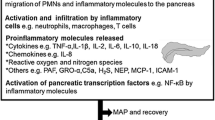
Abstract
Alcohol and gallstones are the most common etiologic factors in acute pancreatitis (AP). Recurrent AP can lead to chronic pancreatitis (CP). Although the underlying pathophysiology of the disease is complex, immune cells are critical in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis and determining disease severity. In this review, we discuss the role of innate and adaptive immune cells in both AP and CP, potential immune-based therapeutic targets, and animal models used to understand our knowledge of the disease. The relative difficulty of obtaining human pancreatic tissue during pancreatitis makes animal models necessary. Animal models of pancreatitis have been generated to understand disease pathogenesis, test therapeutic interventions, and investigate immune responses. Although current animal models do not recapitulate all aspects of human disease, until better models can be developed available models are useful in addressing key research questions. Differences between experimental and clinical pancreatitis need consideration, and when therapies are tested, models with established disease ought to be included.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AP:
-
Acute pancreatitis
- ANS:
-
Anti-neutrophil serum
- CP:
-
Chronic pancreatitis
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- MCP:
-
Monocyte chemotactic protein
- PSCs:
-
Pancreatic stellate cells
- Th:
-
T helper
- Treg:
-
Regulatory T cells
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
References
Apte MV, Wilson JS. Mechanisms of pancreatic fibrosis. Dig Dis. 2004;22:273–9.
Talukdar R, Saikia N, Singal DK, Tandon R. Chronic pancreatitis: evolving paradigms. Pancreatology. 2006;6:440–9.
Talukdar R, Tandon RK. Pancreatic stellate cells: new target in the treatment of chronic pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23:34–41.
Steer ML. Pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Digestion. 1997;58(Suppl 1):46–9.
Gukovskaya AS, Vaquero E, Zaninovic V, Gorelick FS, Lusis AJ, Brennan ML, Holland S, Pandol SJ. Neutrophils and NADPH oxidase mediate intrapancreatic trypsin activation in murine experimental acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:974–84.
Sandoval D, Gukovskaya A, Reavey P, Gukovsky S, Sisk A, Braquet P, Pandol SJ, Poucell-Hatton S. The role of neutrophils and platelet-activating factor in mediating experimental pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1996;111:1081–91.
Bhatia M, Saluja AK, Hofbauer B, Lee HS, Frossard JL, Steer ML. The effects of neutrophil depletion on a completely noninvasive model of acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury. Int J Pancreatol. 1998;24:77–83.
Abdulla A, Awla D, Thorlacius H, Regner S. Role of neutrophils in the activation of trypsinogen in severe acute pancreatitis. J Leukoc Biol. 2011;90:975–82.
Dunay IR, Fuchs A, Sibley LD. Inflammatory monocytes but not neutrophils are necessary to control infection with Toxoplasma gondii in mice. Infect Immun. 2010;78:1564–70.
Rinderknecht H. Fatal pancreatitis, a consequence of excessive leukocyte stimulation? Int J Pancreatol. 1988;3:105–12.
Zaninovic V, Gukovskaya AS, Gukovsky I, Mouria M, Pandol SJ. Cerulein upregulates ICAM-1 in pancreatic acinar cells, which mediates neutrophil adhesion to these cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000;279:G666–76.
Frossard JL, Saluja A, Bhagat L, Lee HS, Bhatia M, Hofbauer B, Steer ML. The role of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and neutrophils in acute pancreatitis and pancreatitis-associated lung injury. Gastroenterology. 1999;116:694–701.
Hartman H, Abdulla A, Awla D, Lindkvist B, Jeppsson B, Thorlacius H, Regner S. P-selectin mediates neutrophil rolling and recruitment in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 2012;99:246–55.
Awla D, Abdulla A, Zhang S, Roller J, Menger MD, Regner S, Thorlacius H. Lymphocyte function antigen-1 regulates neutrophil recruitment and tissue damage in acute pancreatitis. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;163:413–23.
Makhija R, Kingsnorth AN. Cytokine storm in acute pancreatitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2002;9:401–10.
McKay C, Imrie CW, Baxter JN. Mononuclear phagocyte activation and acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1996;219:32–6.
