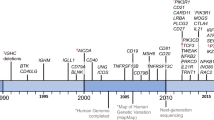
Abstract
While primary immune defects are generally considered to lead to severe and easily recognized disease in infants and children, a number of genetic defects impairing B cell function may not be clinically apparent or diagnosed until adult life. The commonest of these is common variable immune deficiency, the genetic origins of which are beginning to be at least partially understood. CVID affects ≈1/25,000 Caucasians and is characterized by a marked reduction in serum IgG, almost always in serum IgA, and reduced serum IgM in about half of all cases; these defects continue to provide an opportunity to investigate the genes necessary for B cell function in humans. Recently, a small number of genes necessary for normal B cell function have been identified in consanguineous families leading to varying degrees of hypogammaglobulinemia and loss of antibody production. In other studies, whole-exome sequencing and copy number variation, applied to large cohorts, have extended research into understanding both the genetic basis of this syndrome and the clinical phenotypes of CVID.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Notarangelo LD, Fischer A, Geha RS, Casanova JL, Chapel H, Conley ME, et al. Primary immunodeficiencies: 2009 update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124(6):1161–78.
Casanova JL, Abel L. Primary immunodeficiencies: a field in its infancy. Science. 2007;317(5838):617–9.
Waleed Al-Herz AB, Jean-Laurent Casanova, Helen Chapel, Mary Ellen Conley, Charlotte Cunningham-Rundles, Amos Etzioni, Alain Fischer, Jose Luis Franco, Raif S. Geha, Lennart Hammarström, Shigeaki Nonoyama, Luigi Daniele Notarangelo, Hans Dieter Ochs, Jennifer M. Puck, Chaim M. Roifman, Reinhard Seger and Mimi L. K. Tang. Primary immunodeficiency diseases: an update on the classification from the international union of immunological societies expert committee for primary immunodeficiency. Frontiers in immunology 2011;2:published on line 08 November 2011.
Fischer A. Natural mutants of the immune system: a lot to learn! Eur J Immunol. 2002;32(6):1519–23.
Conley ME. Hypogammaglobulinemia: fifty years later. Clin Immunol. 2002;104(3):201–3.
Durandy A. Hyper-IgM syndromes: a model for studying the regulation of class switch recombination and somatic hypermutation generation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002;30(4):815–8.
Imai K, Slupphaug G, Lee WI, Revy P, Nonoyama S, Catalan N, et al. Human uracil-DNA glycosylase deficiency associated with profoundly impaired immunoglobulin class-switch recombination. Nat Immunol. 2003 Sep 7.
Orange JS, Glessner JT, Resnick E, Sullivan KE, Lucas M, Ferry B, et al. Genome-wide association identifies diverse causes of common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127(6):1360–7.
Cunningham-Rundles C, How I. Treat common variable immune deficiency. Blood. 2010;116(1):7–15.
Resnick ES, Moshier EL, Godbold JH, Cunningham-Rundles C. Morbidity and mortality in common variable immune deficiency over 4 decades. Blood. 2011 Dec 16.
Sanford JP, Favour CB, Tribeman MS. Absence of serum gamma globulins in an adult. N Engl J Med. 1954;250(24):1027–9.
Grimbacher B, Hutloff A, Schlesier M, Glocker E, Warnatz K, Drager R, et al. Homozygous loss of ICOS is associated with adult-onset common variable immunodeficiency. Nat Immunol. 2003;4(3):261–8.
Hutloff A, Dittrich AM, Beier KC, Eljaschewitsch B, Kraft R, Anagnostopoulos I, et al. ICOS is an inducible T-cell co-stimulator structurally and functionally related to CD28. Nature. 1999;397(6716):263–6.
Kindler V, Zubler RH. Memory, but not naive, peripheral blood B lymphocytes differentiate into Ig-secreting cells after CD40 ligation and costimulation with IL-4 and the differentiation factors IL-2, IL-10, and IL-3. J Immunol. 1997;159(5):2085–90.
Rousset F, Garcia E, Defrance T, Peronne C, Vezzio N, Hsu DH, et al. Interleukin 10 is a potent growth and differentiation factor for activated human B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89(5):1890–3.
Choe J, Choi YS. IL-10 interrupts memory B cell expansion in the germinal center by inducing differentiation into plasma cells. Eur J Immunol. 1998;28(2):508–15.
Witsch EJ, Peiser M, Hutloff A, Buchner K, Dorner BG, Jonuleit H, et al. ICOS and CD28 reversely regulate IL-10 on re-activation of human effector T cells with mature dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32(9):2680–6.
Salzer U, Maul-Pavicic A, Cunningham-Rundles C, Urschel S, Belohradsky BH, Litzman J, et al. ICOS deficiency in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Clin Immunol. 2004;113(3):234–40.
