic strain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Virology. 2013;435(2):372–84. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2012.09.013.
Choi C, Chae C. Expression of tumour necrosis factor-alpha is associated with apoptosis in lungs of pigs experimentally infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Res Vet Sci. 2002;72(1):45–9. doi:10.1053/rvsc.2001.0519.
Beutler B, Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986;320(6063):584–8. doi:10.1038/320584a0.
Aggarwal BB. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3(9):745–56. doi:10.1038/nri1184.
Cirino NM, Panuska JR, Villani A, Taraf H, Rebert NA, Merolla R, Tsivitse P, Gilbert IA. Restricted replication of respiratory syncytial virus in human alveolar macrophages. J Gen Virol. 1993;74(Pt 8):1527–37.
Kollias G, Douni E, Kassiotis G, Kontoyiannis D. The function of tumour necrosis factor and receptors in models of multi-organ inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999;58(Suppl 1):I32–9.
Lane BR, Markovitz DM, Woodford NL, Rochford R, Strieter RM, Coffey MJ. TNF-alpha inhibits HIV-1 replication in peripheral blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages by inducing the production of RANTES and decreasing C–C chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) expression. J Immunol. 1999;163(7):3653–61.
Carswell EA, Old LJ, Kassel RL, Green S, Fiore N, Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1975;72(9):3666–70.
Tracey D, Klareskog L, Sasso EH, Salfeld JG, Tak PP. Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanisms of action: a comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther. 2008;117(2):244–79. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.10.001.
Pennica D, Nedwin GE, Hayflick JS, Seeburg PH, Derynck R, Palladino MA, Kohr WJ, Aggarwal BB, Goeddel DV. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984;312(5996):724–9.
Black RA, Rauch CT, Kozlosky CJ, Peschon JJ, Slack JL, Wolfson MF, Castner BJ, Stocking KL, Reddy P, Srinivasan S, Nelson N, Boiani N, Schooley KA, Gerhart M, Davis R, Fitzner JN, Johnson RS, Paxton RJ, March CJ, Cerretti DP. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumour-necrosis factor-alpha from cells. Nature. 1997;385(6618):729–33. doi:10.1038/385729a0.
Edwards DR, Handsley MM, Pennington CJ. The ADAM metalloproteinases. Mol Asp Med. 2008;29(5):258–89.
Wang Y, Liang Y, Han J, Burkhart KM, Vaughn EM, Roof MB, Faaberg KS. Attenuation of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus strain MN184 using chimeric construction with vaccine sequence. Virology. 2008;371(2):418–29. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2007.09.032.
Barlaam B, Bird TG, Lambert-Van Der Brempt C, Campbell D, Foster SJ, Maciewicz R. New alpha-substituted succinate-based hydroxamic acids as TNFalpha convertase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1999;42(23):4890–908.
Moore CB, Guthrie EH, Huang MT, Taxman DJ. Short hairpin RNA (shRNA): design, delivery, and assessment of gene knockdown. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;629:141–58. doi:10.1007/978-1-60761-657-3_10.
Guo L, Niu J, Yu H, Gu W, Li R, Luo X, Huang M, Tian Z, Feng L, Wang Y. Modulation of CD163 expression by metalloprotease ADAM17 regulates porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus entry. J Virol. 2014;88(18):10448–58. doi:10.1128/jvi.01117-14.
Gu W, Guo L, Yu H, Niu J, Huang M, Luo X, Li R, Tian Z, Feng L, Wang Y. Involvement of CD16 in antibody-dependent enhancement of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. J Gen Virol. 2015;. doi:10.1099/vir.0.000118.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262.
Moore CT, Lonsdorf EV, Knutson MG, Laskowski HP, Lor SK. Adaptive management in the U.S. National Wildlife Refuge System: science–management partnerships for conservation delivery. J Environ Manag. 2011;92(5):1395–402. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.10.065.
Maini RN, Elliott MJ, Brennan FM, Feldmann M. Beneficial effects of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) blockade in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1995;101(2):207–12.
Aggarwal BB, Gupta SC, Kim JH. Historical perspectives on tumor necrosis factor and its superfamily: 25 years later, a golden journey. Blood. 2012;119(3):651–65. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-04-325225.
Choi C, Cho WS, Kim B, Chae C. Expression of interferon-gamma and tumour necrosis factor-alpha in pigs experimentally infected with Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus (PRRSV). J Comp Pathol. 2002;127(2–3):106–13.
Mestan J, Digel W, Mittnacht S, Hillen H, Blohm D, Moller A, Jacobsen H, Kirchner H. Antiviral effects of recombinant tumour necrosis factor in vitro. Nature. 1986;323(6091):816–9. doi:10.1038/323816a0.
Rio C, Buxbaum JD, Peschon JJ, Corfas G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme is required for cleavage of erbB4/HER4. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(14):10379–87.
