Abstract
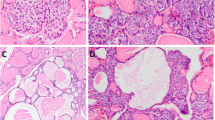
Medullary thyroid carcinomas display cytologic and architectural features that can simulate various primary and metastatic neoplasms. PAX8 immunoexpression in neuroendocrine neoplasms yielded antibody-dependent findings. Since the data regarding the expression profile of monoclonal PAX8 (MRQ-50) antibody is limited in large series of medullary thyroid carcinomas, this study investigated the expression profile of PAX8 (MRQ-50) in a series of 45 medullary thyroid carcinomas. PAX8 (MRQ-50) expression was noted in the thyroid follicular epithelial cells surrounding the tumor and was negative in all medullary thyroid carcinomas. In addition, twenty medullary thyroid carcinomas showed scattered entrapped thyroid follicular epithelial cells at the periphery of the tumor. Entrapped follicular epithelial cells were positive for PAX8 and thyroglobulin, and were negative for monoclonal CEA and calcitonin. A panel approach combining monoclonal antibodies to transcription factors, hormones and cell-specific peptides often assist diagnosticians in the workup of the cellular origin of a neuroendocrine neoplasm. Since PAX8 immunostaining is dependent on the antibody characteristics in neuroendocrine neoplasms, pathologists should be aware of the details of the PAX8 antibody used in a particular case.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duan K, Mete O. Algorithmic approach to neuroendocrine tumors in targeted biopsies: Practical applications of immunohistochemical markers. Cancer Cytopathol. 2016;124(12):871–884.
Sangoi AR, Ohgami RS, Pai RK, Beck AH, McKenney JK, Pai RK. PAX8 expression reliably distinguishes pancreatic well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors from ileal and pulmonary well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors and pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2011;24(3):412–424.
Ordóñez NG. Value of PAX 8 immunostaining in tumor diagnosis: a review and update. Adv Anat Pathol. 2012;19(3):140–151.
Liau JY, Tsai JH, Jeng YM, Kuo KT, Huang HY, Liang CW, Yang CY The Diagnostic Utility of PAX8 for Neuroendocrine Tumors: An Immunohistochemical Reappraisal. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2016;24:57–63.
Nonaka D, Tang Y, Chiriboga L, Rivera M, Ghossein R. Diagnostic utility of thyroid transcription factors Pax8 and TTF-2 (FoxE1) in thyroid epithelial neoplasms. Mod Pathol 2008;21:192–200.
Tacha D, Zhou D, Cheng L. Expression of PAX8 in normal and neoplastic tissues: a comprehensive immunohistochemical study. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2011;19:293–299.
Erickson LA, Mete O. Immunohistochemistry in Diagnostic Parathyroid Pathology. Endocr Pathol. 2018;29(2):113–129.
Ozcan A, Shen SS, Hamilton C, Anjana K, Coffey D, Krishnan B, Truong LD. PAX8 expression in non-neoplastic tissues, primary tumors, and metastatic tumors: a comprehensive immunohistochemical study. Mod Pathol. 2011;24(6):751–764.
Trueba SS, Auge J, Mattei G, Etchevers H, Martinovic J, Czernichow P et al. PAX8, TITF1, and FOXE1 gene expression patterns during human development: new insights into human thyroid development and thyroid dysgenesis-associated malformations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:455–462.
Baloch Z, Mete O, Asa SL. Immunohistochemical Biomarkers in Thyroid Pathology. Endocr Pathol. 2018;29(2):91–112.
Christophe D. The control of thyroid-specific gene expression: what exactly have we learned as yet? Mol Cell Endocrinol 2004;223:1–4.
Mansouri A, Chowdhury K, Gruss P. Follicular cells of the thyroid gland require Pax8 gene function. Nat Genet 1998;19:87–90.
Pasca di Magliano M, Di Lauro R, Zannini M. Pax8 has a key role in thyroid cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000;97:13144–13149.
