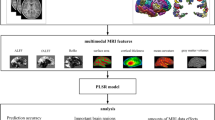
Abstract
Recent studies have demonstrated that neuroimaging data can be used to estimate biological brain age, as it captures information about the neuroanatomical and functional changes the brain undergoes during development and the aging process. However, researchers often have limited access to neuroimaging data because of its challenging and expensive acquisition process, thereby limiting the effectiveness of the predictive model. Decentralized models provide a way to build more accurate and generalizable prediction models, bypassing the traditional data-sharing methodology. In this work, we propose a decentralized method for biological brain age estimation using support vector regression models and evaluate it on three different feature sets, including both volumetric and voxelwise structural MRI data as well as resting functional MRI data. The results demonstrate that our decentralized brain age regression models can achieve similar performance compared to the models trained with all the data in one location.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aledhari, M., Razzak, R., Parizi, R. M., & Saeed, F. (2020). Federated learning: A survey on enabling technologies, protocols, and applications. IEEE Access, 8, 140699–140725.
Ashburner, J., Barnes, G., Chen, C.-C., Daunizeau, J., Flandin, G., Friston, K., Kiebel, S., Kilner, J., Litvak, V., Moran, R., et al. (2014). Spm12 manual. Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging, London, UK 2464.
Bostami, B., Vergara, V., & Calhoun, V. D. (2021a). Harmonization of multi-site dynamic functional connectivity network data. IEEE BIBE.
Bostami, B., Vergara, V., Calhoun, V. D., & Hillary, F. (2021b). Networking brain networks: Federated harmonization of neuroimaging data. Complex Networks, Madrid, Spain.
Chaudhuri, K., Monteleoni, C., & Sarwate, A. D. (2011). Differentially private empirical risk minimization. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12, 3.
COINSTAC. http://coinstac.trendscenter.org.
Cole, J. H., Marioni, R. E., Harris, S. E., & Deary, I. J. (2019). Brain age and other bodily ages: implications for neuropsychiatry. Molecular psychiatry, 24(2), 266–281.
Cole, J. H., Poudel, R. P., Tsagkrasoulis, D., Caan, M. W., Steves, C., Spector, T. D., & Montana, G. (2017). Predicting brain age with deep learning from raw imaging data results in a reliable and heritable biomarker. NeuroImage, 163, 115–124.
Cole, J. H., Ritchie, S. J., Bastin, M. E., Hernández, M. V., Maniega, S. M., Royle, N., et al. (2018). Brain age predicts mortality. Molecular psychiatry, 23(5), 1385–1392.
Du, Y., Fu, Z., Sui, J., Gao, S., Xing, Y., Lin, D., Salman, M., Rahaman, M. A., Abrol, A., Chen, J., et al. (2019). Neuromark: a fully automated ica method to identify effective fmri markers of brain disorders. medRxiv, 19008631.
Du, Y., Pearlson, G. D., Liu, J., Sui, J., Yu, Q., He, H., et al. (2015). A group ica based framework for evaluating resting fmri markers when disease categories are unclear: application to schizophrenia, bipolar, and schizoaffective disorders. Neuroimage, 122, 272–280.
Elliott, M. L., Belsky, D. W., Knodt, A. R., Ireland, D., Melzer, T. R., Poulton, R., Ramrakha, S., Caspi, A., Moffitt, T. E., & Hariri, A. R. (2019). Brain-age in midlife is associated with accelerated biological aging and cognitive decline in a longitudinal birth cohort. Molecular psychiatry, 1–10.
Fischl, B. (2012). Freesurfer. Neuroimage, 62(2), 774–781.
Franke, K., & Gaser, C. Ten. (2019). years of brainage as a neuroimaging biomarker of brain aging: what insights have we gained? Frontiers in neurology, 10, 789.
Gazula, H., Holla, B., Zhang, Z., Xu, J., Verner, E., Kelly, R., Schumann, G., & Calhoun, V. D. (2019). Decentralized multi-site vbm analysis during adolescence shows structural changes linked to age, body mass index, and smoking: A coinstac analysis. bioRxiv, 846386.
Jafri, M. J., Pearlson, G. D., Stevens, M., & Calhoun, V. D. (2008). A method for functional network connectivity among spatially independent resting-state components in schizophrenia. Neuroimage, 39(4), 1666–1681.
Jónsson, B. A., Bjornsdottir, G., Thorgeirsson, T., Ellingsen, L. M., Walters, G. B., Gudbjartsson, D., et al. (2019). Brain age prediction using deep learning uncovers associated sequence variants. Nature communications, 10(1), 1–10.
Li, T., Sahu, A. K., Talwalkar, A., & Smith, V. (2020). Federated learning: Challenges, methods, and future directions. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 37(3), 50–60.
Liem, F., Varoquaux, G., Kynast, J., Beyer, F., Masouleh, S. K., Huntenburg, J. M., et al. (2017). Predicting brain-age from multimodal imaging data captures cognitive impairment. Neuroimage, 148, 179–188.