Kumakura S, Ishikura H, Maniwa Y, Munemasa S, Tsumura H, Masuda J, Kobayashi S. Activation of protein kinase C enhances TNF-alpha-induced differentiation by preventing apoptosis via rapid up-regulation of c-Myc protein expression in HL-60 cells. Leuk Lymphoma. 2003;44(3):497–503. doi:10.1080/1042819021000047010.
Poli G, Kinter A, Justement JS, Kehrl JH, Bressler P, Stanley S, Fauci AS. Tumor necrosis factor alpha functions in an autocrine manner in the induction of human immunodeficiency virus expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87(2):782–5.
Moss ML, Jin SL, Milla ME, Bickett DM, Burkhart W, Carter HL, Chen WJ, Clay WC, Didsbury JR, Hassler D, Hoffman CR, Kost TA, Lambert MH, Leesnitzer MA, McCauley P, McGeehan G, Mitchell J, Moyer M, Pahel G, Rocque W, Overton LK, Schoenen F, Seaton T, Su JL, Becherer JD, et al. Cloning of a disintegrin metalloproteinase that processes precursor tumour-necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1997;385(6618):733–6. doi:10.1038/385733a0.
Gomez-Laguna J, Salguero FJ, Pallares FJ, Fernandez de Marco M, Barranco I, Ceron JJ, Martinez-Subiela S, Van Reeth K, Carrasco L. Acute phase response in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010;33(6):e51–8. doi:10.1016/j.cimid.2009.11.003.
von Rosen T, Lohse L, Nielsen J, Uttenthal A. Classical swine fever virus infection modulates serum levels of INF-alpha, IL-8 and TNF-alpha in 6-month-old pigs. Res Vet Sci. 2013;95(3):1262–7. doi:10.1016/j.rvsc.2013.09.011.
Kim B, Ahn KK, Ha Y, Lee YH, Kim D, Lim JH, Kim SH, Kim MY, Cho KD, Lee BH, Chae C. Association of tumor necrosis factor-alpha with fever and pulmonary lesion score in pigs experimentally infected with swine influenza virus subtype H1N2. J Vet Med Sci. 2009;71(5):611–6.
Gao W, Sun W, Qu B, Cardona CJ, Powell K, Wegner M, Shi Y, Xing Z. Distinct regulation of host responses by ERK and JNK MAP kinases in swine macrophages infected with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 influenza virus. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(1):e30328. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030328.
Gimeno M, Darwich L, Diaz I, de la Torre E, Pujols J, Martin M, Inumaru S, Cano E, Domingo M, Montoya M, Mateu E. Cytokine profiles and phenotype regulation of antigen presenting cells by genotype-I porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus isolates. Vet Res. 2011;42:9. doi:10.1186/1297-9716-42-9.
Lopez-Fuertes L, Campos E, Domenech N, Ezquerra A, Castro JM, Dominguez J, Alonso F. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus down-modulates TNF-alpha production in infected macrophages. Virus Res. 2000;69(1):41–6.
Van Reeth K, Labarque G, Nauwynck H, Pensaert M. Differential production of proinflammatory cytokines in the pig lung during different respiratory virus infections: correlations with pathogenicity. Res Vet Sci. 1999;67(1):47–52. doi:10.1053/rvsc.1998.0277.
Le J, Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987;56(3):234–48.
Lehmann C, Sprenger H, Nain M, Bacher M, Gemsa D. Infection of macrophages by influenza A virus: characteristics of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF alpha) gene expression. Res Virol. 1996;147(2–3):123–30.
Seo SH, Webster RG. Tumor necrosis factor alpha exerts powerful anti-influenza virus effects in lung epithelial cells. J Virol. 2002;76(3):1071–6.
Li S, Wang J, He WR, Feng S, Li Y, Wang X, Liao Y, Qin HY, Li LF, Dong H, Sun Y, Luo Y, Qiu HJ. Thioredoxin 2 is a novel E2-interacting protein that inhibits the replication of classical swine fever virus. J Virol. 2015;. doi:10.1128/jvi.00429-15.
Scheller J, Chalaris A, Garbers C, Rose-John S. ADAM17: a molecular switch to control inflammation and tissue regeneration. Trends Immunol. 2011;32(8):380–7. doi:10.1016/j.it.2011.05.005.
Etzerodt A, Rasmussen MR, Svendsen P, Chalaris A, Schwarz J, Galea I, Moller HJ, Moestrup SK. Structural basis for inflammation-driven shedding of CD163 ectodomain and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(2):778–88. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.520213.
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31372416).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Guo, L., Gu, W. et al. Production of porcine TNFα by ADAM17-mediated cleavage negatively regulates porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. Immunol Res 64, 711–720 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-015-8772-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-015-8772-8