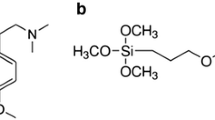
Abstract
In this paper we report a novel, sensitive, and rapid method of magnetic solid phase extraction based on surface modified magnetic nanoparticles as a novel nano sorbent for HPLC determination of morphine with diode array detection in human hair samples. Factors affecting the extraction efficiency of the proposed method, including the sample pH, quantity of magnetic nanoparticles, sample volume, desorption solvent type and its volume, and extraction time were investigated and optimized. Under the optimized experimental conditions, a good linearity was observed in the range of 1–800 µgL−1 for the morphine, with a correlation coefficient (R 2) of 0.990. The pre-concentration factor of 208.69 was achieved in this method. The detection limit of the method was 0.1 μgL−1 based on S/N = 3 and good reproducibility with a relative standard deviations lower than (n = 5) 2.59 %. The proposed method has been successfully applied to the analysis of trace amounts of morphine in human hair samples with satisfactory results. This method can be applied in medical toxicology research and forensic medical centers.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drummer OH. Postmortem toxicology of drugs of abuse. Forensic Sci Int. 2004;142(2):101–13.
Gallardo E, Queiroz JA. The role of alternative specimens in toxicological analysis. Biomed Chromatogr. 2008;22(8):795–821.
Paterson S, Cordero R, Stearns E. Chronic drug use confirmed by hair analysis: its role in understanding both the medical cause of death and the circumstances surrounding the death. J Forensic Leg Med. 2009;16(3):143–7.
Hill V, Cairns T, Schaffer M. Hair analysis for cocaine: factors in laboratory contamination studies and their relevance to proficiency sample preparation and hair testing practices. Forensic Sci Int. 2008;176(1):23–33.
Fuller D. A statistical approach to the prediction of verifiable heroin use from total codeine and total morphine concentrations in urine. J Forensic Sci. 1997;42(4):685.
Sawynok J. The therapeutic use of heroin: a review of the pharmacological literature. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1986;64(1):1–6.
Peñalver A, Pocurull E, Borrull F, Marcé RM. Determination of phthalate esters in water samples by solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography with mass spectrometric detection. J Chromatogr A. 2000;872(1–2):191–201.
Kim TY, Yamazaki Y, Hirano T. Magneto-optical properties of Bi-YIG nanoparticle with polymethacrylate matrix materials. Phys Status Solidi B. 2004;241(7):1601–4.
Kodama RH. Magnetic nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater. 1999;200(1–3):359–72.
Pankhurst QA, Connolly J, Jones S, Dobson J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2003;36(13):R167.
Sounderya N, Zhang Y. Use of core/shell structured nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Recent Pa Biomed Eng. 2008;1(1):34–42.
Li Q, Lam MHW, Wu RSS, Jiang B. Rapid magnetic-mediated solid-phase extraction and pre-concentration of selected endocrine disrupting chemicals in natural waters by poly(divinylbenzene-co-methacrylic acid) coated Fe3O4 core-shell magnetite microspheres for their liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry determination. J Chromatogr A. 2010;1217(8):1219–26.
Qin L, He XW, Li WY, Zhang YK. Molecularly imprinted polymer prepared with bonded β-cyclodextrin and acrylamide on functionalized silica gel for selective recognition of tryptophan in aqueous media. J Chromatogr A. 2008;1187(1–2):94–102.
Faraji M, Yamini Y, Rezaee M. Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, functionalization, characterization, and applications. JICS. 2010;7(1):1–37.
Lu AH, Salabas EL, Schüth F. Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2007;46(8):1222–44.
Park J, An K, Hwang Y, Park JG, Noh HJ, Kim JY, et al. Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat Mater. 2004;3(12):891–5.
Jang JH, Lim HB. Characterization and analytical application of surface modified magnetic nanoparticles. Microchem J. 2010;94(2):148–58.
Shen HY, Zhu Y, Wen XE, Zhuang YM. Preparation of Fe3O4-C18 nano-magnetic composite materials and their cleanup properties for organophosphorous pesticides. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;387(6):2227–37.
Banerjee SS, Chen DH. Fast removal of copper ions by gum arabic modified magnetic nano-adsorbent. J Hazard Mater. 2007;147(3):792–9.
Safarik I, Rego LFT, Borovska M, Mosiniewicz-Szablewska E, Weyda F, Safarikova M. New magnetically responsive yeast-based biosorbent for the efficient removal of water-soluble dyes. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2007;40(6):1551–6.
Li J, Zhao X, Shi Y, Cai Y, Mou S, Jiang G. Mixed hemimicelles solid-phase extraction based on cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-coated nano-magnets Fe3O4 for the determination of chlorophenols in environmental water samples coupled with liquid chromatography/spectrophotometry detection. J Chromatogr A. 2008;1180(1–2):24–31.
Takafuji M, Ide S, Ihara H, Xu Z. Preparation of poly(1-vinylimidazole)-grafted magnetic nanoparticles and their application for removal of metal ions. Chem Mater. 2004;16(10):1977–83.
Sabzevari O, Abdi K, Amini M, Shafiee A. Application of a simple and sensitive GC–MS method for determination of morphine in the hair of opium abusers. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2004;379(1):120–4.
Clavijo C, Hoffman K, Thomas J, Carvalho B, Chu L, Drover D, et al. A sensitive assay for the quantification of morphine and its active metabolites in human plasma and dried blood spots using high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;400(3):715–28.
Cruces-Blanco C, García-Campaña AM. Capillary electrophoresis for the analysis of drugs of abuse in biological specimens of forensic interest. Trends Anal Chem. 2012;31:85–95.
