Abstract
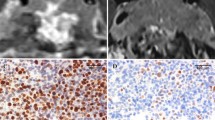
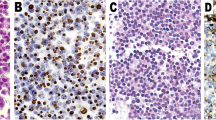
MGMT expression in tumors has been correlated with response to treatment with temozolomide therapy. Few medical therapies are available for Nelson syndrome, and the efficacy of such therapeutics remains limited. The aim of the present study was to assess immunohistochemical expression of MGMT in ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas of patients with Nelson syndrome. Our material consisted of eight specimens from ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas of patients with Nelson syndrome. Immunohistochemical staining for MGMT was performed using the streptavidin-biotin-peroxidase complex method. MGMT immunoreactivity was assessed microscopically and recorded as an estimated percentage of nuclear MGMT immunostaining (0 = none, 1 = <10%, 2 = <25%, 3 = <50%, 4=>50%). Five of the eight specimens (65%) exhibited no MGMT immunoreactivity, with two out of eight cases (25%) showing slight MGMT staining (<10%) and one out of eight cases (12%) demonstrating moderate MGMT positivity (<25%). Patient male/female ratio was 3:5, with average patient age being 62.4 (range 57–66). Our findings suggest that temozolomide therapy may be of potential use in patients with Nelson syndrome, as these tumors express absent/low levels of MGMT. Absent or low MGMT staining in brain and other neoplasms has been shown to correlate with successful treatment with temozolomide, and recent reports of aggressive pituitary adenomas suggest similar outcomes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moyes VJ, Alusi G, Sabin HI, Evanson J, Berney DM, Kovacs K, et al. Treatment of Nelson’s syndrome with temozolomide. Eur J Endocrinol 160:115–119, 2009.
Kovacs K, Horvath E, Syro LV, Uribe H, Penagos LC, Ortiz LD, et al. Temozolomide therapy in a man with an aggressive prolactin-secreting pituitary neoplasm: Morphological findings. Hum Pathol 38:185–189, 2007.
Vidal S, Kovacs K, Horvath E, Scheithauer BW, Kuroki T, Lloyd RV. Microvessel density in pituitary adenomas and carcinomas. Virchows Arch 438:595–602, 2001.
Kovacs K, Scheithauer BW, Lombardero M, McLendon RE, Syro LV, Uribe H, et al. MGMT immunoexpression predicts responsiveness of pituitary tumors to temozolomide therapy. Acta Neuropathol 115:261–262, 2008.
Mohammed S, Kovacs K, Mason W, Smyth H, Cusimano MD. Use of temozolomide in aggressive pituitary tumors: case report. Neurosurgery. 64:E773–774, 2009.
Syro LV, Uribe H, Penagos LC, Ortiz LD, Fadul CE, Horvath E, et al. Antitumour effects of temozolomide in a man with a large, invasive prolactin-producing pituitary neoplasm. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 65: 552–553, 2006.
Casorelli I, Russo MT, Bignami M. Role of mismatch repair and MGMT in response to anticancer therapies. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 8:368–380, 2008.
Nagane M, Kobayashi K, Ohnishi A, Shimizu S, Shiokawa Y. Prognostic significance of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase protein expression in patients with recurrent glioblastoma treated with temozolomide. Jpn J Clin Oncol 37:897–906, 2007.
Pollack IF, Hamilton RL, Sobol RW, Burnham J, Yates AJ, Holmes EJ, et al. O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase expression strongly correlates with outcome in childhood malignant gliomas: results from the CCG-945 Cohort. J Clin Oncol 24:3431–3437, 2006.
Chinot OL, Barrie M, Fuentes S, Eudes N, Lancelot S, Metellus P, et al. Correlation between O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase and survival in inoperable newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients treated with neoadjuvant temozolomide. J Clin Oncol 25:1470–1475, 2007.
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, Hamou MF, de Tribolet N, Weller M, et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:997–1003, 2005.
Banasiak MJ, Malek AR. Nelson syndrome: comprehensive review of pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Neurosurg Focus 23:E13, 2007.
McCormack AI, McDonald KL, Gill AJ, Clark SJ, Burt MG, Campbell KA, et al. Low O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) expression and response to temozolomide in aggressive pituitary tumours. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 71:226–233, 2009.
Syro LV, Scheithauer BW, Ortiz LD, Fadul CE, Horvath E, Rotondo F, et al. Effect of temozolomide in a patient with recurring oncocytic gonadotroph pituitary adenoma. Hormone (Athens) 8:303–306, 2009.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Jarislowsky Foundation and the Lloyd Carr-Harris Foundation for their generous support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salehi, F., Scheithauer, B.W., Moyes, V.J. et al. Low Immunohistochemical Expression of MGMT in ACTH Secreting Pituitary Tumors of Patients with Nelson Syndrome. Endocr Pathol 21, 227–229 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-010-9138-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-010-9138-3