Mahia PE, Lapi P, Krude H, Pirro MT, Missero C, Chiovato L et al. PAX8 mutations associated with congenital hypothyroidism caused by thyroid dysgenesis. Nat Genet 1998;19:83–86.
Bishop JA, Sharma R, Westra WH. PAX8 immunostaining of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: a reliable means of discerning thyroid origin for undifferentiated tumors of the head and neck. Hum Pathol 2011;42:1873–1877.
Laury AR, Perets R, Piao H, Krane JF, Barletta JA, French C, Chirieac LR, Lis R, Loda M, Hornick JL, Drapkin R, Hirsch MS A comprehensive analysis of PAX8 expression in human epithelial tumors. Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:816–826.
Zhang P, Zuo H, Nakamura Y, Nakamura M, Wakasa T, Kakudo K. Immunohistochemical analysis of thyroid-specific transcription factors in thyroid tumors. Pathol Int 2006;56:240–245.
Puglisi F, Cesselli D, Damante G, Pellizzari L, Beltrami CA, Di Loreto C. Expression of Pax-8, p53 and bcl-2 in human benign and malignant thyroid diseases. Anticancer Res 2000;20:311–316.
Dörfler P, Busslinger M. C-terminal activating and inhibitory domains determine the transactivation potential of BSAP (Pax-5), Pax-2 and Pax-8. EMBO J. 1996;15(8):1971–1982.
Peters H, Neubüser A, Kratochwil K, Balling R. Pax9-deficient mice lack pharyngeal pouch derivatives and teeth and exhibit craniofacial and limb abnormalities. Genes Dev. 1998;12(17):2735–2747.
Kameda Y. Cellular and molecular events on the development of mammalian thyroid C cells. Dev Dyn. 2016;245(3):323–341.
Johansson E, Andersson L, Örnros J, Carlsson T, Ingeson-Carlsson C, Liang S, Dahlberg J, Jansson S, Parrillo L, Zoppoli P, Barila GO, Altschuler DL, Padula D, Lickert H, Fagman H, Nilsson M. Revising the embryonic origin of thyroid C cells in mice and humans. Development. 2015;142(20):3519–3528.
Singh K, Hanley LC, Sung CJ, Quddus MR. Comparison of PAX8 Expression in Breast Carcinoma Using MRQ50 and BC12 Monoclonal Antibodies. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/PAI.0000000000000796.
Asa SL, Mete O. Cytology and Pathology of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Pitfalls and Challenges. In Douglas Evans and Tracy S. Wang (eds). Medullary Thyroid Cancer, Springer, Berlin 2016; pp: 33–46.
DeLellis RA, Al Ghuzlan A, Abores Saavedra J, Baloch ZW, Basolo F, Elisei R, Kaserer K, LiVolsi V, Matias-Guiu X, Mete O, Moley JF, Nikiforov YE, Nose V, Pinto AE. Medullary Thyroid Carcinomas. In Lloyd RV, Osamura RY, Kloppel G, Rosai J. (eds). WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs. 4th edition. IARC: Lyon 2017; pp: 108–113.
Hyrcza MD, Winer D, Mete O. Images in endocrine pathology: papillary variant of medullary thyroid carcinoma with cystic change. Endocr Pathol. 2015;26(1):87–89.
Suster S. Thyroid tumors with a follicular growth pattern: problems in differential diagnosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006;130(7):984–988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HG: concept and design of the study, literature review, data analysis, material contribution and manuscript writing. SC, MK: material contribution and data analysis. OM: concept and design of the study, literature review, manuscript writing, and confirmation of the final version of the submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Statement
Institutional REB approvals were obtained.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gucer, H., Caliskan, S., Kefeli, M. et al. Do You Know the Details of Your PAX8 Antibody? Monoclonal PAX8 (MRQ-50) Is Not Expressed in a Series of 45 Medullary Thyroid Carcinomas. Endocr Pathol 31, 33–38 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-019-09603-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-019-09603-3