Takahashi N, Matsumoto K, Saito H, Nanki T, Miyasaka N, Kobata T, et al. Impaired CD4 and CD8 effector function and decreased memory T cell populations in ICOS-deficient patients. J Immunol. 2009;182(9):5515–27.
van Zelm MC, Reisli I, van der Burg M, Castano D, van Noesel CJ, van Tol MJ, et al. An antibody-deficiency syndrome due to mutations in the CD19 gene. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(18):1901–12.
Carter RH, Fearon DT. CD19: lowering the threshold for antigen receptor stimulation of B lymphocytes. Science. 1992;256(5053):105–7.
Kanegane H, Agematsu K, Futatani T, Sira MM, Suga K, Sekiguchi T, et al. Novel mutations in a Japanese patient with CD19 deficiency. Genes Immun. 2007;8(8):663–70.
Vince N, Boutboul D, Mouillot G, Just N, Peralta M, Casanova JL, et al. Defects in the CD19 complex predispose to glomerulonephritis, as well as IgG1 subclass deficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127(2):538–41.
van Zelm MC, Smet J, Adams B, Mascart F, Schandene L, Janssen F, et al. CD81 gene defect in humans disrupts CD19 complex formation and leads to antibody deficiency. J Clin Investig. 2010;120(4):1265–74.
Maecker HT, Levy S. Normal lymphocyte development but delayed humoral immune response in CD81-null mice. J Exp Med. 1997;185(8):1505–10.
Miyazaki T, Muller U, Campbell KS. Normal development but differentially altered proliferative responses of lymphocytes in mice lacking CD81. EMBO J. 1997;16(14):4217–25.
Tsitsikov EN, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Geha RS. Impaired CD19 expression and signaling, enhanced antibody response to type II T independent antigen and reduction of B-1 cells in CD81-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(20):10844–9.
Tedder TF, Engel P. CD20: a regulator of cell-cycle progression of B lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 1994;15(9):450–4.
Tedder TF, Boyd AW, Freedman AS, Nadler LM, Schlossman SF. The B cell surface molecule B1 is functionally linked with B cell activation and differentiation. J Immunol. 1985;135(2):973–9.
Tedder TF, Forsgren A, Boyd AW, Nadler LM, Schlossman SF. Antibodies reactive with the B1 molecule inhibit cell cycle progression but not activation of human B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1986;16(8):881–7.
Kuijpers TW, Bende RJ, Baars PA, Grummels A, Derks IA, Dolman KM, et al. CD20 deficiency in humans results in impaired T cell-independent antibody responses. J Clin Investig. 2010;120(1):214–22.
Thiel J, Kimmig L, Salzer U, Grudzien M, Lebrecht D, Hagena T, et al. Genetic CD21 deficiency is associated with hypogammaglobulinemia. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 Oct 27.
Fearon DT, Carroll MC. Regulation of B lymphocyte responses to foreign and self-antigens by the CD19/CD21 complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:393–422.
Ombrello MJ, Remmers EF, Sun G, Freeman AF, Datta S, Torabi-Parizi P, et al. Cold urticaria, immunodeficiency, and autoimmunity related to PLCG2 deletions. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(4):330–8.
Batten M, Groom J, Cachero TG, Qian F, Schneider P, Tschopp J, et al. BAFF mediates survival of peripheral immature B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 2000;192(10):1453–66.
Gross JA, Dillon SR, Mudri S, Johnston J, Littau A, Roque R, et al. TACI-Ig neutralizes molecules critical for B cell development and autoimmune disease. Impaired B cell maturation in mice lacking BLyS. Immunity. 2001;15(2):289–302.
Schiemann B, Gommerman JL, Vora K, Cachero TG, Shulga-Morskaya S, Dobles M, et al. An essential role for BAFF in the normal development of B cells through a BCMA-independent pathway. Science. 2001;293(5537):2111–4.
Yan M, Brady JR, Chan B, Lee WP, Hsu B, Harless S, et al. Identification of a novel receptor for B lymphocyte stimulator that is mutated in a mouse strain with severe B cell deficiency. Curr Biol. 2001;11(19):1547–52.
Sasaki Y, Casola S, Kutok JL, Rajewsky K, Schmidt-Supprian M. TNF family member B cell-activating factor (BAFF) receptor-dependent and -independent roles for BAFF in B cell physiology. J Immunol. 2004;173(4):2245–52.
Shulga-Morskaya S, Dobles M, Walsh ME, Ng LG, MacKay F, Rao SP, et al. B cell-activating factor belonging to the TNF family acts through separate receptors to support B cell survival and T cell-independent antibody formation. J Immunol. 2004;173(4):2331–41.