Francis PS, Adcock JL, Costin JW, Purcell SD, Pfeffer FM, Barnett NW. Chemiluminescence detection of opium poppy (Papaver somniferum) alkaloids. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008;48(3):508–18.
Sarwar M, Aman T. Spectrophotometric determination of morphine. Microchem J. 1984;30(3):304–9.
Khayamian T, Tabrizchi M, Jafari MT. Quantitative analysis of morphine and noscapine using corona discharge ion mobility spectrometry with ammonia reagent gas. Talanta. 2006;69(4):795–9.
McCooeye MA, Ells B, Barnett DA, Purves RW, Guevremont R. Quantitation of morphine and codeine in human urine using high-field asymmetric waveform ion mobility spectrometry (FAIMS) with mass spectrometric detection. J Anal Toxicol. 2001;25(2):81–7.
Sakai G, Ogata K, Uda T, Miura N, Yamazoe N. A surface plasmon resonance-based immunosensor for highly sensitive detection of morphine. Sens Actuators B Chem. 1998;49(1–2):5–12.
Xu F, Gao M, Wang L, Zhou T, Jin L, Jin J. Amperometric determination of morphine on cobalt hexacyanoferrate modified electrode in rat brain microdialysates. Talanta. 2002;58(3):427–32.
Salimi A, Hallaj R, Khayatian GR. Amperometric detection of morphine at preheated glassy carbon electrode modified with multiwall carbon nanotubes. Electroanalysis. 2005;17(10):873–9.
Ensafi A, Rezaei B, Krimi-Maleh H. An ionic liquid-type multiwall carbon nanotubes paste electrode for electrochemical investigation and determination of morphine. Ionics. 2011;17(7):659–68.
Afsharmanesh E, Karimi-Maleh H, Pahlavan A, Vahedi J. Electrochemical behavior of morphine at ZnO/CNT nanocomposite room temperature ionic liquid modified carbon paste electrode and its determination in real samples. J Mol Liq. 2013;181:8–13.
Li F, Song J, Gao D, Zhang Q, Han D, Niu L. Simple and rapid voltammetric determination of morphine at electrochemically pretreated glassy carbon electrodes. Talanta. 2009;79(3):845–50.
Ho KC, Chen CY, Hsu HC, Chen LC, Shiesh SC, Lin XZ. Amperometric detection of morphine at a Prussian blue-modified indium tin oxide electrode. Biosens Bioelectron. 2004;20(1):3–8.
Niazi A, Ghasemi J, Zendehdel M. Simultaneous voltammetric determination of morphine and noscapine by adsorptive differential pulse stripping method and least-squares support vector machines. Talanta. 2007;74(2):247–54.
Pournaghi-Azar MH, Saadatirad A. Simultaneous voltammetric and amperometric determination of morphine and codeine using a chemically modified-palladized aluminum electrode. J Electroanal Chem. 2008;624(1–2):293–8.
Yang G, Chen Y, Li L, Yang Y. Direct electrochemical determination of morphine on a novel gold nanotube arrays electrode. Clin Chim Acta. 2011;412(17–18):1544–9.
Shou WZ, Pelzer M, Addison T, Jiang X, Naidong W. An automatic 96-well solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the analysis of morphine, morphine-3-glucuronide and morphine-6-glucuronide in human plasma. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2002;27(1–2):143–52.
Moller M, Aleksa K, Walasek P, Karaskov T, Koren G. Solid-phase microextraction for the detection of codeine, morphine and 6-monoacetylmorphine in human hair by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci Int. 2010;196(1–3):64–9.
Yazdi AS. Es’haghi Z. Surfactant enhanced liquid-phase microextraction of basic drugs of abuse in hair combined with high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2005;1094(1–2):1–8.
Bagheri H, Zandi O, Aghakhani A. Extraction of fluoxetine from aquatic and urine samples using sodium dodecyl sulfate-coated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles followed by spectrofluorimetric determination. Anal Chim Acta. 2011;692(1–2):80–4.
Ebrahimi M, Ebrahimitalab A, Es’haghi Z, Mohammadinejad A. Magnetized silane-coupling agent KH-570 based solid-phase extraction followed by gas chromatography–flame ionization detection to determine venlafaxine in human hair and aqueous environmental samples. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2015;68(2):412–20.
Ebrahimi M, Es’haghi Z, Samadi F, Hosseini MS. Ionic liquid mediated sol-gel sorbents for hollow fiber solid-phase microextraction of pesticide residues in water and hair samples. J Chromatogr A. 2011;1218(46):8313–21.
Zhao X, Shi Y, Cai Y, Mou S. Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-coated magnetic nanoparticles for the preconcentration of phenolic compounds from environmental water samples. Environ Sci Technol. 2008;42(4):1201–6.
Mehdinia A, Roohi F, Jabbari A. Rapid magnetic solid phase extraction with in situ derivatization of methylmercury in seawater by Fe3O4/polyaniline nanoparticle. J Chromatogr A. 2011;1218(28):4269–74.
He Z, Liu D, Li R, Zhou Z, Wang P. Magnetic solid-phase extraction of sulfonylurea herbicides in environmental water samples by Fe3O4@dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride@silica magnetic particles. Anal Chim Acta. 2012;747:29–35.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of this work by the Legal Medicine Organization of Mashhad and the Islamic Azad University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boojaria, A., Masrournia, M., Ghorbani, H. et al. Silane modified magnetic nanoparticles as a novel adsorbent for determination of morphine at trace levels in human hair samples by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 11, 497–503 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-015-9702-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-015-9702-8