Bhatia M, Ramnath RD, Chevali L, Guglielmotti A. Treatment with bindarit, a blocker of MCP-1 synthesis, protects mice against acute pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005;288:G1259–65.
Sakai Y, Masamune A, Satoh A, Nishihira J, Yamagiwa T, Shimosegawa T. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is a critical mediator of severe acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:725–36.
Saeki K, Kanai T, Nakano M, Nakamura Y, Miyata N, Sujino T, Yamagishi Y, Ebinuma H, Takaishi H, Ono Y, Takeda K, Hozawa S, Yoshimura A, Hibi T. CCL2-induced migration and SOCS3-mediated activation of macrophages are involved in cerulein-induced pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:1010–20.
Shrivastava P, Bhatia M. Essential role of monocytes and macrophages in the progression of acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:3995–4002.
Bedrosian AS, Nguyen AH, Hackman M, Connolly MK, Malhotra A, Ibrahim J, Cieza-Rubio NE, Henning JR, Barilla R, Rehman A, Pachter HL, Medina-Zea MV, Cohen SM, Frey AB, Acehan D, Miller G. Dendritic cells promote pancreatic viability in mice with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(1915–1926):e1911–4.
Ochi A, Nguyen AH, Bedrosian AS, Mushlin HM, Zarbakhsh S, Barilla R, Zambirinis CP, Fallon NC, Rehman A, Pylayeva-Gupta Y, Badar S, Hajdu CH, Frey AB, Bar-Sagi D, Miller G. MyD88 inhibition amplifies dendritic cell capacity to promote pancreatic carcinogenesis via Th2 cells. J Exp Med. 2012;209:1671–87.
Dib M, Zhao X, Wang XD, Andersson R. Role of mast cells in the development of pancreatitis-induced multiple organ dysfunction. Br J Surg. 2002;89:172–8.
Yonetci N, Oruc N, Ozutemiz O, Ak Celik H, Yuce G. Effects of mast-cell stabilization in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. Int J Gastrointest Cancer. 2001;29:163–72.
Kempuraj D, Twait EC, Williard DE, Yuan Z, Meyerholz DK, Samuel I. The novel cytokine interleukin-33 activates acinar cell proinflammatory pathways and induces acute pancreatic inflammation in mice. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e56866.
Pezzilli R, Billi P, Gullo L, Beltrandi E, Maldini M, Mancini R, Incorvaia L, Miglioli M. Behavior of serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor, soluble CD8 and soluble CD4 in the early phases of acute pancreatitis. Digestion. 1994;55:268–73.
Demols A, Le Moine O, Desalle F, Quertinmont E, Van Laethem JL, Deviere J. CD4(+)T cells play an important role in acute experimental pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:582–90.
Xue J, Nguyen DT, Habtezion A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates pancreatic IL-22 production and protects mice from acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:1670.
Braganza JM, Lee SH, McCloy RF, McMahon MJ. Chronic pancreatitis. Lancet. 2011;377:1184–97.
Omary MB, Lugea A, Lowe AW, Pandol SJ. The pancreatic stellate cell: a star on the rise in pancreatic diseases. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:50–9.
Apte MV, Haber PS, Applegate TL, Norton ID, McCaughan GW, Korsten MA, Pirola RC, Wilson JS. Periacinar stellate shaped cells in rat pancreas: identification, isolation, and culture. Gut. 1998;43:128–33.
Bachem MG, Schneider E, Gross H, Weidenbach H, Schmid RM, Menke A, Siech M, Beger H, Grunert A, Adler G. Identification, culture, and characterization of pancreatic stellate cells in rats and humans. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:421–32.
Treiber M, Neuhofer P, Anetsberger E, Einwachter H, Lesina M, Rickmann M, Liang S, Kehl T, Nakhai H, Schmid RM, Algul H. Myeloid, but not pancreatic, RelA/p65 is required for fibrosis in a mouse model of chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:1473–85.
Schmid-Kotsas A, Gross HJ, Menke A, Weidenbach H, Adler G, Siech M, Beger H, Grunert A, Bachem MG. Lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages stimulate the synthesis of collagen type I and C-fibronectin in cultured pancreatic stellate cells. Am J Pathol. 1999;155:1749–58.
