Abstract
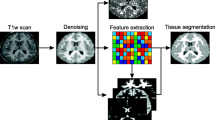
Automatically segmenting anatomical structures from 3D brain MRI images is an important task in neuroimaging. One major challenge is to design and learn effective image models accounting for the large variability in anatomy and data acquisition protocols. A deformable template is a type of generative model that attempts to explicitly match an input image with a template (atlas), and thus, they are robust against global intensity changes. On the other hand, discriminative models combine local image features to capture complex image patterns. In this paper, we propose a robust brain image segmentation algorithm that fuses together deformable templates and informative features. It takes advantage of the adaptation capability of the generative model and the classification power of the discriminative models. The proposed algorithm achieves both robustness and efficiency, and can be used to segment brain MRI images with large anatomical variations. We perform an extensive experimental study on four datasets of T1-weighted brain MRI data from different sources (1,082 MRI scans in total) and observe consistent improvement over the state-of-the-art systems.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akselrod-Ballin, A., Galun, M., Gomori, J., Basri, R., Brandt, A. (2006). Atlas guided identification of brain structures by combining 3D segmentation and SVM classification. In Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI’06), Part I (Vol. 4191, pp. 209–216).
Akselrod-Ballin, A., Galun, M., Gomori, J., Brandt, A., Basri, R. (2007). Prior knowledge driven multiscale segmentation of brain MRI. In Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI’07), Part II (pp.118–126).
Aljabar, P., Heckemann, R., Hammers, A., Hajnal, J., Rueckert, D. (2007). Classifier selection strategies for label fusion using large atlas databases. In Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI’07), Part I (Vol. 4791, pp. 523–531).
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. (2005). Unified segmentation. NeuroImage, 26(3), 839–851.
Avants, B., Epstein, C., Grossman, M., Gee, J. (2008). Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Medical Image Analysis, 12, 26–41.
Bauer, S., Nolte, L.P., Reyes, M. (2011). Fully automatic segmentation of brain tumor images using support vector machine classification in combination with hierarchical conditional random field regularization. In Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI’11), Part III (Vol. 6893, pp. 354–361).
Bazin, P.L., & Pham, D. (2007). Topology-preserving tissue classification of magnetic resonance brain images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 26(4), 487–496.
Bazin, P.L., & Pham, D. (2009). Homeomorphic brain image segmentation with topological and statistical atlases. Medical Image Analysis, 12, 616–625.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning, 45(1), 5–32.
Caldairou, B., Passat, N., Habas, P.A., Studholme, C., Rousseau, F. (2011). A non-local fuzzy segmentation method: application to brain MRI. Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, 44(9), 1916–1927.
Calinon, S., Guenter, F., Billard, A. (2007). On learning, representing and generalizing a task in a humanoid robot. Special issue on robot learning by observation, demonstration and imitation. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part B, 37(2), 286–298.
Chan, T., & Vese, L. (2001). Active contours without edges. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 10(2), 266–277.
Chen, H.M., & Varshney, P. (2003). Mutual information-based CT-MR brain image registration using generalized partial volume joint histogram estimation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 22(9), 1111–1119.
Corso, J., Sharon, E., Dube, S., El-Saden, S., Sinha, U., Yuille, A. (2008). Efficient multilevel brain tumor segmentation with integrated Bayesian model classification. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 27, 629–640.
Du, J., Younes, L., Qiu, A. (2011). Whole brain diffeomorphic metric mapping via integration of sulcal and gyral curves, cortical surfaces, and images. NeuroImage, 56(1), 162–173.
Essen, D.C.V., Dickson, J., Harwell, J., Hanlon, D., Anderson, C.H., Drury, H.A. (2001). An integrated software system for surface-based analyses of cerebral cortex. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association, 8(5), 443–459.
Fan, Y., Shen, D., Gur, R.C., Gur, R.E., Davatzikos, C. (2007). COMPARE: classification of morphological patterns using adaptive regional elements. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 1, 93–105.