Luders, E., Cherbuin, N., & Gaser, C. (2016). Estimating brain age using high-resolution pattern recognition: Younger brains in long-term meditation practitioners. Neuroimage, 134, 508–513.
Miller, K. L., Alfaro-Almagro, F., Bangerter, N. K., Thomas, D. L., Yacoub, E., Xu, J., et al. (2016). Multimodal population brain imaging in the uk biobank prospective epidemiological study. Nature neuroscience, 19(11), 1523–1536.
Ming, J., Verner, E., Sarwate, A., Kelly, R., Reed, C., Kahleck, T., Silva, R., Panta, S., Turner, J., Plis, S., et al. (2017). Coinstac: Decentralizing the future of brain imaging analysis. F1000Research 6.
Niu, X., Zhang, F., Kounios, J., & Liang, H. (2020). Improved prediction of brain age using multimodal neuroimaging data. Human brain mapping, 41(6), 1626–1643.
Plis, S. M., Sarwate, A. D., Wood, D., Dieringer, C., Landis, D., Reed, C., et al. (2016). Coinstac: a privacy enabled model and prototype for leveraging and processing decentralized brain imaging data. Frontiers in neuroscience, 10, 365.
Ray, B., Duan, K., Chen, J., Fu, Z., Suresh, P., Johnson, S., Calhoun, V. D., & Liu, J. (2021). Multimodal brain age prediction with feature selection and comparison. EMBC.
Reeve, A., Simcox, E., & Turnbull, D. (2014). Ageing and parkinson’s disease: why is advancing age the biggest risk factor? Ageing research reviews, 14, 19–30.
Rolls, E. T., Huang, C.-C., Lin, C.-P., Feng, J., & Joliot, M. (2020). Automated anatomical labelling atlas 3. Neuroimage, 206, 116189.
Sajedi, H., & Pardakhti, N. (2019). Age prediction based on brain mri image: a survey. Journal of medical systems, 43(8), 279.
Sarwate, A. D., Plis, S. M., Turner, J. A., Arbabshirani, M. R., & Calhoun, V. D. (2014). Sharing privacy-sensitive access to neuroimaging and genetics data: a review and preliminary validation. Frontiers in neuroinformatics, 8, 35.
Satterthwaite, T. D., Elliott, M. A., Ruparel, K., Loughead, J., Prabhakaran, K., Calkins, M. E., et al. (2014). Neuroimaging of the philadelphia neurodevelopmental cohort. Neuroimage, 86, 544–553.
Smith, S., Woolrich, M., Behrens, T., Beckmann, C., Flitney, D., Jenkinson, M., Bannister, P., Clare, S., De Luca, M., Hansen, P., et al. Fmrib software library.
Stankevičiūtė, K., Azevedo, T., Campbell, A., Bethlehem, R. A., & Liò, P. (2020). Population graph gnns for brain age prediction. bioRxiv.
Steffener, J., Habeck, C., O’Shea, D., Razlighi, Q., Bherer, L., & Stern, Y. (2016). Differences between chronological and brain age are related to education and self-reported physical activity. Neurobiology of aging, 40, 138–144.
Sudlow, C., Gallacher, J., Allen, N., Beral, V., Burton, P., Danesh, J., et al. (2015). Uk biobank: an open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. Plos med, 12(3), e1001779.
White, T., Blok, E., & Calhoun, V. D. (2020). Data sharing and privacy issues in neuroimaging research: Opportunities, obstacles, challenges, and monsters under the bed. Human Brain Mapping.
Woolson, R. (2007). Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Wiley encyclopedia of clinical trials, 1–3.
Yang, L., Cao, C., Kantor, E. D., Nguyen, L. H., Zheng, X., Park, Y., et al. (2019). Trends in sedentary behavior among the us population, 2001–2016. Jama, 321(16), 1587–1597.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Debbrata Kumar Saha and Biozid Bostami for their comments. We are also grateful to the funding institutions for their support (National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Drug Abuse and the National Institute of Mental Health).
Funding
This work was funded by the National Institutes of Health (R01DA040487), National Institute on Drug Abuse (R01DA049238) and the National Institute of Mental Health (R01MH121246)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors helped improve the manuscript. SB designed decentralized models for FNC features, performed the data analysis for all the models and wrote the initial manuscript. RR and HG designed the decentralized model for FreeSurfer and GM features. BR designed feature extraction strategies. AS and SP designed and provided insights into the decentralized regression models and helped in tuning their performances. JL provided guidance about feature extraction and decentralized model design. EV manages the COINSTAC project and helped write the paper. VDC supervised all the stages of the project and also funded the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
All the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basodi, S., Raja, R., Ray, B. et al. Decentralized Brain Age Estimation Using MRI Data. Neuroinform 20, 981–990 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-022-09570-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-022-09570-x