Tessem JS, Jensen JN, Pelli H, Dai XM, Zong XH, Stanley ER, Jensen J, DeGregori J. Critical roles for macrophages in islet angiogenesis and maintenance during pancreatic degeneration. Diabetes. 2008;57:1605–17.
Goecke H, Forssmann U, Uguccioni M, Friess H, Conejo-Garcia JR, Zimmermann A, Baggiolini M, Buchler MW. Macrophages infiltrating the tissue in chronic pancreatitis express the chemokine receptor CCR5. Surgery. 2000;128:806–14.
Esposito I, Friess H, Kappeler A, Shrikhande S, Kleeff J, Ramesh H, Zimmermann A, Buchler MW. Mast cell distribution and activation in chronic pancreatitis. Hum Pathol. 2001;32:1174–83.
Zimnoch L, Szynaka B, Puchalski Z. Mast cells and pancreatic stellate cells in chronic pancreatitis with differently intensified fibrosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002;49:1135–8.
Hunger RE, Mueller C, Z’Graggen K, Friess H, Buchler MW. Cytotoxic cells are activated in cellular infiltrates of alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:1656–63.
Grundsten M, Liu GZ, Permert J, Hjelmstrom P, Tsai JA. Increased central memory T cells in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2005;5:177–82.
Schmitz-Winnenthal H, Pietsch DH, Schimmack S, Bonertz A, Udonta F, Ge Y, Galindo L, Specht S, Volk C, Zgraggen K, Koch M, Buchler MW, Weitz J, Beckhove P. Chronic pancreatitis is associated with disease-specific regulatory T-cell responses. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:1178–88.
Rongione AJ, Kusske AM, Kwan K, Ashley SW, Reber HA, McFadden DW. Interleukin 10 reduces the severity of acute pancreatitis in rats. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:960–7.
Van Laethem JL, Marchant A, Delvaux A, Goldman M, Robberecht P, Velu T, Deviere J. Interleukin 10 prevents necrosis in murine experimental acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1995;108:1917–22.
Malleo G, Mazzon E, Siriwardena AK, Cuzzocrea S. TNF-alpha as a therapeutic target in acute pancreatitis—lessons from experimental models. Sci World J. 2007;7:431–48.
Werner J, Z’Graggen K, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Lewandrowski KB, Compton CC, Warshaw AL. Specific therapy for local and systemic complications of acute pancreatitis with monoclonal antibodies against ICAM-1. Ann Surg. 1999;229:834–40 (discussion 841-832).
Norman JG, Franz MG, Fink GS, Messina J, Fabri PJ, Gower WR, Carey LC. Decreased mortality of severe acute pancreatitis after proximal cytokine blockade. Ann Surg. 1995;221:625–31 (discussion 631-624).
Hofbauer B, Saluja AK, Bhatia M, Frossard JL, Lee HS, Bhagat L, Steer ML. Effect of recombinant platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase on two models of experimental acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:1238–47.
Dumot JA, Conwell DL, Zuccaro G Jr, Vargo JJ, Shay SS, Easley KA, Ponsky JL. A randomized, double blind study of interleukin 10 for the prevention of ERCP-induced pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:2098–102.
Deviere J, Le Moine O, Van Laethem JL, Eisendrath P, Ghilain A, Severs N, Cohard M. Interleukin 10 reduces the incidence of pancreatitis after therapeutic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Gastroenterology. 2001;120:498–505.
Johnson CD, Kingsnorth AN, Imrie CW, McMahon MJ, Neoptolemos JP, McKay C, Toh SK, Skaife P, Leeder PC, Wilson P, Larvin M, Curtis LD. Double blind, randomised, placebo controlled study of a platelet activating factor antagonist, lexipafant, in the treatment and prevention of organ failure in predicted severe acute pancreatitis. Gut. 2001;48:62–9.
Triantafillidis JK, Cheracakis P, Hereti IA, Argyros N, Karra E. Acute idiopathic pancreatitis complicating active Crohn’s disease: favorable response to infliximab treatment. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:3334–6.
Clayton H, Flatz L, Vollenweider-Roten S, Schoepfer A, Gilliet M, Conrad C. Anti-TNF therapy in the treatment of psoriasis in a patient with acute-on-chronic pancreatitis. Dermatology. 2013;227:193–6.