Felzenszwalb, P.F. (2005). Representation and detection of deformable shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 27(2), 208–220.
Fischl, B., & et al. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33, 341–355.
Fischl, B., Salat, D.H., van der Kouwe, A.J., Makris, N., Segonne, F., Quinn, B.T., Dale, A.M. (2004). Sequence-independent segmentation of magnetic resonance images. NeuroImage, 23, S69–S84.
Fitzpatrick, J., Wang, M.Y., Dawant, B.M., Maurer, C.R.J., Kessler, R.M., Maciunas, R.J. (1999). Retrospective intermodality registration techniques for images of the head: surface-based versus volume-based. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 18(2), 144–150.
Frackowiak, R., Friston, K., Frith, C., Dolan, R., Price, C., Zeki, S., Ashburner, J., Penny, W. (2003). Human brain function. New York: Academic Press.
Freund, Y., & Schapire, R. (1997). A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. Journal of Comparative and System Sciences, 55(1), 119–139.
Geremia, E., Clatz, O., Menze, B.H., Konukoglu, E., Criminisi, A., Ayache, N. (2011). Spatial decision forests for ms lesion segmentation in multi-channel magnetic resonance images. NeuroImage, 57(2), 378–390.
Geremia, E., Menze, B.H., Clatz, O., Konukoglu, E., Criminisi, A., Ayache, N. (2010). Spatial decision forests for MS lesion segmentation in multi-channel MR images. In Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI’10), Part I (Vol. 6361, pp. 111–118).
Gouttard, S., & et al. (2007). Subcortical structure segmentation using probabilistic atlas priors. Medical Imaging, 6512, 1–11.
Heckemann, R., Hajnal, J., Aljabar, P., Rueckert, D., Hammers, A. (2006). Automatic anatomical brain MRI segmentation combining label propagation and decision fusion. NeuroImage, 33(1), 115–126.
Holub, A., Welling, M., Perona, P. (2008). Hybrid generative-discriminative visual categorization.International Journal of Computer Vision, 77(1–3), 239–258.
Hou, Z. (2006). A review on MR image intensity inhomogeneity correction. International Journal of Biomedical Imaging, 2006, 1–11.
Hua, X., & et al. (2009). Optimizing power to track brain degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment with tensor-based morphometry: an ADNI study of 515 subjects. NeuroImage, 48, 668–681.
Jack, C., & et al. (2008). The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI): The MR imaging protocol. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 24, 685–691.
Jebara, T. (2003). Machine learning: discriminative and generative. Boston: Kluwer.
Khan, A., Chung, M., Beg, M. (2009). Robust atlas-based brain segmentation using multi-structure confidence-weighted registration. In Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI’09), Part II (pp. 549–557).
Klauschen, F., Goldman, A., Barra V., Meyer-Lindenberg, A., Lundervold, A. (2009). Evaluation of automated brain MR image segmentation and volumetry methods. Human Brain Mapping, 30, 1310–1327.
Klein, A., & et al. (2009). Evaluation of 14 nonlinear deformation algorithms applied to human brain MRI registration. NeuroImage, 46(3), 786–802.
Lao, Z., Shen, D., Jawad, A., Karacali, B., Liu, D., Melhem, E., Bryan, N., Davatzikos, C. (2006). Automated segmentation of whitematter lesions in 3D brain MR images, using multivariate pattern classification. In Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI’06) (pp. 307–310). Arlington.
Lasserre, J., Bishop, C., Minka, T. (2006). Principled hybrids of generative and discriminative models. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR’06) (Vol. 1, pp. 87–94).
Lee, C., Schmidt, M., Murtha, A., Bistritz, A., Sander, J., Greiner, R. (2005). Segmenting brain tumor with conditional random fields and support vector machines. In Proceedings of workshop of computer vision for biomedical image application: current techniques and future trends (pp. 469–478). Beijing.
