Abstract
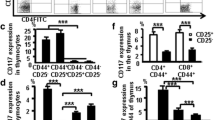
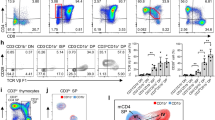
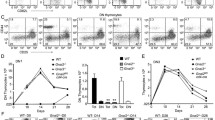
In human T cell development, the mechanisms that regulate cell fate decisions after TCRβ expression remain unclear. We defined the stages of T cell development that flank TCRβ expression and found distinct patterns of human T cell development. In half the subjects, T cell development progressed from the CD4–CD8– double-negative stage to the CD4+CD8+ double-positive (DP) stage through an immature single-positive (ISP) CD4+ intermediate. However, in some patients, CD4 and CD8 were expressed simultaneously and the ISP population was small. In each group of patients, CD3– ISP and DP thymocytes were subdivided into ISP1, ISP2, DP1, DP2, DP3, DP4, and DP5 developmental stages according to their expression of CD28, CD44, CD1a, CD7, CD45RO, and CD38. The ISP2, DP2, and DP3 thymocyte populations proliferated more robustly than ISP1 and DP1 and expressed markers consistent with TCRβ expression. After the DP3 stage, proliferation returned to baseline levels. We then analyzed protein levels of Ikaros, Helios, and Aiolos, the three Ikaros family members most abundantly expressed in human thymocytes. Ikaros and Helios expression increased transiently at the ISP2, DP2, and DP3 populations. Aiolos expression also increased at the ISP2, DP2, and DP3 stages, but its expression remained elevated throughout the DP4 and DP5 stages. In summary, we propose a model of human T cell development that reflects the asynchronous nature of TCRβ expression and we define the subpopulations of thymocytes that are highly proliferative and express Ikaros family members.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dik WA, Pike-Overzet K, Weerkamp F, et al. New insights on human T cell development by quantitative T cell receptor gene rearrangement studies and gene expression profiling. J Exp Med. 2005;201:1715–23.
Taghon T, Van de Walle I, De Smet G, De Smedt M, Leclercq G, Vandekerckhove B, Plum J. Notch signaling is required for proliferation but not for differentiation at a well-defined beta-selection checkpoint during human T-cell development. Blood. 2009;113:3254–63.
Carrasco YR, Trigueros C, Ramiro AR, de Yebenes VG, Toribio ML. Beta-selection is associated with the onset of CD8 beta chain expression on CD4(+)CD8 alpha alpha(+) pre-T cells during human intrathymic development. Blood. 1999;94:3491–8.
Blom B, Verschuren MC, Heemskerk MH, et al. TCR gene rearrangements and expression of the pre-T cell receptor complex during human T-cell differentiation. Blood. 1999;93:3033–43.
Joachims ML, Chain JL, Hooker SW, Knott-Craig CJ, Thompson LF. Human alpha beta and gamma delta thymocyte development: tCR gene rearrangements, intracellular TCR beta expression, and gamma delta developmental potential–differences between men and mice. J Immunol. 2006;176:1543–52.
Michie AM, Zuniga-Pflucker JC. Regulation of thymocyte differentiation: pre-TCR signals and beta-selection. Semin Immunol. 2002;14:311–23.
Aifantis I, Gounari F, Scorrano L, Borowski C, von Boehmer H. Constitutive pre-TCR signaling promotes differentiation through Ca2+ mobilization and activation of NF-kappaB and NFAT. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:403–9.
Fehling HJ, Krotkova A, Saint-Ruf C, von Boehmer H. Crucial role of the pre-T-cell receptor alpha gene in development of alpha beta but not gamma delta T cells. Nature. 1995;375:795–8.
Hahm K, Cobb BS, McCarty AS, et al. Helios, a T cell-restricted Ikaros family member that quantitatively associates with Ikaros at centromeric heterochromatin. Genes Dev. 1998;12:782–96.
Kelley CM, Ikeda T, Koipally J, Avitahl N, Wu L, Georgopoulos K, Morgan BA. Helios, a novel dimerization partner of Ikaros expressed in the earliest hematopoietic progenitors. Curr Biol. 1998;8:508–15.
Morgan B, Sun L, Avitahl N, et al. Aiolos, a lymphoid restricted transcription factor that interacts with Ikaros to regulate lymphocyte differentiation. EMBO J. 1997;16:2004–13.
Perdomo J, Holmes M, Chong B, Crossley M. Eos and pegasus, two members of the Ikaros family of proteins with distinct DNA binding activities. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:38347–54.
Sun L, Liu A, Georgopoulos K. Zinc finger-mediated protein interactions modulate Ikaros activity, a molecular control of lymphocyte development. EMBO J. 1996;15:5358–69.
Cortes M, Wong E, Koipally J, Georgopoulos K. Control of lymphocyte development by the Ikaros gene family. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999;11:167–71.
Ma S, Pathak S, Trinh L, Lu R. Interferon regulatory factors 4 and 8 induce the expression of Ikaros and Aiolos to down-regulate pre-B-cell receptor and promote cell-cycle withdrawal in pre-B-cell development. Blood. 2008;111:1396–403.