Mackay F, Schneider P, Rennert P, Browning J. BAFF AND APRIL: a tutorial on B cell survival. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:231–64.
Losi CG, Silini A, Fiorini C, Soresina A, Meini A, Ferrari S, et al. Mutational analysis of human BAFF receptor TNFRSF13C (BAFF-R) in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol. 2005;25(5):496–502.
Warnatz K, Salzer U, Rizzi M, Fischer B, Gutenberger S, Bohm J, et al. B-cell activating factor receptor deficiency is associated with an adult-onset antibody deficiency syndrome in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(33):13945–50.
von Bulow GU, van Deursen JM, Bram RJ. Regulation of the T-independent humoral response by TACI. Immunity. 2001;14(5):573–82.
Litinskiy MB, Nardelli B, Hilbert DM, He B, Schaffer A, Casali P, et al. DCs induce CD40-independent immunoglobulin class switching through BLyS and APRIL. Nat Immunol. 2002;3(9):822–9.
Castigli E, Wilson SA, Scott S, Dedeoglu F, Xu S, Lam KP, et al. TACI and BAFF-R mediate isotype switching in B cells. J Exp Med. 2005;201(1):35–9.
Salzer U, Chapel HM, Webster AD, Pan-Hammarstrom Q, Schmitt-Graeff A, Schlesier M, et al. Mutations in TNFRSF13B encoding TACI are associated with common variable immunodeficiency in humans. Nat Genet. 2005;37(8):820–8.
Castigli E, Wilson SA, Garibyan L, Rachid R, Bonilla F, Schneider L, et al. TACI is mutant in common variable immunodeficiency and IgA deficiency. Nat Genet. 2005;37(8):829–34.
Zhang L, Radigan L, Salzer U, Behrens TW, Grimbacher B, Diaz G, et al. Transmembrane activator and calcium-modulating cyclophilin ligand interactor mutations in common variable immunodeficiency: clinical and immunologic outcomes in heterozygotes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120(5):1178–85.
Pan-Hammarstrom Q, Salzer U, Du L, Bjorkander J, Cunningham-Rundles C, Nelson DL, et al. Reexamining the role of TACI coding variants in common variable immunodeficiency and selective IgA deficiency. Nat Genet. 2007;39(4):429–30.
Martinez-Pomar N, Detkova D, Arostegui JI, Alvarez A, Soler-Palacin P, Vidaller A, et al. Role of TNFRSF13B variants in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Blood. 2009;114(13):2846–8.
Vorechovsky I, Cullen M, Carrington M, Hammarstrom L, Webster AD. Fine mapping of IGAD1 in IgA deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency: identification and characterization of haplotypes shared by affected members of 101 multiple-case families. J Immunol. 2000;164(8):4408–16.
Kralovicova J, Hammarstrom L, Plebani A, Webster AD, Vorechovsky I. Fine-scale mapping at IGAD1 and genome-wide genetic linkage analysis implicate HLA-DQ/DR as a major susceptibility locus in selective IgA deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency. J Immunol. 2003;170(5):2765–75.
Waldrep ML, Zhuang Y, Schroeder HW Jr. Analysis of TACI mutations in CVID & RESPI patients who have inherited HLA B*44 or HLA*B8. BMC Med Genet. 2009;10:100.
Hermaszewski RA, Webster AD. Primary hypogammaglobulinaemia: a survey of clinical manifestations and complications. Q J Med. 1993;86(1):31–42.
Cunningham-Rundles C, Bodian C. Common variable immunodeficiency: clinical and immunological features of 248 patients. Clin Immunol. 1999;92(1):34–48.
Kainulainen L, Nikoskelainen J, Ruuskanen O. Diagnostic findings in 95 finnish patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol. 2001;21(2):145–9.
Quinti I, Soresina A, Spadaro G, Martino S, Donnanno S, Agostini C, et al. Long-term follow-up and outcome of a large cohort of patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol. 2007;27(3):308–16.
Chapel H, Lucas M, Lee M, Bjorkander J, Webster D, Grimbacher B, et al. Common variable immunodeficiency disorders: division into distinct clinical phenotypes. Blood. 2008;112(2):277–86.
Chapel H, Cunningham-Rundles C. Update in understanding common variable immunodeficiency disorders (CVIDs) and the management of patients with these conditions. Br J Haematol. 2009 Mar 27.
Ferreira RC, Pan-Hammarstrom Q, Graham RR, Gateva V, Fontan G, Lee AT, et al. Association of IFIH1 and other autoimmunity risk alleles with selective IgA deficiency. Nat Genet. 2010;42(9):777–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cunningham-Rundles, C. Human B cell defects in perspective. Immunol Res 54, 227–232 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-012-8318-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-012-8318-2