Leemput, K.V., Maes F., Vandermeulen, D., Colchester, A., Suetens, P. (2001). Automated segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions by model outlier detection. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 20(8), 677–688.
Leemput, K.V., Maes, F., Vandermeulen, D., Suetens, P. (1999). Automated model-based tissue classification of MR images of the brain. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 18(10), 897–908.
Li, C., Goldgof, D., Hall, L. (1993). Knowledge-based classification and tissue labeling of MR images of human brain. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 12(4), 740–750.
Li, H., & Fan, Y. (2012). Label propagation with robust initialization for brain tumor segmentation. In IEEE international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI’12) (pp. 1715–1718).
Li, Z., & Fan, J. (2008). 3D MRI brain image segmentation based on region restricted EM algorithm In: Proceedings of SPIE (Vol. 6914, pp. 69,1400.1–69,140.8).
Liang P., & Jordan M. (2008). An asymptotic analysis of generative, discriminative, and pseudo-likelihood estimators. In Proceedings of international conference on machine learning (ICML’08) (pp. 584–591).
Loncaric, S. (1998). A survey of shape analysis techniques. Pattern Recognition, 31(8), 983–1001.
Luo, Y., & Chung, A.C.S. (2011). An atlas-based deep brain structure segmentation method: from coarse positioning to fine shaping. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP’11) (pp. 1085–1088).
Menze, B.H., Leemput, K.V., Lashkari, D., Weber, M.A., Ayache, N., Golland, P. (2010). A generative model for brain tumorsegmentation in multi-modal images. In Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI’10), Part II (Vol. 6362, pp. 151–159).
Morra, J.H., Tu, Z., Apostolova, L., Green, A.E., Toga, A., Thompson, P. (2010). Comparison of adaboost and support vector machines for detecting Alzheimer’ss disease through automated hippocampal segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 29(1), 30–43.
Ng A., & Jordan M. (2002). On discriminative vs. generative classifiers: a comparison of logistic regression and naive Bayes. In Advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS’02) (Vol. 14, pp. 841–848).
Pham, D., & Prince, J. (1999). Adaptive fuzzy segmentation of magnetic resonance images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 18(9), 737–752.
Pieper, S., Lorensen, B., Schroeder, W., Kikinis, R. (2006). The NA-MIC kit: ITK, VTK, pipelines, grids and 3D slicer as an open platform for the medical image computing community. In Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI’06) (pp. 698–701).
Pizer, S.M., & et al. (2003). Deformable m-reps for 3D medical image segmentation.International Journal of Computer Vision, 55(2), 85–106.
Pohl, K., Fisher, J., Kikinis, R., Grimson, W., Wells, W. (2006). A Bayesian model for joint segmentation and registration. NeuroImage, 31(1), 228–239.
Prastawa, M., Bullitt, E., Moon, N., Leemput, K.V., Gerig, G. (2003). Automatic brain tumor segmentation by subject specific modification of atlas priors. Academic Radiology, 10(12), 134–1348.
Quddus, A., Fieguth, P., Basir, O. (2005). Adaboost and support vector machines for white matter lesion segmentation in MR images. In IEEE annual conference on engineering in medicine and biology (EMBS’05).
Raina, R., Shen, Y., Ng, A., McCallum, A. (2003). Classification with hybrid generative/discriminative models. In Advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS’03) (Vol. 16, pp. 545–552).
Sabuncu, M., Yeo, B., Leemput, K.V., Fischl, B., Golland, P. (2010). A generative model for image segmentation based on label fusion. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 29(10), 1714–1729.
Scherrer, B., Dojat, M., Forbes, F., Garbay, C. (2007). LOCUS: local cooperative unified segmentation of MRI brain scans. In Medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI’07), Part I (pp. 219–227).
Scherrer, B., Forbes, F., Garbay, C., Dojat, M. (2009). Distributed local MRF models for tissue and structure brain segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 28, 1278–1295.