Thompson EC, Cobb BS, Sabbattini P, et al. Ikaros DNA-binding proteins as integral components of B cell developmental-stage-specific regulatory circuits. Immunity. 2007;26:335–44.
Mitchell JL, Seng A, Yankee TM. Expression and splicing of Ikaros family members in murine and human thymocytes. Mol Immunol. 2015 (in revision).
Xiong J, Parker BL, Dalheimer SL, Yankee TM. Interleukin-7 supports survival of T-cell receptor-beta-expressing CD4(−) CD8(−) double-negative thymocytes. Immunology. 2013;138:382–91.
Zeng L, Dalheimer SL, Yankee TM. Gads−/− mice reveal functionally distinct subsets of TCRbeta+ CD4−CD8− double-negative thymocytes. J Immunol. 2007;179:1013–21.
Fujii Y, Okumura M, Inada K, Nakahara K, Matsuda H. CD45 isoform expression during T cell development in the thymus. Eur J Immunol. 1992;22:1843–50.
von Boehmer H, Aifantis I, Feinberg J, et al. Pleiotropic changes controlled by the pre-T-cell receptor. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999;11:135–42.
Varas A, Jimenez E, Sacedon R, Rodriguez-Mahou M, Maroto E, Zapata AG, Vicente A. Analysis of the human neonatal thymus: evidence for a transient thymic involution. J Immunol. 2000;164:6260–7.
Weerkamp F, de Haas EF, Naber BA, Comans-Bitter WM, Bogers AJ, van Dongen JJ, Staal FJ. Age-related changes in the cellular composition of the thymus in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:834–40.
Murphy M, Epstein LB. Down syndrome (trisomy 21) thymuses have a decreased proportion of cells expressing high levels of TCR alpha, beta and CD3. A possible mechanism for diminished T cell function in Down syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990;55:453–67.
Harker N, Garefalaki A, Menzel U, Ktistaki E, Naito T, Georgopoulos K, Kioussis D. Pre-TCR signaling and CD8 gene bivalent chromatin resolution during thymocyte development. J Immunol. 2011;186:6368–77.
Ramiro AR, Trigueros C, Marquez C, San Millan JL, Toribio ML. Regulation of pre-T cell receptor (pT alpha-TCR beta) gene expression during human thymic development. J Exp Med. 1996;184:519–30.
Penit C, Lucas B, Vasseur F. Cell expansion and growth arrest phases during the transition from precursor (CD4−8−) to immature (CD4+8+) thymocytes in normal and genetically modified mice. J Immunol. 1995;154:5103–13.
Webb LM, Vigorito E, Wymann MP, Hirsch E, Turner M. Cutting edge: T cell development requires the combined activities of the p110gamma and p110delta catalytic isoforms of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Immunol. 2005;175:2783–7.
Saborit-Villarroya I, Vaisitti T, Rossi D, D’Arena G, Gaidano G, Malavasi F, Deaglio S. E2A is a transcriptional regulator of CD38 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2011;25:479–88.
Hsu LY, Lauring J, Liang HE, Greenbaum S, Cado D, Zhuang Y, Schlissel MS. A conserved transcriptional enhancer regulates RAG gene expression in developing B cells. Immunity. 2003;19:105–17.
Chen Z, Xiao Y, Zhang J, et al. Transcription factors E2A, FOXO1 and FOXP1 regulate recombination activating gene expression in cancer cells. PLoS One. 2011;6:e20475.
Dovat S, Montecino-Rodriguez E, Schuman V, Teitell MA, Dorshkind K, Smale ST. Transgenic expression of Helios in B lineage cells alters B cell properties and promotes lymphomagenesis. J Immunol. 2005;175:3508–15.
Winandy S, Wu L, Wang JH, Georgopoulos K. Pre-T cell receptor (TCR) and TCR-controlled checkpoints in T cell differentiation are set by Ikaros. J Exp Med. 1999;190:1039–48.
Mandal M, Powers SE, Ochiai K, Georgopoulos K, Kee BL, Singh H, Clark MR. Ras orchestrates exit from the cell cycle and light-chain recombination during early B cell development. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:1110–7.
Ferreirós Vidal I, Carroll T, Taylor B, et al. Genome-wide identification of Ikaros targets elucidates its contribution to mouse B-cell lineage specification and pre-B-cell differentiation. Blood. 2013;121(10):1769–82.
Collins B, Clambey ET, Scott-Browne J, White J, Marrack P, Hagman J, Kappler JW. Ikaros promotes rearrangement of TCR alpha genes in an Ikaros null thymoma cell line. Eur J Immunol. 2013;43:521–32.
Kathrein KL, Lorenz R, Innes AM, Griffiths E, Winandy S. Ikaros induces quiescence and T-cell differentiation in a leukemia cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:1645–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitchell, J.L., Seng, A. & Yankee, T.M. Ikaros, Helios, and Aiolos protein levels increase in human thymocytes after β selection. Immunol Res 64, 565–575 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-015-8754-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-015-8754-x