Gloor B, Blinman TA, Rigberg DA, Todd KE, Lane JS, Hines OJ, Reber HA. Kupffer cell blockade reduces hepatic and systemic cytokine levels and lung injury in hemorrhagic pancreatitis in rats. Pancreas. 2000;21:414–20.
Gea-Sorli S, Closa D. In vitro, but not in vivo, reversibility of peritoneal macrophages activation during experimental acute pancreatitis. BMC Immunol. 2009;10:42.
Nakamichi I, Habtezion A, Zhong B, Contag CH, Butcher EC, Omary MB. Hemin-activated macrophages home to the pancreas and protect from acute pancreatitis via heme oxygenase-1 induction. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:3007–14.
Habtezion A, Kwan R, Akhtar E, Wanaski SP, Collins SD, Wong RJ, Stevenson DK, Butcher EC, Omary MB. Panhematin provides a therapeutic benefit in experimental pancreatitis. Gut. 2011;60:671–9.
Xue J, Nguyen DT, Habtezion A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates pancreatic IL-22 production and protects mice from acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:1670–80.
Chen P, Sun B, Chen H, Wang G, Pan S, Kong R, Bai X, Wang S. Effects of carbon monoxide releasing molecule-liberated CO on severe acute pancreatitis in rats. Cytokine. 2010;49:15–23.
Xue J, Habtezion A. Carbon monoxide-based therapy ameliorates acute pancreatitis via TLR4 inhibition. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:437–47.
Pandol SJ, Saluja AK, Imrie CW, Banks PA. Acute pancreatitis: bench to the bedside. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:1127–51.
Banks PA, Freeman ML. Practice guidelines in acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:2379–400.
Rattner DW. Experimental models of acute pancreatitis and their relevance to human disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1996;219:6–9.
Buchler M, Friess H, Uhl W, Beger HG. Clinical relevance of experimental acute pancreatitis. Eur Surg Res. 1992;24(Suppl 1):85–8.
Steinberg WM, Schlesselman SE. Treatment of acute pancreatitis. Comparison of animal and human studies. Gastroenterology. 1987;93:1420–7.
Su KH, Cuthbertson C, Christophi C. Review of experimental animal models of acute pancreatitis. HPB. 2006;8:264–86.
Chan YC, Leung PS. Acute pancreatitis: animal models and recent advances in basic research. Pancreas. 2007;34:1–14.
Chari ST, Singer MV. The problem of classification and staging of chronic pancreatitis. Proposals based on current knowledge of its natural history. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1994;29:949–60.
Andersen BN, Pedersen NT, Scheel J, Worning H. Incidence of alcoholic chronic pancreatitis in Copenhagen. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1982;17:247–52.
Lerch MM, Gorelick FS. Models of acute and chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:1180–93.
Aghdassi AA, Mayerle J, Christochowitz S, Weiss FU, Sendler M, Lerch MM. Animal models for investigating chronic pancreatitis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2011;4:26.
Marrache F, Tu SP, Bhagat G, Pendyala S, Osterreicher CH, Gordon S, Ramanathan V, Penz-Osterreicher M, Betz KS, Song Z, Wang TC. Overexpression of interleukin-1beta in the murine pancreas results in chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1277–87.
Vonlaufen A, Phillips PA, Xu Z, Zhang X, Yang L, Pirola RC, Wilson JS, Apte MV. Withdrawal of alcohol promotes regression while continued alcohol intake promotes persistence of LPS-induced pancreatic injury in alcohol-fed rats. Gut. 2011;60:238–46.
Vonlaufen A, Xu Z, Daniel B, Kumar RK, Pirola R, Wilson J, Apte MV. Bacterial endotoxin: a trigger factor for alcoholic pancreatitis? Evidence from a novel, physiologically relevant animal model. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1293–303.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation grant (to A.H.), the National Institutes of Health Grant DK092421 (to A.H.), and Digestive Disease Center Grant DK56339 (to Stanford University).
Conflict of interest
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, J., Sharma, V. & Habtezion, A. Immune cells and immune-based therapy in pancreatitis. Immunol Res 58, 378–386 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-014-8504-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-014-8504-5