Schuff, N., Tosun, D., Insel, P., Chiang, G., Truran, D., Aisen, P., Jack, C.J., Weiner, M.A.D.N. (2012). Initiative: nonlinear time course of brain volume loss in cognitively normal and impaired elders. Neurobiology of Aging, 33, 845–855.
Shattuck, D., Sandor-Leahy, S., Schaper, K., Rottenberg, D., Leahy, R. (2001). Magnetic resonance image tissue classification using a partial volume model. NeuroImage, 13, 856–876.
Shattuck, D.W., & et al. (2008). Construction of a 3D probabilistic atlas of human cortical structures. NeuroImage, 39, 1064–1080.
Simpson, I.J.A., Woolrich, M.W., Groves, A.R., Schnabel, J.A. (2011). Longitudinal brain MRI analysis with uncertain registration uncertain registration. In Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI’11), Part II (Vol. 6892, pp. 647–654).
Sled, J., Zijdenbos, A., Evans, A. (1998). A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity non-uniformity in MRI data. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 17, 87–97.
Smith, S. (2002). Fast robust automated brain extraction. Human Brain Mapping, 17, 143–155.
Tibshirani, R. (1996). Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 58(1), 267–288.
Tu, Z. (2007). Learning generative models via discriminative approaches. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR’07) (pp. 1–8).
Tu Z., & Bai X. (2010). Auto-context and its application to high-level vision tasks and 3D brain image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on PAMI, 32(10), 1744–1757.
Tu, Z., Narr, K., Dollar, P., Dinov, I., Thompson, P., Toga, A. (2008). Brain anatomical structure segmentation by hybrid discriminative/generative models. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 27, 495–508.
Unay, D., Ekin, A., Jasinschi, R. (2008). Medical image search and retrieval using local binary patterns and KLT feature points. In IEEE conference on image processing (ICIP’08) (pp. 997–1000).
Vapnik, V. (1982). Estimation of dependences based on empirical data. Berlin: Springer.
Vapnik, V. (1998). Statistical learning theory. New York: Wiley.
Verma, R., Zacharaki, E.I., Ou, Y., Cai, H., Chawl, S., Lee, S.K., Melhem, E.R., Wolf, R., Davatzikos, C. (2008). Multi-parametric tissue characterization of brain neoplasms and their recurrence using pattern classification of MR images. Academic Radiology, 15(8), 966–977.
Wang, H., Das, S., Suh, J., Altinay, M., Pluta, J., Craige, C., Avants, B., Yushkevich, P. (2011). The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative: a learning-based wrapper method to correct systematic errors in automatic image segmentation: consistently improved performance in hippocampus, cortex and brain segmentation. NeuroImage, 55(3), 968–985.
Wells, W., Kikinis, R., Grimson, W., Jolesz, F. (1996). Adaptive segmentation of MRI data. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 15(4), 429–442.
Wels, M., Zheng, Y., Carneiro, G., Huber, M., Hornegger, J., Comaniciu, D. (2009). Fast and robust 3-D MRI brain structure segmentation. In Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI’09), Part II (pp. 575–583).
Wels, M., Zheng, Y., Huber, M., Hornegger, J., Comaniciu, D. (2011). A discriminative model-constrained EM approach to 3D MRI brain tissue classification and intensity non-uniformity correction. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 56(11), 3269–3300.
Wolz R., Aljabar P., Rueckert D., Heckemann R., Hammers A. (2009). Segmentation of subcortical structures and the hippocampus in brain MRI using graph-cuts and subject–specific a-priori information. In Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI’09) (pp. 470–473).
Woods, R., Mazziotta, J., Cherry, S. (1993). MRI-PET registration with automated algorithm. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, 17, 536–546.
Woolrich, M., & Behrens, T. (2006). Variational Bayes inference of spatial mixture models for segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2(10), 1380–1391.
Wu, J., & Chung, A. (2005). A new solver for Markov random field modeling and applications to medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI’05), Part I (pp. 229–237).
