Abstract
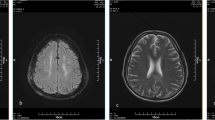
Toxic leukoencephalopathy represents a process of structural alteration of the white matter. It is caused by substance abuse including drugs such as heroin, cocaine, toluene and ethanol. We reported the clinical, radiological and autopsy findings of a rare case of toxic leukoencephalopathy following chronic methamphetamine (MA) usage. A 34-year-old man with a 3-year history of MA abuse experienced progressive sluggish state, limb weakness, inability to stand and eating disorders, followed by rapid progression to coma and death. Imaging revealed hypodense CT and long T1 and T2 signals in MRI in the white matter of the bilateral periventricular and centrum semiovale regions. Histologically, white matter rarefaction, loss of myelin and axonal injury were observed. This pattern of clinical presentation, radiological manifestations and histological findings show a certain degree of particularity in toxic leukoencephalopathy. Clinically, the condition may be easily misdiagnosed as withdrawal symptoms. In suspected cases, MRI is recommended for diagnosis. The case reported here reminds clinicians and forensic pathologist of the possibility of toxic leukoencephalopathy related to MA abuse.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Filley CM, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK. Toxic leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:425–32.
Cottencin O, Rolland B, Guardia D, et al. Current data on methamphetamine. La Revue Du Praticien. 2012;62:679–81.
Thompson PM, Hayashi KM, Simon SL, et al. Structural abnormalities in the brains of human subjects who use methamphetamine. J Neurosci. 2004;24:6028–36.
Filley CM, Toxic leukoencephalopathy. Chin Neuropharmaco. 1999;345:249–60.
Long H, Deore K, Hoffman RS, et al. A fatal case of spongiform leukoencephalopathy linked to "chasing the dragon". Clin Toxicol. 2003;41:887–91.
Sun L, Xu J, Li Y, et al. CT and MRI features of toxic encephalopathy. Chinese J Med Comp Imaging. 2004;10:4–7.
Ginat DT. MRI of toxic leukoencephalopathy syndrome associated with methylenedioxymethamphetamine. Neurology. 2015;84:757.
Bae SC, Lyoo IK, Sung YH, et al. Increased white matter hyperintensities in male methamphetamine abusers. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2006;4(81):83–8.
Bach AG, Jordan B, Wegener NA, et al. Heroin spongiform leukoencephalopathy (HSLE). Clin Neuroradiol. 2012;22:345–9.
Larsen KE, Fon EA, Hastings TG, et al. Methamphetamine-induced degeneration of dopaminergic neurons involves autophagy and upregulation of dopamine synthesis. J Neurosci. 2002;22:8951–60.
Yin R, Lu C, Chen Q, et al. Microvascular damage is involved in the pathogenesis of heroin induced spongiform leukoencephalopathy. Int J Med Sci. 2013;10:299–306.
Offiah C, Hall E. Heroin-induced leukoencephalopathy: characterization using MRI, diffusion-weighted imaging, and MR spectroscopy. Clin Radiol. 2008;63:146–52.
Kriegstein AR, Shungu DC, Millar WS, et al. Leukoencephalopathy and raised brain lactate from heroin vapor inhalation ("chasing the dragon"). Neurology. 2000;54:2027–8.
Yin RX, Lu JY, Lu BX, et al. Roles of bcl-2/bax expression and oligodendrocyte apoptosis in the pathogenesis of heroin-induced spongiform leucoencephalopathy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008;88:749–53.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81471821) and Hebei Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. H2017405021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, J., Li, M., Guo, Y. et al. Methamphetamine-induced toxic leukoencephalopathy: clinical, radiological and autopsy findings. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 13, 362–366 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-017-9893-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-017-9893-2