Wu J., & Chung A. (2008). Markov dependence tree-based segmentation of deep brain structures. In Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI’08), Part II (Vol. 5242, pp. 1092–1100).
Wu, J., & Chung, A. (2009). A novel framework for segmentation of deep brain structures based on Markov dependence tree. NeuroImage, 49, 1027–1036.
Yang, F., Shan, Z.Y., Kruggel, F. (2010). White matter lesion segmentation based on feature joint occurrence probability and χ 2 random field theory from magnetic resonance (MR) images. Pattern Recognition Letters, 31(9), 781–790.
Yang, J., Staib, L., Duncan, J. (2004). Neighbor-constrained segmentation with level set based 3D deformable models. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 23(8), 940–948.
Yaqub, M., Javaid, M.K., Cooper, C., Noble, J.A. (2011). Improving the classification accuracy of the classic rf method by intelligent feature selection and weighted voting of trees with application to medical image segmentation. In International conference on machine learning in medical imaging (MLMI’11) (pp. 184–192).
Yi, Z., Criminisi, A., Shotton, J., Blake, A. (2009). Discriminative, semantic segmentation of brain tissue in MR images. In Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI’09), Part II (Vol. 5762, pp. 558–565).
Yushkevich, P.A., Piven, J., Hazlett, H.C., Smith, R.G., Ho, S., Gee, J.C., Gerig, G. (2006). User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: significantly improved efficiency and reliability. NeuroImage, 31(3), 1116–1128.
Zhang, N., Ruan, S., Lebonvallet, S., Liao, Q., Zhu, Y. (2009). Multi-kernel SVM based classification for brain tumor segmentation of MRI multi-sequence. In IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP’09) (pp. 3373–3376).
Zhou, J., & Rajapakse, J. (2005). Segmentation of subcortical brain structures using fuzzy templates. NeuroImage, 28(4), 915–924.
Zhu S., & Yuille A. (1996). Region competition: unifying snake/balloon, region growing and Bayes/MDL/energy for multi-band image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on PAMI, 18(9), 884–900.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by NSF CAREER award IIS-0844566, ONR award no. N000140910099, and NSF award IIS-1216528.
Data collection and sharing for this project was also funded by the ADNI (National Institutes of Health grant U01 AG024904). ADNI is funded by the National Institute on Aging, the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, and through generous contributions from the following: Abbott, Alzheimer’s Association, Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, Amorfix Life Sciences Ltd., AstraZeneca, Bayer HealthCare, BioClinica, Inc., Biogen Idec Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co., Eisai Inc., Elan Pharmaceuticals Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. and its affiliated company Genentech, Inc., GE Healthcare, Innogenetics, N.V., IXICO Ltd., Janssen Alzheimer Immunotherapy Research & Development, LLC, Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development LLC, Medpace, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Meso Scale Diagnostics, LLC, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp., Pfizer Inc., Servier, Synarc Inc., and Takeda Pharmaceutical Co.. The Canadian Institutes of Health Research is providing funds to support ADNI clinical sites in Canada. Private sector contributions are facilitated by the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (www.fnih.org). The grantee organization is the Northern California Institute for Research and Education, and the study is coordinated by the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study at the University of California, San Diego. ADNI data are disseminated by the Laboratory for Neuro Imaging at the University of California, Los Angeles. This research was also supported by NIH grants P30 AG010129 and K01 AG030514.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Data used in preparation of this article were obtained from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) database (adni.loni.ucla.edu). As such, the investigators within the ADNI contributed to the design and implementation of ADNI and/or provided data but did not participate in analysis or writing of this report. A complete listing of ADNI investigators can be found at:http://adni.loni.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/how_to_apply/ADNI_Acknowledgement_List.pdf
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, CY., Iglesias, J.E., Tu, Z. et al. Deformable Templates Guided Discriminative Models for Robust 3D Brain MRI Segmentation. Neuroinform 11, 447–468 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-013-9190-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-013-9190-5